问题及代码:
运行结果:
Problem E Tempter of the Bone
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 7 Accepted Submission(s) : 4
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
The doggie found a bone in an ancient maze, which fascinated him a lot. However, when he picked it up, the maze began to shake, and the doggie could feel the ground sinking. He realized that the bone was a trap, and he tried desperately to get out of this maze.
The maze was a rectangle with sizes N by M. There was a door in the maze. At the beginning, the door was closed and it would open at the T-th second for a short period of time (less than 1 second). Therefore the doggie had to arrive at the door on exactly the T-th second. In every second, he could move one block to one of the upper, lower, left and right neighboring blocks. Once he entered a block, the ground of this block would start to sink and disappear in the next second. He could not stay at one block for more than one second, nor could he move into a visited block. Can the poor doggie survive? Please help him.
The maze was a rectangle with sizes N by M. There was a door in the maze. At the beginning, the door was closed and it would open at the T-th second for a short period of time (less than 1 second). Therefore the doggie had to arrive at the door on exactly the T-th second. In every second, he could move one block to one of the upper, lower, left and right neighboring blocks. Once he entered a block, the ground of this block would start to sink and disappear in the next second. He could not stay at one block for more than one second, nor could he move into a visited block. Can the poor doggie survive? Please help him.
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains three integers N, M, and T (1 < N, M < 7; 0 < T < 50), which denote the sizes of the maze and the time at which the door will open, respectively. The next N lines give the maze layout, with each line containing M characters. A character is one of the following:
'X': a block of wall, which the doggie cannot enter;
'S': the start point of the doggie;
'D': the Door; or
'.': an empty block.
The input is terminated with three 0's. This test case is not to be processed.
'X': a block of wall, which the doggie cannot enter;
'S': the start point of the doggie;
'D': the Door; or
'.': an empty block.
The input is terminated with three 0's. This test case is not to be processed.
Output
For each test case, print in one line "YES" if the doggie can survive, or "NO" otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 5 S.X. ..X. ..XD .... 3 4 5 S.X. ..X. ...D 0 0 0
Sample Output
NO YES
奇偶剪枝:
个人学习后的想法:从起点到终点,除了abs ( (sx - ex ) + abs (sy - ey ); 即 当前点(x,y)到终点(ex,ey)的最短距离外,
如果不能直接到达,那么肯定要绕路走:绕过一个障碍要多走2步,那绕过n个障碍就要多走n*2步,所以剩余步数一定是偶数步才能绕到终点。
搜索时要用到的剪枝:
1.如果当前时间即步数(step) >= T 而且还没有找到D点,则剪掉。
2.设当前位置(x, y)到D点(dx, dy)的最短距离为s,到达当前位置(x, y)已经花费时间(步数)step,那么,如果题目要求的时间T - step < s,则剪掉。
3.对于当前位置(x, y),如果,(T-step-s)是奇数,则剪掉(奇偶剪枝)。
4.如果地图中,可走的点的数目(xnum) < 要求的时间T,则剪掉(路径剪枝)。
//以上为引用/*
*Copyright (c)2015,烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院
*All rights reserved.
*文件名称:HDU.cpp
*作 者:单昕昕
*完成日期:2015年2月27日
*版 本 号:v1.0
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
char maze[9][9];
int starti,startj,endi,endj,t,n,m;
int flag;
int direction[4][2]= {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
void DFS(int px,int py,int time)
{
int i;
if(flag==1)return;
if(maze[px][py]=='X')return;
if(px==endi&&py==endj&&time==t)//到达
{
flag=1;
return;
}
if(px<1||px>n||py<1||py>m)return;
if(time>t)return;//剪枝1
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
{
maze[px][py]='X';//走过的路不能再走,变成墙
DFS(px+direction[i][0],py+direction[i][1],time+1);
maze[px][py]='.';//还原成路,以便下次搜索
if(flag==1)return;
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,block;
char temp;
while(cin>>n>>m>>t)
{
block=0;
flag=0;
if(n==0&&m==0&&t==0)break;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(j=1; j<=m; j++)
{
cin>>maze[i][j];
if(maze[i][j]=='S')
{
starti=i;
startj=j;
continue;
}
if(maze[i][j]=='X')
{
block++;
continue;
}
if(maze[i][j]=='D')
{
endi=i;
endj=j;
}
}
}
if(t>(n*m-block)) //剪枝4
{
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
continue;
}
if((endi+starti+startj+endj+t)%2==1)//剪枝3
{
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
continue;
}
DFS(starti,startj,0);
if(flag==1)cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
递归搜索。
学习心得:
奇偶剪枝:根据题目,doggie必须在第t秒到达门口。也就是需要走t-1步。设doggie开始的位置为(sx,sy),目标位置为(ex,ey).如果abs(ex-x)+abs(ey-y)为偶数,则abs(ex-x)和abs(ey-y)奇偶性相同,所以需要走偶数步;
当abs(ex-x)+abs(ey-y)为奇数时,则abs(ex-x)和abs(ey-y)奇偶性不同,到达目标位置就需要走奇数步。先判断奇偶性再搜索可以节省很多时间,不然的话容易超时。t-sum为到达目标位置还需要多少步。因为题目要求doggie必须在第t秒到达门的位置,所以(t-step)和abs(ex-x)+abs(ey-y)的奇偶性必然相同。因此temp=(t-step)-abs(ex-x)+abs(ey-y)必然为偶数。
问题的大概意思是,狗在S点,门在D点,门只有在T时刻才开,迷宫为N*M矩阵,迷宫内有X代表的墙。问是否狗能准时逃出来。我们要制造一个计划,让狗能在T时刻刚好到达门口,一般思路可以来回走动,快到T时候再到门口。但是题目要求狗每次走的地方都将会陷下去,不能回走,只能绕路走,能绕路走可定要多出偶数的步数,就算是墙挡着也一样如此,可以看草图:
问题的大概意思是,狗在S点,门在D点,门只有在T时刻才开,迷宫为N*M矩阵,迷宫内有X代表的墙。问是否狗能准时逃出来。我们要制造一个计划,让狗能在T时刻刚好到达门口,一般思路可以来回走动,快到T时候再到门口。但是题目要求狗每次走的地方都将会陷下去,不能回走,只能绕路走,能绕路走可定要多出偶数的步数,就算是墙挡着也一样如此,可以看草图:
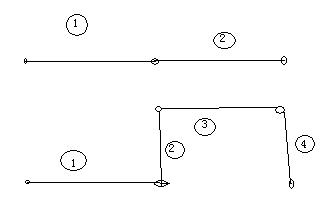
两种不同的走法,下面那一种可以控制时间刚好在T时刻。因为差出的是偶数,所以奇数的话要剪枝掉,省掉搜索时间。而另一个剪枝,路径剪枝,是在开始的时候,将如迷宫的每个地方都走过了,而还没到门开的时间,这时也逃生不了,因为没地方回走了,都塌陷了。
深度搜索下去,直到所用的步数刚好等于给定的T时间,退出递归搜索。

























 155
155

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








