本文的读者应该是已经掌握了基本的Java多线程开发技巧,但不熟悉Java
Concurrency包的程序员。本文是本系列的第七篇文章,前六篇文章请看这里:
Java Concurrency代码实例之一执行者与线程池
Java Concurrency代码实例之二并发队列
Java Concurrency代码实例之三原子变量
Java Concurrency代码实例之四-锁
Java Concurrency代码实例之五-同步工具
Java Concurrency代码实例之六-ConcurrentHashMap
1. 前言
按照用途与特性,Concurrency包中包含的工具被分为六类(外加一个工具类TimeUnit),即:
- 执行者与线程池
- 并发队列
- 同步工具
- 并发集合
- 锁
- 原子变量
本系列的前五篇文章分别介绍这六类中的一类。自第六篇起,一次仅介绍一个具体类。本文介绍的是并发集合中最奇特的一个类ConcurrentSkipListMap。此类的奇特性在于,它与TreeMap一样,实现了对有序队列的快速查找,但同时,它还是多线程安全的。在多线程环境下,它要比加锁的TreeMap效率高。为什么ConcurrentSkipListMap没有一个对应的单线程环境下的SkipListMap呢?后面会慢慢解答。
2. 跳表SkipList简介
跳表(skip list)是一种允许在有序队列中进行快速查找的数据结构。其插入、删除、查找的时间复杂度均为O(logN),这一点与JDK中的TreeMap一样。跳表通过用空间换时间的策略,为有序链表建立并维护了一个多级的索引群,其中高层的索引会跨越更多的元素(因此索引数更少),底层的索引会跨因更少的元素(因此索引数更多),而低层的索引一定会包含高层索引所指向的元素,通过这种索引结构实现元素的快速定位。跳表的结构如下图所示(图形来自https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list):
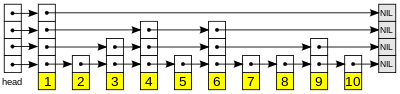
在对key进行查找时,从高层索引开始依次比较,直至找到一个比key大的值,在此索引的前一个索引处下降一级索引后继续查找,依次直至在某级索引处找到,或者在元素链表中找到key对应的节点。由于高层的索引非常稀疏,而低层的索引比较密集,因此在高层索引的查找能够一次跨越较多的元素,从而比直接在链表中查找速度要快很多。
跳表是分层构建的,最底层就是一个节点的单向链表,然后依次往上就是一层层的索引。我们假设第i层的元素出现在第i+1层的概率为一个固定的概率p(常用的p值为1/2或者1/4),则可知平均来说,每一个元素会出现在1/(1-p)层,而最高层的元素会出现在每一层。通过一系列计算,可知对跳表进行查找,其平均时间复杂度均为O(logN)。而可知,增加、删除、修改跳表最大的时间耗费就是查找元素位置,因此这些方法的时间复杂度也是O(logN)。具体的讨论见:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list。那里还有一个动图详细的说明了跳表的查询流程:

3. 一个简单的跳表实现
JDK中提供了ConcurrentSkipListMap,但却没有提供SkipListMap,我想这是因为在单线程环境下,TreeMap所使用的红黑树要优于跳表,因为它们的时间复杂性一样,但跳表要多占用多级索引的空间。而在JUC包中提供了ConcurrentSkipListMap,但却没有提供ConcurrentTreeMap,是因为红黑树本身就已经非常复杂了,要把它改写为并发数据结构,其难度实在是太大了。
由于ConcurrentSkipListMap也比较复杂,难以直接理解,因此我根据JDK1.7中它的实现,给出了一个简化版的单线程环境下的跳表SimpleSkipListMap,其源代码可以直接运行。待理解了此类后,再看ConcurrentSkipListMap就比较容易理解了。
3.1 源代码
说明:
1. SimpleSkipListMap提供了main方法,这个方法主要是为了测试;
2. 去掉了ConcurrentNavigableMap接口,因此减少了很多关于排序、子集的方法,这些方法实际上与跳表关系不大;
3. 增加了printContent方法,用于调试,可打印出所有索引和节点信息;
4.在remove节点时,直接将value赋值为null,然后在后续操作中慢慢删除节点和其索引。这种思想是与ConcurrentSkipListMap相同的,但ConcurrentSkipListMap是将value赋值为null的同时,在这个节点后还插入一个标志节点;
5.在源代码之后,我会一一介绍代码中较为重要的方法。
public class SimpleSkipListMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleSkipListMap<Integer, String> map = new SimpleSkipListMap<>();
System.out.println("============== test put ================");
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
map.put(i, "Alex" + i);
}
map.printContent();
System.out.println("============== test get(5) ================");
System.out.println(map.get(5));
System.out.println("=========== test remove 5 ============");
map.remove(5);
map.printContent();
System.out.println("=========== test size and isEmpty ============");
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("============== test keyset ================");
Iterator<Integer> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("============== test values ================");
Iterator<String> stringIterator = map.values().iterator();
while (stringIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(stringIterator.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("============== test entrySet ================");
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entryIterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(entryIterator.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 种子生成器
*/
private static final Random seedGenerator = new Random();
/**
* Special value used to identify base-level header,节点头部
*/
private static final Object BASE_HEADER = new Object();
/**
* The topmost head index of the skiplist,最高层的索引头(索引最多31层),插入节点时,每次最多增加一层
*/
private transient volatile HeadIndex<K, V> head;
/**
* 用来排序的Comparator,若为空则使用自然排序
*/
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
/**
* 随机种子
*/
private transient int randomSeed;
/**
* Lazily initialized key set
*/
private transient KeySet keySet;
/**
* Lazily initialized entry set
*/
private transient EntrySet entrySet;
/**
* Lazily initialized values collection
*/
private transient Values values;
/**
* 初始化Map
*/
final void initialize() {
// keySet = null;
// entrySet = null;
// values = null;
randomSeed = seedGenerator.nextInt() | 0x0100; // ensure nonzero
head = new HeadIndex<K, V>(new Node<K, V>(null, BASE_HEADER, null),
null, null, 1);
}
public SimpleSkipListMap() {
this.comparator = null;
initialize();
}
public SimpleSkipListMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
initialize();
}
public SimpleSkipListMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.comparator = null;
initialize();
putAll(m);
}
/**
* 节点类,注意两点:1.value为null时,表示此节点已经删除;2.value的类型为Object是因为一些特殊情况它不为V类型,例如BASE_HEADER
*/
static final class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
Object value;
Node<K, V> next;
Node(K key, Object value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
V getValidValue() {
Object v = value;
if (v == null || v == BASE_HEADER)
return null;
return (V) v;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" + key + "," + value + "}";
}
}
/**
* 索引类
*/
static class Index<K, V> {
Node<K, V> node; //指向被索引的节点
Index<K, V> down; //指向下一层的索引,该索引都是node的索引
Index<K, V> right; //指向同层右侧(后续)的索引
Index(Node<K, V> node, Index<K, V> down, Index<K, V> right) {
this.node = node;
this.down = down;
this.right = right;
}
}
/**
* 索引头类,增加了一个层次level
*/
static final class HeadIndex<K, V> extends Index<K, V> {
int level;
HeadIndex(Node<K, V> node, Index<K, V> down, Index<K, V> right, int level) {
super(node, down, right);
this.level = level;
}
}
/**
* 用于调试的方法,按层打印出所有的索引和节点
*/
public void printContent() {
Index<K, V> h = head;
for (int i = head.level; i > 0; i--) {
System.out.println("Index level:" + i);
for (Index<K, V> idx = h; idx != null; idx = idx.right) {
if (idx.node.value != BASE_HEADER && idx.node.value != null) {
System.out.print(idx.node + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
h = h.down;
}
System.out.println("Node List:");
for (Node<K, V> node = head.node.next; node != null; node = node.next) {
if (node.value != null) {
System.out.print(node + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/* ---------------- Comparison utilities -------------- */
/**
* 使用一个Comarator构造一个Comparable
*/
static final class ComparableUsingComparator<K> implements Comparable<K> {
final K actualKey;
final Comparator<? super K> cmp;
ComparableUsingComparator(K key, Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
this.actualKey = key;
this.cmp = cmp;
}
public int compareTo(K k2) {
return cmp.compare(actualKey, k2);
}
}
/**
* 使用key来构造一个Comparable对象
*/
private Comparable<? super K> comparable(Object key)
throws ClassCastException {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (comparator != null)
return new ComparableUsingComparator<K>((K) key, comparator);
else
return (Comparable<? super K>) key;
}
/**
* 比较两个key,使用comparator或者自然排序
*/
int compare(K k1, K k2) throws ClassCastException {
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
if (cmp != null)
return cmp.compare(k1, k2);
else
return ((Comparable<? super K>) k1).compareTo(k2);
}
/* ---------------- put、remove、update、get utilities -------------- */
/**
* 新添加一个节点,在遍历的同时删除已经无效的节点(value==null);在添加时如果key与链表中的某个节点的key相等,则直接替换
*
* @param kkey 插入的key值
* @param value 插入的value值
* @return 被替换节点的原value值,若无则返回null
*/
public V put(K kkey, V value) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(kkey);
Node<K, V> b = findPredecessor(key); //一般用b来表示前序节点
Node<K, V> n = b.next; //一般用n来表示当前节点
Node<K, V> f = null; //一般用f来表示后续节点
for (; ; ) {
if (n != null) {
f = n.next;
if (n.value == null) { //如果n已经被删除,从链表中删除
b.next = f;
n = f;
continue;
}
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = n.next;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) { //如果key相等,直接替换value
V oldValue = (V) n.value;
n.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
} else
break;
}
Node<K, V> z = new Node<>(kkey, value, n);
b.next = z;
int level = randomLevel();
if (level > 0)
insertIndex(z, level);
return null;
}
/**
* 为新加入的节点建立索引,注意,每次总索引最多增加一层
*
* @param z 节点
* @param level 节点层级
*/
private void insertIndex(Node<K, V> z, int level) {
HeadIndex<K, V> h = head;
int max = h.level;
if (max >= level) {
Index<K, V> idx = null;
//从第1层到第level层建立索引,并设置好索引的down引用
for (int i = 1; i <= level; i++) {
idx = new Index<>(z, idx, null);
}
addIndex(idx, h, level); //设置索引的right引用
} else {
//总索引层+1,重新设置head
level = max + 1;
HeadIndex<K, V> tmpHead = new HeadIndex<>(head.node, head, null, level);
head = tmpHead;
Index<K, V> idx = null;
//从第1层到第max+1层建立索引,并设置好索引的down引用
for (int i = 1; i <= level; i++) {
idx = new Index<>(z, idx, null);
}
addIndex(idx, head, level);
}
}
/**
* 将插入的索引的right引用在索引结构的每一层中设置好,本方法仅在insertIndex方法中被调用,本方法还在遍历的同时删除无效节点的索引
*
* @param idx 插入的索引
* @param h 当前的索引头
* @param indexLevel 被插入索引的层级
*/
private void addIndex(Index<K, V> idx, HeadIndex<K, V> h, int indexLevel) {
int insertionLevel = indexLevel; //当前要设置的索引的层次
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(idx.node.key);
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Index<K, V> q = h;
Index<K, V> r = q.right;
Index<K, V> t = idx;
int j = h.level; //索引遍历的层次
for (; ; ) {
if (r != null) {
Node<K, V> n = r.node;
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (n.value == null) { //如果n已经被删除
q.right = r.right;
r = q.right;
continue;
}
if (c > 0) { //c>0则同层向右搜索
q = r;
r = q.right;
continue;
}
}
//此处开始设置每层的t的right,将t插入至q和r之间
if (j == insertionLevel) { //如果当前遍历的索引层次等于要设置索引的层次
q.right = t;
t.right = r;
if (--insertionLevel == 0) {
return;
}
}
if (--j >= insertionLevel && j < indexLevel) //如果j处于适当的层次,要设置的索引t下降一层
t = t.down;
q = q.down; //要索引遍历的层次下降
r = q.right;
}
}
/**
* 为新加入的节点计算索引层级,k=1, 每一层的概率p=0.5, max 31,照抄了JDK1.7中的实现
*
* @return 根据概率计算出的索引层级
*/
private int randomLevel() {
int x = randomSeed;
x ^= x << 13;
x ^= x >>> 17;
randomSeed = x ^= x << 5;
if ((x & 0x80000001) != 0) // test highest and lowest bits
return 0;
int level = 1;
while (((x >>>= 1) & 1) != 0) ++level;
return level;
}
/**
* 找到前序节点,遍历索引的过程中删除作废的索引(已删除节点的索引)
*
* @param key
* @return 前序节点,若没有找到则返回HEAD
*/
private Node<K, V> findPredecessor(Comparable<? super K> key) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
Index<K, V> q = head; //一般用q来表示前一个索引
Index<K, V> r = q.right; //一般用r来表示q的right索引
for (; ; ) {
if (r != null) {
Node<K, V> n = r.node;
K k = n.key;
//处理作废的索引
if (n.value == null) {
q.right = r.right;
r = q.right;
continue;
}
int c = key.compareTo(k);
if (c > 0) { //同层向后遍历
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
//下降一层
Index<K, V> d = q.down;
if (d != null) {
q = d;
r = q.right;
} else
return q.node;
}
}
/**
* 根据key寻找匹配的节点,过程中删除无效的节点
*
* @param key
* @return 找到则返回匹配的节点,否则返回null
*/
private Node<K, V> findNode(Comparable<? super K> key) {
Node<K, V> b = findPredecessor(key);
Node<K, V> n = b.next;
for (; ; ) {
if (n != null) {
if (n.value == null) {
b.next = n.next;
n = b.next;
continue;
}
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c > 0) {
n = n.next;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) {
return n;
}
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* 寻找第一个有效节点
*
* @return
*/
Node<K, V> findFirst() {
for (; ; ) {
Node<K, V> b = head.node;
Node<K, V> n = b.next;
if (n == null)
return null;
if (n.value != null)
return n;
}
}
/**
* 通过key寻找相应的节点,并返回节点值
*
* @param kkey
* @return
*/
public V get(Object kkey) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(kkey);
Node<K, V> n = findNode(key);
if (n.value != null) {
return (V) n.value;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 删除key指向的节点,删除时直接将找到的节点的value设置为null即可,后续遍历操作会逐步删除节点和它的各级索引
*
* @param kkey
* @return 成功则返回原节点的值,否则返回null
*/
public V remove(Object kkey) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(kkey);
Node<K, V> b = findPredecessor(key);
Node<K, V> n = b.next;
for (; ; ) {
if (n != null) {
if (n.value == null) {
b.next = n.next;
n = b.next;
continue;
}
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = n.next;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) {
//通过将value设置为null使得该节点作废,在后续的各种遍历操作中会逐步删除节点以及它的索引
V v = (V) n.value;
n.value = null;
return v;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public int size() {
int i = 0;
for (Node<K, V> n = findFirst(); n != null; n = n.next) {
if (n.value != null) {
i++;
}
}
return i;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return findFirst() != null;
}
/* ---------------- Iterators -------------- */
/**
* 三种Iterator类的虚基类,没有实现next方法,留待子类实现
*/
abstract class Iter<T> implements Iterator<T> {
/**
* the last node returned by next()
*/
Node<K, V> lastReturned;
/**
* the next node to return from next();
*/
Node<K, V> next;
/**
* Cache of next value field to maintain weak consistency
*/
V nextValue;
Iter() {
next = findFirst();
nextValue = (V) next.value;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
/**
* 移动到下一个节点,在next()中使用
*/
public void advance() {
if (next == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
for (; ; ) {
next = next.next;
if (next == null) {
break;
}
Object x = next.value;
if (x != null) {
nextValue = (V) x;
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void remove() {
Node<K, V> l = lastReturned;
if (l == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
SimpleSkipListMap.this.remove(l.key);
lastReturned = null;
}
}
/**
* 三种Iterator类的具体实现类
*/
final class KeyIterator extends Iter<K> {
@Override
public K next() {
Node<K, V> node = next;
advance();
return node.key;
}
}
final class ValueIterator extends Iter<V> {
@Override
public V next() {
Node<K, V> node = next;
advance();
return (V) node.value;
}
}
final class EntryIterator extends Iter<Map.Entry<K, V>> {
@Override
public Entry<K, V> next() {
Node<K, V> node = next;
advance();
return new SimpleImmutableEntry<K, V>(node.key, (V) node.value);
}
}
private Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
return new KeyIterator();
}
private Iterator<V> valueIterator() {
return new ValueIterator();
}
private Iterator<Map.Entry<K, V>> entryIterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
/* ----------------KeySet Values EntrySet utilities -------------- */
//内部类,KeySet
static final class KeySet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> {
private final SimpleSkipListMap<E, Object> m;
KeySet(SimpleSkipListMap<E, Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.keyIterator();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
}
@Override
public Set<K> keySet() {
KeySet ks = keySet;
return (ks != null) ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet(this));
}
//内部类,Values
static final class Values<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> {
private final SimpleSkipListMap<Object, E> m;
Values(SimpleSkipListMap<Object, E> m) {
this.m = m;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.valueIterator();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
}
@Override
public Collection<V> values() {
Values vs = values;
return (vs != null) ? vs : (values = new Values(this));
}
//内部类,EntrySet
static final class EntrySet<K, V> extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K, V>> {
private final SimpleSkipListMap<K, V> m;
EntrySet(SimpleSkipListMap<K, V> m) {
this.m = m;
}
@Override
public Iterator<Entry<K, V>> iterator() {
return m.entryIterator();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
}
@Override
public Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet<K, V> es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet(this));
}
}3.2 findPredecessor
这是本类中最常用的一个方法,用来找到指定节点的前一个节点:
1. 索引头部开始查找;
2. 在每一层索引中从左至右比较key值的大小,注意由于跳表是有序表,所以后面元素的key值一定比前面大,而索引中也是如此;
3. 在进行key值比较时,处理作废的索引,即节点value为null的索引,这种索引直接从本层的索引列表中删除;
4. 同层比较到合适的位置时,即下一个索引的key值要大于本身时,下降一级索引;
5. 如此比较直至找到,或者到达底层单向链表;
6. 若找到,则返回前一个节点,否则返回头部标志节点HEAD。
3.3 Put
在插入一个节点时,调用put方法:
1. 调用findPredecessor找到前序节点;
2. 从该节点处依次向后找到匹配的节点(因为有可能该节点后续跟着一串已经作废的节点);
3. 如果找到匹配节点,直接替换value;
4. 否则在合适的位置插入一个新节点;
5. 为新插入的节点建立索引。
建立索引又分为好几个步骤:
1. 使用randomLevel方法计算新节点的索引层次,记得前面的内容么?每个节点都有一个固定的概率p(此时=0.5)出现在上一层的索引中,那么就有p*p的概率出现在上两层中,总之计算出节点的层次(randomLevel照抄JDK了);
2. 如果索引层次大于0,则调用insertIndex方法建立索引;
3. 在insertIndex方法中,为这个level层的节点建立level个索引,自下而上将这一竖列的索引的down引用设置好;
4. 然后调用addIndex方法为每一层中的这个索引设置right引用;
5. 在addIndex方法中,用类似findPredecessor类似的方法遍历整个索引,为每层的每个索引找到合适的位置,然后插入。
至此,put方法才算完成。运行main函数时,你会发现每次建立的索引是不一样的,因为它是基于概率来给每个节点建立索引的,这也就是为什么有人称它为概率数据结构的原因。
3.4 Get
Get方法用来根据key查找value:
1. 调用findNode方法来查找节点;
2. 在findNode中先调用了findPredecessor来查找前一个节点;
3. 然后依次检查后续的节点是否为有效节点,有效则返回,无效则删除;
4. 最后得到该节点的value值。
3.5 Remove
节点的删除使用remove方法,但是remove方法实际上仅仅将节点的value赋值为null,这表示该节点是一个无效节点了,而实际上节点的删除工作要在findPredecessor方法中完成,相关索引的删除工作要在addIndex方法中完成。这样做的原因固然是因为模仿ConcurrentSkipListMap,实际上这也是一个非常好的策略。因为findPredecessor是本类中最经常调用的操作,addIndex也是在put一个节点时必须调用的方法,那么在调用这些方法时顺便将无效节点和索引删除不会增加时间复杂性,而如果要在remove方法中将这些操作全部完成,则remove方法的时间耗费将大大增加。
Remove方法如下:
1. 调用findPredecessor方法找到前一个节点;
2. 然后依次检查后续的节点是否为有效节点,无效则删除该节点;
3. 比较key值,找到符合且有效的节点,将其value赋值为null。
3.6 迭代子
要对Map进行遍历,需要用到三个集合和三个迭代子。本类中也提供了这些集合和迭代子,并在main方法中进行了测试。观察这些集合和迭代子时要注意以下几点:
1. keySet、entrySet、values这三个变量都是延迟加载的,不真正调用相关方法时,它们不会被创建出来;
2. KeySet类、Values类和EntrySet
4. ConcurrentSkipListMap的并发技巧
看完SimpleSikpListMap类后,再来看JDK中的ConcurrentSkipListMap就有脉络可寻了。前面已经谈到过,TreeMap没有对应的并发类,那是因为红黑树在插入删除时要旋转子树,那么使用并发方法很难做到让多个线程同时旋转子树而不需要加锁。而SkipList不同,它的插入、删除、搜索和替换(替换实际上并入了put方法)只是在操作多个单向链表(包括一个节点链表和最多31个索引链表),因此就有了使用无锁算法的可能。注意,本文使用的是JDK1.7版本。
4.1 使用volatile关键字获得可见性
索引头部private transient volatile HeadIndex
4.2 使用Unsafe的CAS操作确保对属性赋值的原子性
关于UnSafe类的详细介绍,见本系列的另一篇文章Java Concurrency代码实例之三原子变量。UnSafe类的CAS操作可以保证赋值操作的原子性,因此上面使用volatile关键字修饰的四个变量head,Node中的value和next,Index类中的right,都使用相关的CAS方法进行赋值,以Node为例,见如下代码片段:
/**
* compareAndSet value field
*/
boolean casValue(Object cmp, Object val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* compareAndSet next field
*/
boolean casNext(Node<K,V> cmp, Node<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long valueOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = Node.class;
valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("value"));
nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}通过volatile和CAS,就有了使用自旋锁对这些变量进行并发操作的可能。
4.3 使用自旋锁模式实现对节点属性的无锁并发操作
自旋锁在前面的文章中也介绍过,它不是一种互斥锁,而是采用反复尝试直至成功的程序结构。由于volatile和CAS保证了操作的原子性,因此采用自旋锁就可以让多个线程同时操作某些属性,达到无锁并发的目的。
观察ConcurrentSkipListMap中的findPredecessor方法,它与前面SimpleSkipListMap最大的区别就是加入了自旋锁。一般来说,自旋锁包括一个无限循环和其中的一个CAS方法,该CAS成功则继续,失败就重新进入循环。代码如下:
private Node<K,V> findPredecessor(Comparable<? super K> key) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
//多出的这一层循环就是自旋锁使用的
for (;;) {
Index<K,V> q = head;
Index<K,V> r = q.right;
for (;;) {
if (r != null) {
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
K k = n.key;
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break; // CAS失败,跳出本层循环,重新开始
r = q.right; // reread r
continue;
}
if (key.compareTo(k) > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
Index<K,V> d = q.down;
if (d != null) {
q = d;
r = d.right;
} else
return q.node;
}
}
}
final boolean unlink(Index<K,V> succ) {
return !indexesDeletedNode() && casRight(succ, succ.right);
}
final boolean casRight(Index<K,V> cmp, Index<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, rightOffset, cmp, val);
}这种自旋锁模式被广泛的使用于各个重要的并发方法中,再来看看插入方法doPut:
private V doPut(K kkey, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(kkey);
for (;;) {
Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);
Node<K,V> n = b.next;
for (;;) { //多出的这一层循环就是自旋锁使用的
if (n != null) {
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // 并发导致读取不一致,则重入
break;
Object v = n.value;
if (v == null) { // 如果n已经被删除,则处理后重入
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (v == n || b.value == null) //如果b已经被删除,则重入
break;
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) {
if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value)) //此处使用CAS对value赋值
return (V)v;
else
break; // value的CAS操作失败则重入
}
// else c < 0; fall through
}
Node<K,V> z = new Node<K,V>(kkey, value, n);
if (!b.casNext(n, z)) //此处使用CAS将n替换为z
break; //如果CAS失败则重入
int level = randomLevel();
if (level > 0)
insertIndex(z, level);
return null;
}
}
}可以看到,在doPut方法中,有五个地方使用了重入操作(即跳出当前循环回到第一个循环处重新开始),其中一个是因为读取状态不一致,两个是因为节点被删除,两个是因为CAS操作失败。
仔细阅读代码就会发现,ConcurrentSkipListMap中几乎处处使用到了这个自旋锁结构,因此几乎所有的并发算法都是二重循环的。
4.4 使用标记来进行并发的删除
ConcurrentSkipListMap的删除节点操作由doRemove方法完成。它其实与SimpleSkipListMap中的remove方法很类似,都是在删除操作时将节点标记为作废,然后在后续的各种方法中再具体删除节点和各级索引。
final V doRemove(Object okey, Object value) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(okey);
for (;;) { //多出的这一层循环就是自旋锁使用的
Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);
Node<K,V> n = b.next;
for (;;) {
if (n == null)
return null;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // 并发导致读取不一致,则重入
break;
Object v = n.value;
if (v == null) { // 如果n已经被删除,则处理后重入
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (v == n || b.value == null) //如果b已经被删除,则重入
break;
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c < 0)
return null;
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
if (value != null && !value.equals(v))
return null;
if (!n.casValue(v, null)) //使用CAS将v赋值为null,失败则重入
break;
if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f)) //为n添加一个后续标记节点,同时将b的next从n替换为f
findNode(key); // 若失败则调用findNode
else {
findPredecessor(key); //此处调用为了清除索引
if (head.right == null)
tryReduceLevel();
}
return (V)v;
}
}
}从代码中可以看出ConcurrentSkipListMap与SimpleSkipListMap的区别,除了使用自旋锁以外,前者在删除时还有做一些其他动作。例如会尝试为节点添加一个后续标记节点f,这个f的特征是其value值等于自己的this,成功后则继续尝试直接将n从队列中删除。这些动作就算失败了也不要紧,后续的一些方法会继续完成删除动作。
4.5 迭代子
ConcurrentSkipListMap与SimpleSkipListMap的迭代子几乎一致,区别仅仅在于ConcurrentSkipListMap的Iter类中的方法都改成了自旋锁的样式。
5. ConcurrentSkipListMap的性能
下面三段程序(代码比较类似,因此只给出了场景二的代码)比较了ConcurrentSkipListMap和加锁的TreeMap的性能。
应用场景一:100个线程同时插入数据,每个线程插入10万条数据。
ConcurrentSkipListMap结果:
time span = 15351, map size = 7869679
time span = 18580, map size = 7870682
time span = 14383, map size = 7868385
TreeMap结果:
time span = 17955, map size = 7869116
time span = 18268, map size = 7868110
time span = 17909, map size = 7868835
应用场景二:90个线程同时插入数据,每个线程插入10万条数据,10个线程同时删除数据,每个节点删除10万条数据。
public class ConcurrentSkipListMapExam2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 90; i++) {
service.execute(new Putter(i,map));
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
service.execute(new Remover(i,map));
}
service.shutdown();
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("time span = "+(end-start)+", map size = "+map.size());
}
private static class Putter implements Runnable {
private final int num ;
private final ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String> map;
private static Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
private Putter(int num, ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String> map) {
this.num = num;
this.map = map;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
int key = rand.nextInt(200 * 100000); //在200万中随机产生key
map.put(key, "Alex" + key);
}
}
}
private static class Remover implements Runnable {
private final int num ;
private final ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String> map;
private static Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
private Remover(int num, ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String> map) {
this.num = num;
this.map = map;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
int key = rand.nextInt(200 * 100000); //在200万中随机产生key
map.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
public class TreeMapExam2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 90; i++) {
service.execute(new Putter(i, map));
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
service.execute(new Remover(i, map));
}
service.shutdown();
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("time span = " + (end - start) + ", map size = " + map.size());
}
private static class Putter implements Runnable {
private final int num;
private final TreeMap<Integer, String> map;
private static Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
private Putter(int num, TreeMap<Integer, String> map) {
this.num = num;
this.map = map;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
int key = rand.nextInt(200 * 100000); //在200万中随机产生key
synchronized (map) {
map.put(key, "Alex" + key);
}
}
}
}
private static class Remover implements Runnable {
private final int num;
private final TreeMap<Integer, String> map;
private static Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
private Remover(int num, TreeMap<Integer, String> map) {
this.num = num;
this.map = map;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
int key = rand.nextInt(200 * 100000); //在200万中随机产生key
synchronized (map) {
map.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
}ConcurrentSkipListMap结果:
time span = 15366, map size = 6946030
time span = 15278, map size = 7058776
time span = 16922, map size = 7104564TreeMap结果:
time span = 17321, map size = 7018860
time span = 18690, map size = 7012174
time span = 18121, map size = 7064320应用场景三:10个线程同时插入数据,每个线程插入10万条数据,90个线程同时读取数据,每个节点读取10万条数据。
ConcurrentSkipListMap结果:
time span = 5104, map size = 975495
time span = 5523, map size = 975249
time span = 6085, map size = 975213TreeMap结果:
time span = 7365, map size = 975387
time span = 8208, map size = 975491
time span = 8061, map size = 975543由上面的结果可以看出,几乎在每种应用场景下,ConcurrentSkipListMap的并发性能都要优于加锁的TreeMap,它唯一的缺点在于使用了更多的存储空间。
6. 小结
跳表是一种允许在有序队列中进行快速查找的数据结构。其插入、删除、查找的时间复杂度均为O(logN),这一点与TreeMap类似。跳表本质上是一条单向链表,其中按照顺序存储了节点,并为每个节点按照一定的概率生成了多级索引,下层的索引必定包含上层索引。本文给出了一个简单的跳表实现。ConcurrentSkipListMap是跳表的并发实现方式,它利用了volatile关键字、Unsafe的CAS方法、自旋锁等并发技巧实现了无锁算法,获得了更加优秀的并发性能。
























 262
262

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








