堆分为大根堆和小根堆两种,其存储方式是通过数组来实现的。这里我们只说一下小根堆。
对于一个小根堆,每个节点的左右儿子编号分别是当前节点编号*2,当前编号*2+1;利用一个数组,进行存储。
图例如下
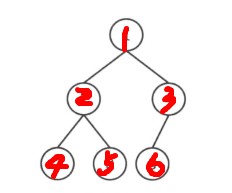
对于两个儿子,只需满足比他的父亲节点大(小根堆性质),两个儿子谁大谁小无所谓。讲一下堆的两个操作push 和pop
push操作
对于每次读入,从堆的末尾插入元素。为了满足性质,每次读入后与其一层层的父亲,依次比较,若比较小,就交换。
代码如下:
void push(int x)
{
cnt++;
int now=cnt; //当前点的编号
heap[now]=x; //当前点所记录的数据
while(now>1) //编号大于1
{
if(heap[now]<heap[now/2]) //与父亲比较
{
swap(heap[now],heap[now/2]);
now/=2; //更改标记
}
else break; //原本已满足性质,不找
}
}pop操作
从堆中删除最小的数时,我们把堆的最后一个节点强行放到一号点,再利用堆的性质重新排一下位置。这里要注意,在排序时要与较小的点进行交换,否则的话,交换后要再进行交换,就无法满足性质,
代码如下:
void pop()
{
heap[1]=heap[cnt]; //用堆末端元素强行覆盖掉最小的元素
int now=1;
while(now*2+1<=cnt) //边界条件,当达到最大值的时候便不再往下寻找
{
int l=now*2,r=now*2+1; //l为左儿子(left)r为右儿子(right)
if(heap[l]<heap[now])
{
if(heap[r]<heap[l]&&heap[r]<heap[now]) //为了节省代码,我们就在左儿子<当前时,对左儿子与当前交换 。对于右儿子比左儿子小的特殊情况,我们就把两个点的标记交换一下
swap(r,l);
swap(heap[l],heap[now]);
now=l; //修改标记
}
else if(heap[r]<heap[now])
{
swap(heap[r],heap[now]);
now=r;
}
else break ;
}
cnt--
}这样手打的堆就大致讲完了。。
是不是感觉有些麻烦,STL就可以啦!!!
我们可以利用STL中的优先队列来实现
但是优先队列默认的是大根堆,因此我们需要重载一下运算符
代码如下:
struct dqs
{
int num;
};
bool operator <(dqs a,dqs b)
{
return a.num>b.num;
}
priority_queue <dqs> q;//优先队列需要头文件#include<queue>堆排完整代码(无优化)如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int heap[100005],cnt=0;
void push(int x)
{
cnt++;
int now=cnt;
heap[now]=x;
while(now>1)
if(heap[now]<heap[now/2])
{
swap(heap[now],heap[now/2]);
now/=2;
}
else
break;
}
void pop()
{
heap[1]=heap[cnt];
int now=1;
while(now*2+1<=cnt)
{
int l=now*2,r=now*2+1;
if(heap[l]<heap[now])
{
if(heap[r]<heap[l]&&heap[r]<heap[now])
swap(r,l);
swap(heap[l],heap[now]);
now=l;
}
else if(heap[r]<heap[now])
{
swap(heap[r],heap[now]);
now=r;
}
else break;
}
cnt--;
}
int main()
{
int n,x;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
push(x);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("%d ",heap[1]);
pop();
}
}STL优化代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct dqs
{
int num;
};
bool operator <(dqs a,dqs b)
{
return a.num>b.num;
}
dqs t;
priority_queue<dqs>q;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t.num );
q.push(t);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
printf("%d ",q.top());
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}





















 1363
1363

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








