计算带权边的单源最短路径,如果边不带权重,直接用bfs计算就行(例如675. 为高尔夫比赛砍树)
对于 得到要求路径的最小带权子图 这个题的理解:
题目要求 从scr1和scr2出发,到达dest的边权和最小子图。很容易想到dijkstra最短路径,但是,dijkstra最短路径可以求scr1出发到dest的最短路径,也可以求scr2出发到dest的最短路径,求既经过scr1,又经过scr2,到dest的最短路径,就有一点难度。
难点在于如何去遍历图才能得到想要的结果。思路是 dest 反向遍历,存在一个节点mid_node,scr1出发到mid_node最短,scr2出发到mid_node最短,dest出发到mid_node最短。
类似的思想有 1245. 树的直径(多叉树) leetcode-树-v2_林冲风雪山神庙的博客-CSDN博客
此外,考察图的遍历方式的,还有:
最小高度树,leetcode-拓扑排序算法_林冲风雪山神庙的博客-CSDN博客_leetcode拓扑排序
节点序列的最大得分 leetcode-广度优先遍历/图_林冲风雪山神庙的博客-CSDN博客
理论基础
Dijsktra迪杰斯特拉算法的证明(数学归纳法)和代码实现 - 知乎


单源最短路径-Dijkstra算法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili

https://www.cxyzjd.com/article/AivenZhong/84385736
每次从cost里找最短路径的点,这一步体现了贪心的思想。最开始是遍历起点的边,更新costs数组(已经更新过的就不要再动了),然后是找上一步更新过的cost的最短边,继续往下遍历。

parent可以不要
# dijjkstra算法(原生最短路径,还未优化)
def dij(start, graph):
n = len(graph)
# 初始化各项数据,把costs[start]初始化为0,其他为无穷大
# 把各个顶点的父结点设置成-1
costs = [99999 for _ in range(n)]
costs[start] = 0
parents = [-1 for _ in range(n)]
visited = [False for _ in range(n)] # 标记已确定好最短花销的点
t = [] # 已经确定好最短花销的点列表
while len(t) < n:
# 从costs里面找最短花销(找还没确定的点的路径),标记这个最短边的顶点,把顶点加入t中
minCost = 99999
minNode = None
for i in range(n):
if not visited[i] and costs[i] < minCost:
minCost = costs[i]
minNode = i
t.append(minNode)
visited[minNode] = True
# 从这个顶点出发,遍历与它相邻的顶点的边,计算最短路径,更新costs和parents
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]] and minCost + edge[1] < costs[edge[0]]:
costs[edge[0]] = minCost + edge[1]
parents[edge[0]] = minNode
return costs, parents# 用优先队列实现的dijkstra算法
def dij_pq(start, graph):
n = len(graph)
pq = pQueue() # 队列中的元素为[cost, v]形式,cost是该路径的花销, v是去往的结点
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
t = {}
parents = [-1 for _ in range(n)]
pq.put([0, start, -1])
while len(t) < n:
# 从优先队列中找出未被确定的最短路径
minPath = pq.get()
while visited[minPath[1]]:
minPath = pq.get()
minNode = minPath[1]
visited[minNode] = True
t[minNode] = minPath[0]
parents[minNode] = minPath[2]
# 从该最短路径的结点开始找邻边,入队
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]]:
pq.put([edge[1] + t[minNode], edge[0], minNode])
return t, parents743. 网络延迟时间

朴素dij
class Solution(object):
def networkDelayTime(self, times, n, k):
"""
:type times: List[List[int]]
:type n: int
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
def dij(start,graph):
n=len(graph)
# 初始化各项数据,把costs[start]初始化为0,其他为无穷大
costs=[float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
costs[start]=0
# 标记已确定好最短花销的点
visited=[False for _ in range(n)]
#已经确定好的最小花销列表
t=[]
while len(t)<n:
# 从costs里面找最短花销(找还没确定的点的路径),标记这个最短边的顶点,把顶点加入t中
minCost = float("inf")
minNode = -1
for i in range(n):
if not visited[i] and costs[i] < minCost:
minCost = costs[i]
minNode = i
if minNode>=0:
t.append(minNode)
visited[minNode] = True
# 从这个顶点出发,遍历与它相邻的顶点的边,计算最短路径,更新costs
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]] and minCost + edge[1] < costs[edge[0]]:
costs[edge[0]] = minCost + edge[1]
else:
break
return costs
# 邻接矩阵
# graph = [[float('inf')] * n for _ in range(n)]
graph=[[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y, time in times:
# graph[x - 1][y - 1] = time
graph[x-1].append((y-1,time))
costs=dij(k-1,graph)
if max(costs)==float("inf"):
return -1
return max(costs)堆优化dij
# 有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
#
# 给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点,
# wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
#
# 现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
#
#
#
# 示例 1:
#
#
#
#
# 输入:times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2
# 输出:2
#
#
# 示例 2:
#
#
# 输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1
# 输出:1
#
#
# 示例 3:
#
#
# 输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2
# 输出:-1
#
#
#
#
# 提示:
#
#
# 1 <= k <= n <= 100
# 1 <= times.length <= 6000
# times[i].length == 3
# 1 <= ui, vi <= n
# ui != vi
# 0 <= wi <= 100
# 所有 (ui, vi) 对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
#
# Related Topics 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 图 最短路 堆(优先队列) 👍 512 👎 0
# leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class Solution:
def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
def dij(start, graph):
n = len(graph)
# 初始化各项数据,把costs[start]初始化为0,其他为无穷大
costs = [float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
costs[start] = 0
# 标记已确定好最短花销的点
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
# 已经确定好的最小花销列表
t = []
while len(t) < n:
# 从costs里面找最短花销(找还没确定的点的路径),标记这个最短边的顶点,把顶点加入t中
minCost = float("inf")
minNode = -1
for i in range(n):
if not visited[i] and costs[i] < minCost:
minCost = costs[i]
minNode = i
if minNode >= 0:
t.append(minNode)
visited[minNode] = True
# 从这个顶点出发,遍历与它相邻的顶点的边,计算最短路径,更新costs
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]] and minCost + edge[1] < costs[edge[0]]:
costs[edge[0]] = minCost + edge[1]
else:
break
return costs
def dij2(start, graph):
n = len(graph)
heap = [] # 队列中的元素为[cost, v]形式,cost是该路径的花销, v是去往的结点(邻边)
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
t = {}
# pq.put([0, start, -1])
heapq.heappush(heap, (0, start))
while len(t) < n:
# 从优先队列中找出未被确定的最短路径
if len(heap)>0:
minPath = heapq.heappop(heap)
# while visited[minPath[1]]:
# minPath = pq.get()
minNode = minPath[1]
visited[minNode] = True
t[minNode] = minPath[0]
# 从该最短路径的结点开始找邻边,入队
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]]:
# pq.put([edge[1] + t[minNode], edge[0], minNode])
heapq.heappush(heap, (edge[1] + t[minNode], edge[0]))
print(t)
else:
break
return t
# 邻接矩阵
# graph = [[float('inf')] * n for _ in range(n)]
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y, time in times:
# graph[x - 1][y - 1] = time
graph[x - 1].append((y - 1, time))
costs = dij2(k - 1, graph)
if len(costs) < n:
return -1
return max(costs.values())
# leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class Solution(object):
def networkDelayTime(self, times, n, k):
"""
:type times: List[List[int]]
:type n: int
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
#需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?源点到其他点的最短路径的最大值,
#带权路径,贪心的去更新cost数组,cost[i]表示起点到节点i路径的最小值
# 建图
import collections
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i in range(len(times)):
graph[times[i][0]].append((times[i][1], times[i][2]))
costs = [float("inf") for _ in range(n + 1)]
costs[k] = 0
import heapq
heap = []
heapq.heappush(heap, (0,k)) # node,上一个节点到node的权重(该路径的花销)
visited = set()
while len(visited) <= n:
if len(heap) > 0:
cur_weight,cur_node = heapq.heappop(heap)
visited.add(cur_node)
next_nodes = graph[cur_node]
for next_node in next_nodes:
if next_node[0] not in visited:
if cur_weight + next_node[1] < costs[next_node[0]]:
costs[next_node[0]] = cur_weight + next_node[1]
heapq.heappush(heap, (cur_weight + next_node[1],next_node[0]))
else:
break
cost2 = costs[1:]
if max(cost2) != float("inf"):
return max(cost2)
return -16032. 得到要求路径的最小带权子图




朴素dij:超时
class Solution(object):
def minimumWeight(self, n, edges, src1, src2, dest):
"""
:type n: int
:type edges: List[List[int]]
:type src1: int
:type src2: int
:type dest: int
:rtype: int
"""
#三个最短路的交点,src1 和 src2是正向图,dest是反向图
def dij(start, graph):
n = len(graph)
# 初始化各项数据,把costs[start]初始化为0,其他为无穷大
costs = [float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
costs[start] = 0
# 标记已确定好最短花销的点
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
# 已经确定好的最小花销列表
t = []
while len(t) < n:
# 从costs里面找最短花销(找还没确定的点的路径),标记这个最短边的顶点,把顶点加入t中
minCost = float("inf")
minNode = -1
for i in range(n):
if not visited[i] and costs[i] < minCost:
minCost = costs[i]
minNode = i
if minNode >=0:
t.append(minNode)
visited[minNode] = True
# 从这个顶点出发,遍历与它相邻的顶点的边,计算最短路径,更新costs
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]] and minCost + edge[1] < costs[edge[0]]:
costs[edge[0]] = minCost + edge[1]
else:
break
return costs
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
graphf = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y, weight in edges:
# graph[x - 1][y - 1] = time
graph[x].append((y, weight))
graphf[y].append((x, weight))
costs1=dij(src1,graph)
costs2=dij(src2,graph)
costs3=dij(dest,graphf)
ans=float("inf")
for i in range(n):
ans=min(ans,costs1[i]+costs2[i]+costs3[i])
if ans==float("inf"):
return -1
return ans
堆优化dij
思考一下为什么
minPath = heapq.heappop(heap)
while visited[minPath[1]] and len(heap)>0:
minPath = heapq.heappop(heap)
if visited[minPath[1]]:
break
堆里的元素,不是应该都没出现在visited里吗?
为什么删除上面的visited就会报错?
因为可能会有重复的节点。
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
graphf = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y, weight in edges:
# graph[x - 1][y - 1] = time
graph[x].append((y, weight))
graphf[y].append((x, weight))
反向图会有重复节点。
class Solution:
def minimumWeight(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], src1: int, src2: int, dest: int) -> int:
import heapq
# 三个最短路的交点,src1 和 src2是正向图,dest是反向图
def dij2(start, graph):
n = len(graph)
heap = [] # 队列中的元素为[cost, v]形式,cost是该路径的花销, v是去往的结点(邻边)
visited = [False for _ in range(n)]
t = [float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
# pq.put([0, start, -1])
heapq.heappush(heap, (0, start))
while len(heap) > 0:
# 从优先队列中找出未被确定的最短路径
minPath = heapq.heappop(heap)
while visited[minPath[1]] and len(heap)>0:
minPath = heapq.heappop(heap)
if visited[minPath[1]]:
break
minNode = minPath[1]
visited[minNode] = True
t[minNode] = minPath[0]
# 从该最短路径的结点开始找邻边,入队
for edge in graph[minNode]:
if not visited[edge[0]]:
# pq.put([edge[1] + t[minNode], edge[0], minNode])
heapq.heappush(heap, (edge[1] + t[minNode], edge[0]))
return t
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
graphf = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y, weight in edges:
# graph[x - 1][y - 1] = time
graph[x].append((y, weight))
graphf[y].append((x, weight))
costs1 = dij2(src1, graph)
costs2 = dij2(src2, graph)
costs3 = dij2(dest, graphf)
print('costs1', costs1)
print('costs2', costs2)
print('costs3', costs3)
ans = float("inf")
for i in range(n):
ans = min(ans, costs1[i] + costs2[i] + costs3[i])
if ans == float("inf"):
return -1
return ansclass Solution(object):
def minimumWeight(self, n, edges, src1, src2, dest):
"""
:type n: int
:type edges: List[List[int]]
:type src1: int
:type src2: int
:type dest: int
:rtype: int
"""
#狄杰斯特拉最短路径,分别以src1, src2, dest为起点求costs数组
#建图,edges
import collections
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
graphf = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i in range(len(edges)):
graph[edges[i][0]].append((edges[i][1],edges[i][2]))
graphf[edges[i][1]].append((edges[i][0],edges[i][2]))
def dij(start,graph):
costs = [float("inf") for _ in range(n)]
costs[start] = 0
import heapq
heap = []
heapq.heappush(heap,(0,start))
visited = set()
while len(visited) < n:
if len(heap) > 0:
cur_weight,cur_node = heapq.heappop(heap)
visited.add(cur_node)
neighbors = graph[cur_node]
for neighbor in neighbors:
if neighbor[0] not in visited:
if neighbor[1] + cur_weight < costs[neighbor[0]]:
costs[neighbor[0]] = neighbor[1] + cur_weight
heapq.heappush(heap,(neighbor[1] + cur_weight,neighbor[0]))
else:
break
return costs
costs1 = dij(src1,graph)
costs2 = dij(src2,graph)
costs3 = dij(dest,graphf)
ans = float("inf")
for i in range(n):
ans = min(ans,costs1[i] + costs2[i] + costs3[i])
if ans == float("inf"):
return -1
return ans堆优化的最短路径
6081. 到达角落需要移除障碍物的最小数目
class Solution(object):
def minimumObstacles(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
heap = []
import heapq
if grid[0][0] == 0:
heapq.heappush(heap, (0, (0,0)))
else:
heapq.heappush(heap, (1, (0,0)))
visited= {}
visited[(0,0)] = grid[0][0]
dires = [(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)]
res = float("inf")
while len(heap):
d,(cur_x,cur_y), = heapq.heappop(heap)
if cur_x == len(grid)-1 and cur_y == len(grid[0])-1:
return d
for dire in dires:
new_x = cur_x + dire[0]
new_y = cur_y + dire[1]
if new_x >= 0 and new_x <=len(grid)-1 and new_y >=0 and new_y <= len(grid[0])-1:
#别忘了visited[(new_x,new_y)] > d+grid[new_x][new_y]记录路径
if (new_x,new_y) not in visited or visited[(new_x,new_y)] > d+grid[new_x][new_y]:
visited[(new_x, new_y)] = d+grid[new_x][new_y]
heapq.heappush(heap, (d+grid[new_x][new_y],(new_x,new_y)))
return res对比2种写法
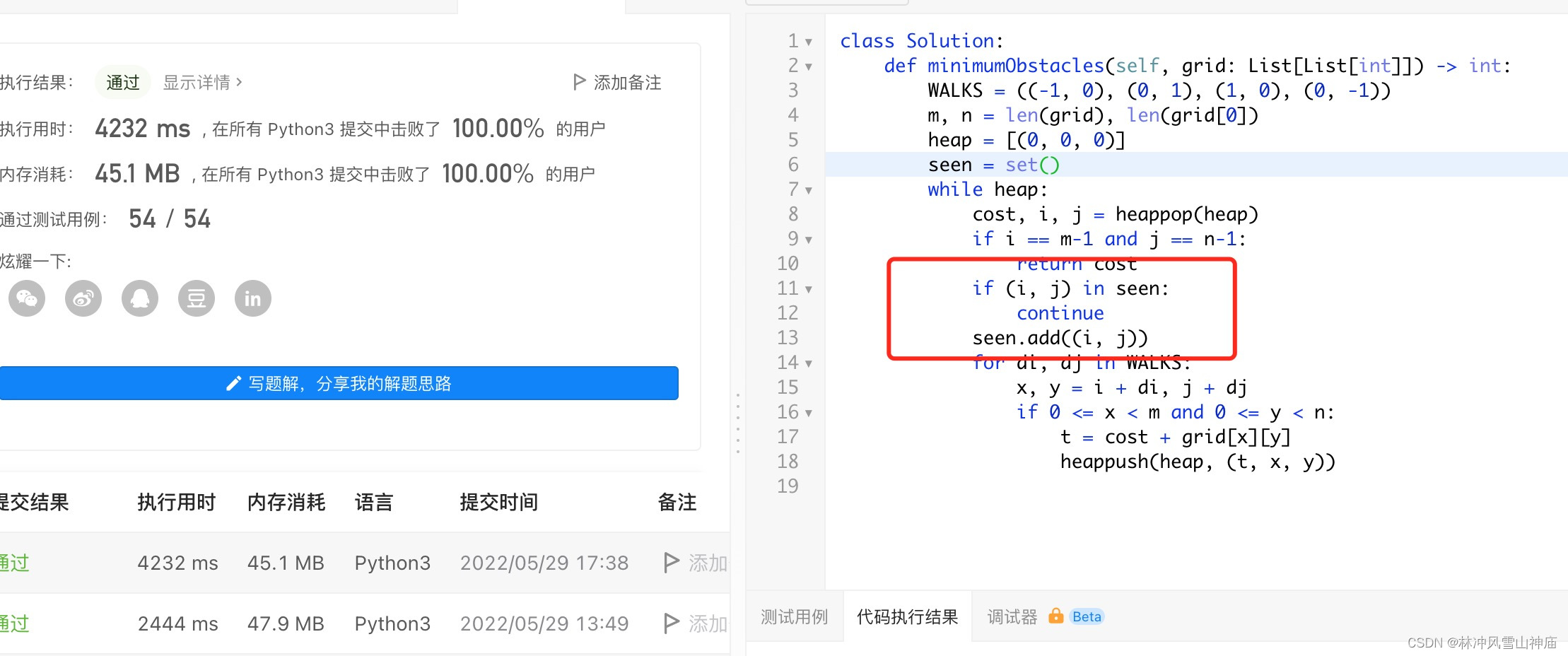

上面那种写法不超时,下面的写法超时!
为什么?

下面这个 相同的 (x,y) 会被重复的加入进入。
比如 (1, 2), 然后这个 1,2 在heap的底层,于是他就一直加入不了 visited,结果下面的(1,2)还是疯狂的向里面加
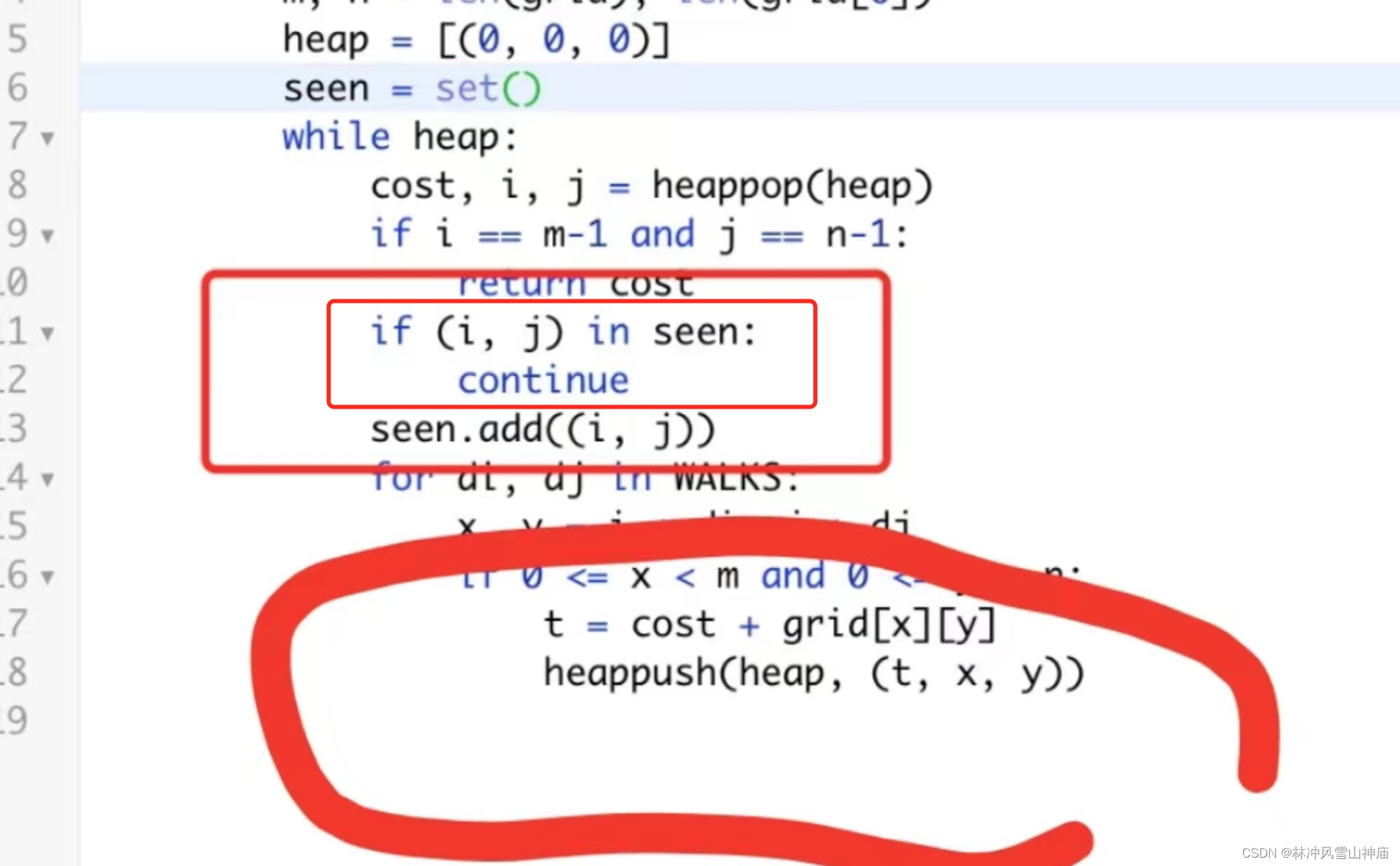
这 if in 就是正好把这种情况给过滤掉了。
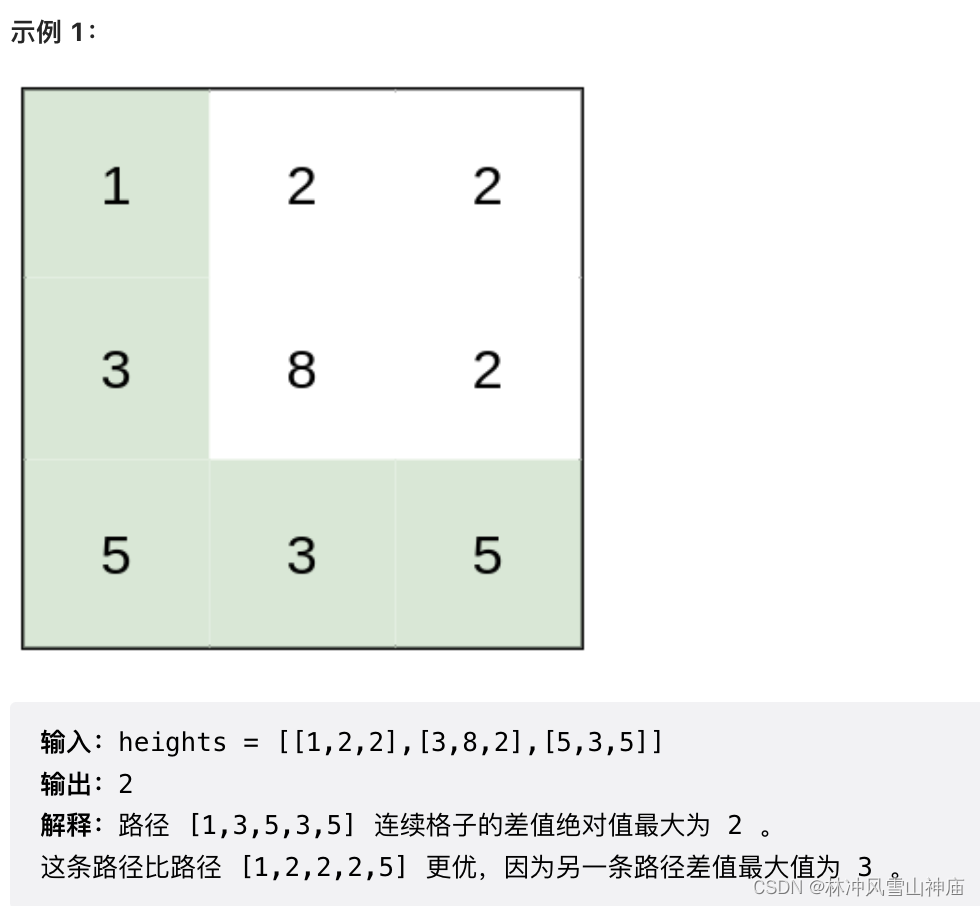
1631. 最小体力消耗路径

class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(heights) == 1 and len(heights[0]) == 1:
return 0
directions = [(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)]
visited = set()
heap = []
import heapq
heapq.heappush(heap,(float("-inf"),(0,0)))
while heap:
#最短路,d为最短路
d,(x,y) = heapq.heappop(heap)
if x == len(heights) - 1 and y == len(heights[0])-1:
return d
if (x,y) in visited:
continue
visited.add((x,y))
for direction in directions:
new_x = x + direction[0]
new_y = y + direction[1]
if 0<=new_x<=len(heights)-1 and 0<=new_y<=len(heights[0])-1:
t = max(d,abs(heights[new_x][new_y] - heights[x][y]))
heapq.heappush(heap,(t,(new_x,new_y)))























 1441
1441











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








