数据类型
标识符: 变量 方法 类 包.....等等标记的名字就是标识符
注意:以下划线字母美元符号¥开头其他部分每个英文单词首字母大写
取名最好用英文命名取名要见名知意增加阅读性
驼峰命名:
类名:首字母大写,其余遵循驼峰命名
方法名,变量名:首字母小写,其余遵循驼峰命名
包名:全部小写,不遵循驼峰命名
关键字
用于定义数据类型的关键字 | |||||
Class: 类 | Interface: 接口 | enum: 枚举 | Byte: 字节 | Short: 短整形 | Int: 整形 |
long: 长整形 | float: 单精度浮点型 | double: 双精度浮点型 | char: 字符 | boolean: true/false | void: 无返回值 |
用于定义流程控制的关键字 | |||||
If: 条件 | else: 反条件 | switch: 多分支结构
| case: 匹配条件 | default: 默认 | while: 循环 |
do: 配合do...while循环条件 | fro: 循环 | break: 停止本次循环 | continue: 结束本次循环继续下一次循环
| return: 跟循环无关 跳出本次方法体 |
|
用于定义访问权限修饰符关键字 | |||||
private: 私有的 | Protected: 受保护的 | public: 公共的 |
|
|
|
用于定义类函数变量修饰符关键字 | |||||
Abstract: 抽象 | Final:常量 | Static: 静态 | Synchronized: 线程安全的 |
|
|
用于定义类和类的封装继承的关键字 | |||||
Extends: 继承类 | Implements: 继承接口 |
|
|
|
|
用于创建实例及引用判断实例的关键字 | |||||
New:创建实例类 | This:本身引用 | Supper:直属父类引用 | Instanceof: 判断实例 |
|
|
用于处理异常的关键字 | |||||
Try:异常代码块 | Catch:异常处理 | Finally:最终处理 | Throw:抛出异常
| Throws: 声明异常
|
|
用于包的关键字 | |||||
Package: 包 | Import:导包 |
|
|
|
|
其他修饰符的关键字 | |||||
Native:一般用于修饰getclass() hascode() Clone() | Strictfp: 规范Java中的浮点类型的计算让计算结果更加精确 | Transient: 修饰的成员变量不是该对象序列化的一部分 | Volatitle: 用来确保将变量的更新操作通知到其他线程 | Assert: 用于程序不准备通过捕获异常来处理的错误 |
|
整数类型:byte short int long 浮点类型:float double 字符类型:char 布尔类型: ture/false
byte | 1字节 | -2^7~2^7(-128~127) |
short | 2字节 | -2^15~2^15(-32768~32767) |
int | 4字节 | -2^31~2^31(约21亿) |
long | 8字节 | -2^63~2^63 |
float | 4个字节 | 大约+/-3.402823(有效位数为6-7位) |
double | 8个字节 | 大约+/-1.797693134862315(有效数字为15-16位) |
char | 以字符集为准 | 字符集(ASCII GBK...) |
true/false | 内存中占一位(不是一个字节 | 用于判断逻辑条件一般用于流程控制 |
public class Idea_ExampleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义整数类型的变量默认情况下赋值就是十进制的情况
int tmpInt = 12 ;
System.out.println(tmpInt);
//定义byte类型的变量:
byte tmpByte = 126;
System.out.println(tmpByte);
//注意:超范围的赋值会报错。
short tmpShort = 30000;
System.out.println(tmpShort);
//整数类型默认就是int类型的,所以12345678910是一个int类型 的数,对于int类型来说,它超出范围了
//要想把一个数给long类型变量,那么后面加上L(推荐)或者l就可以了
long tmpLong = 12345678910L;
System.out.println(tmpLong);
//注意:只有这个数超出int类型的范围了后面才需要加上L,否则无需加L也可以赋值给long类型:
long tmpLong1 = 12;
System.out.println(tmpLong1);
//浮点类型的变量:
//注意:浮点型默认是double类型的,要想将一个double类型的数赋给float类型,必须后面加上F或者f
float tmpFloat = 3.14234567898623F;
System.out.println(tmpFloat);
//注意:double类型后面可以加D或者d,但是一般我们都省略不写
double tmpDouble = 3.14234567898623D;
System.out.println(tmpDouble);
//注意:我们最好不要进行浮点类型的比较:
float tmpFloat1 = 0.3F;
double tmpDouble1 = 0.3;
/*
区别:
= 赋值运算: 将等号右侧的值赋给等号左侧
== 判断==左右两侧的值是否相等 :结果要么相等要么不相等
==运算符的结果就是要么是true,要么是false
*/
System.out.println(tmpFloat1 == tmpDouble1);
//定义boolean类型字段
boolean tmpBl = true;
System.out.println(tmpBl);
boolean tmpBl1 = 5 == 9;
System.out.println(tmpBl1);
}
}
运算符:
4.1.逻辑运算符:&& || !
4. 2.关系运算符:< > <= >= == !=
4. 3.算数运算符:+ - * % /
4.4.扩展运算符:+= -= ++ --
4. 5.位运算符: & | ^ << >> >>>
4. 6.条件运算符:?:(三目运算符)
优先级:赋值< 三目 < 逻辑 < 关系 < 算术 < 单目
public class JavaSE_DataType{
public static void main(String[] args){
byte _by = 127;
short _short = 1245;
int _int = 235252;
//长整数赋值后面加上L标识 用大写L可以区分小写l和1的错误
long _long = 235325235L;
float _float = 2.3532535f;
double _double = 23.3425252525d;
char _char = 'a';
boolean _bool = (4>5);
System.out.println(_bool);
int _intA = 23;
int _intB = 7;
//算数运算符
System.out.println(_intA + _intB);
System.out.println(_intA - _intB);
System.out.println(_intA * _intB);
System.out.println(_intA / _intB);
// 求余数
System.out.println(_intA % _intB);
//关系运算符
System.out.println(_intA <= _intB);
System.out.println(_intA > _intB);
System.out.println(_intA == _intB);
//++a a++ --a a-- 谁在前面 就先运算谁
System.out.println(_intA++);//结果 23
System.out.println(++_intA);//结果 24
//扩展运算符 避免类型转换 整数用+=比较方便
float _float1 = 0.2f;
_float1 += 1;// 如果这里 写成 _float1 = _float1 + 1这里有个整数int转浮点数的错误
System.out.println(_float1);
//位运算符
//& 遇0则0 | 遇1则1 ^异或 做加法(相同取0 异同取1)
System.out.println(4&5);//0100 0101
System.out.println(4|5);//0100 0101
System.out.println(4^5);//0100 0101 --> 0001
//<< 左移 右边符号补0 >> 右移 无符号补0 >>> 无符号补0
System.out.println(6<<1);//0110 --> 01100
System.out.println(6>>1);//0110 --> 0011
System.out.println(6>>>1);//0110--> 0011
//先取正数 取反 加1
System.out.println(~4);//0100 1011 1101
System.out.println(~7);//0101 1010 1100
System.out.println(~6);//0110 1001 1111
}
}
流程控制
控制语句分为三类:顺序、选择和循环
5.1“顺序结构”代表“先执行a,再执行b”的逻辑
5.2“条件判断结构”代表“如果…,则…”的逻辑
5.3“循环结构”代表“如果…,则再继续…”的逻辑
分支结构:
单分支:If(条件){语句块...}
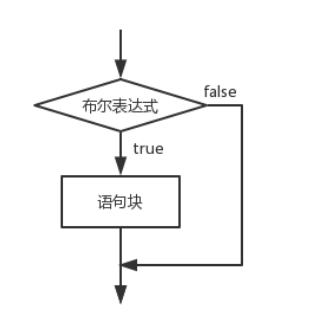
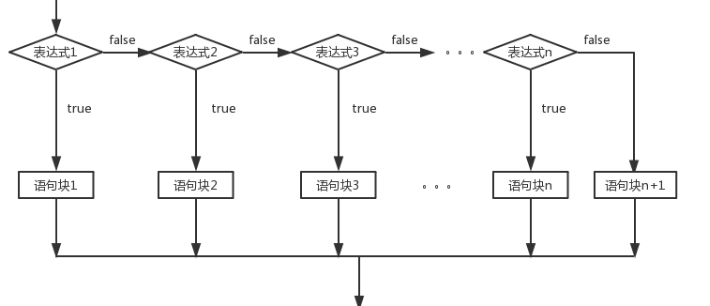
双分支:if( 条件 ){ 语句块... }elseif( 条件 ){ 语句块... } ...... else{ 语句块... }
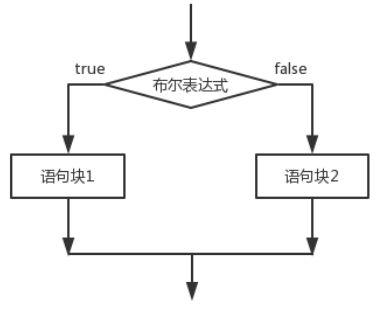
双分支:if( 条件 ){ 语句块... }else{ 语句块... }
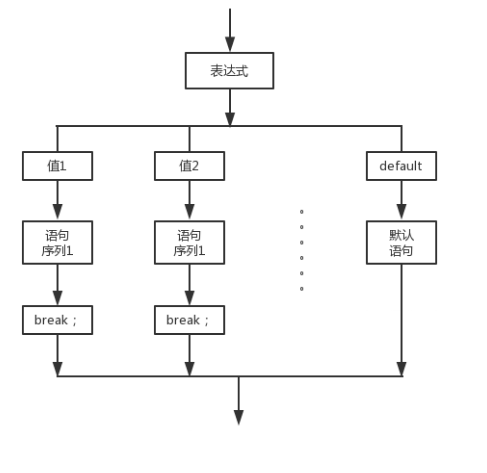
Switch: switch( 条件 ){ case 值:语句块; break; ......default: 默认语句; }
While循环: while(条件){循环体...}
Do-While循环: do{循环体....}while(条件)
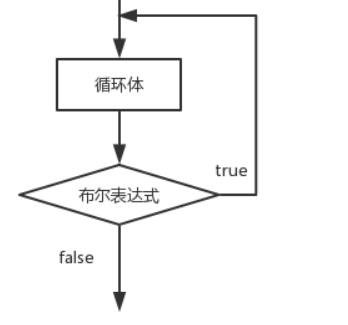
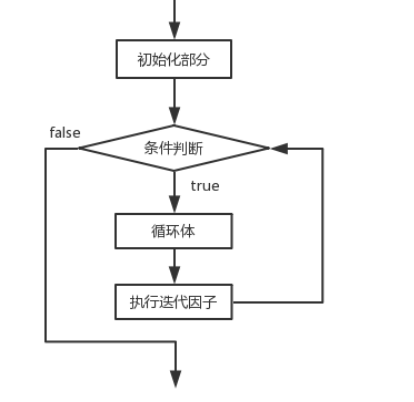
for循环: for(初始化表达式; 条件; 迭代因子){循环体...}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaSE_Flow{
public static void main(String[] args){
//录入会员
// System.out.println("欢迎来到录制会员系统");
// System.out.println("添加会员信息");
// System.out.println("请输入会员号<4位整数>");
// Scanner _scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// String _number = _scan.nextLine();
// System.out.println("会员号: " + _number);
// //获取长度和C#不一样 c#: getLength() java: length()
// if(_number.length() != 4){
// System.out.println("客户号" + _number + "是无效会员号");
// System.out.println("录入信息失败");
// }else{
// System.out.println("请输入会员生日(月/日<2位整数>)");
// _number = _scan.nextLine();
// System.out.println("月日: " + _number);
// System.out.println("请输入积分");
// _number = _scan.nextLine();
// System.out.println("积分: " + _number);
// }
//随意0-100的分数
/*
分数>=90: 优秀
分数>=80: 良好
分数>=60: 中等
分数<60: 差
*/
int _score = (int)(100 * Math.random());
int _gree = 'D';
if(_score >= 90){
_gree = 'A';
}else if(_score >= 80){
_gree = 'B';
}else if(_score >= 70){
_gree = 'C';
}else{
_gree = 'D';
}
//同时 练习if else if else if else Switch case default
switch(_gree){
case 'A':
System.out.println("成绩评测:优秀 " + _score);
break;
case 'B':
System.out.println("成绩评测:良好 " + _score);
break;
case 'C':
System.out.println("成绩评测:中等 " + _score);
break;
default:
System.out.println("成绩评测:差 " + _score);
break;
}
//多重if买车问题
int _money = 500;
if(_money >= 100){
System.out.println("我就买帕沙特!");
}else if(_money >= 50){
System.out.println("我就买依兰拖!");
}else if(_money >= 10){
System.out.println("我就买奥特!");
}else{
System.out.println("我就买安特!");
}
// – 编程实现:计算100以内(包括100)的偶数之和
// – 观察每一次循环中变量值的变化
int _sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){
if(i%2 == 0){
System.out.println("偶数: " + i);
_sum += i;
}
}
System.out.println("0-100偶数和: " + _sum);
System.out.println("课堂作业案例");
//final 修饰的变量 只能初始化一次 变成了常量
final double PI = 3.14;
double r = 4;
double area = PI * r * r;//求面积
double circle = 2 * PI * r;//求周长
System.out.println("area = " + area);
System.out.println("circe = " + circle);
//谁在前 先算谁
int _a = 3;
int _b = _a++;//3
int _c = ++_a;//5
System.out.println("_b: " + _b + "_c: " + _c);
//基础数据 类型转换 低--------高 byte--short--int--long--folat--double
byte _by = 10;
int _n = _by;
//_by = _n; 搞到低会出现不兼容类型
System.out.println("_n: " + _n);//隐式转换 低--------高
//循环语句结构
//如何产生10-15的随机数
int _random = (int)(Math.random() * 16);//强制转换
System.out.println("10-15只能随机产生: " + _random);
double _i = 8 * Math.random();
double _j = 8 * Math.random();
double _k = 8 * Math.random();
int _count = (int)(_i + _j + _k);
if(_count > 15){
System.out.println("今天手气不错 中奖了");
}else if(_count >= 10){
System.out.println("今天手气较差");
}else{
System.out.println("今天手气极差");
}
double _rr = 4 * Math.random();
double _area1 = Math.PI * Math.pow(_rr, 2);
double circe = 2 * Math.PI * _rr;
System.out.println("半径:" + _rr);
System.out.println("面积:" + _area1);
System.out.println("周长:" + circe);
if(_area1 > circe){
System.out.println("面积大于周长");
}else{
System.out.println("周长大于面积");
}
// 淡旺季机票的价格,原价机票价格为5000元,
// ? 淡季头等舱打5折,经济舱打4折
// ? 旺季头等舱打9折,经济舱打8折
// ? 要求
// ? 编写程序实现:
// ? 输入任意的月份与舱位来计算机票的价格
// ? 1代表头等舱,2代表经济舱
// ? 4-10月为旺季,其他月份为淡季
Scanner _sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入月份(1-12)");
int _month = _sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入舱位(1-2)");
int _seat = _sc.nextInt();
float _price = 5000f;
int _seatDisCount = 5;
if(_month >= 4 && _month <= 10){
_seat = _seat == 1 ? 9 : 8;
}else{
_seat = _seat == 1 ? 5 : 4;
}
System.out.println("您需要花费: " + _price * _seatDisCount * 0.1f);
}
}
**总结**
本文简单介绍了基础数据类型 运算符 流程控制相关知识点
后续将会持续更新JAVA相关的知识点 案例 demo 资源 面试题...
希望对各位小伙伴有所帮助
刚开始有些东西排版不好 不太熟悉版块内容 多多谅解 后续会慢慢改善







 本文详细介绍了Java中的数据类型,包括整数、浮点、字符和布尔类型,以及变量命名规则。同时,讲解了关键字的作用,如Class、Interface、enum等,并阐述了不同类型的运算符,如逻辑、关系和算术运算符。此外,还涵盖了流程控制结构,如if-else、switch、while和for循环。
本文详细介绍了Java中的数据类型,包括整数、浮点、字符和布尔类型,以及变量命名规则。同时,讲解了关键字的作用,如Class、Interface、enum等,并阐述了不同类型的运算符,如逻辑、关系和算术运算符。此外,还涵盖了流程控制结构,如if-else、switch、while和for循环。
















 1399
1399

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








