题目: Codeforces Round 942 (Div. 2)
A. Contest Proposal
题意
两个升序(不降)的序列a和b,可以在a的任意位置插入任意数(要保持升序),使对任意i,有a[i] <= b[i],问最少插入几次
思路
对于某个位置i插入什么数不用考虑,总有保持升序又满足a[i] <= b[i]的办法的,插入这个操作就相当于把a数组在i之后的部分后移一格
可以从前往后依次插入,这样前边的序列都是满足条件的不用管,后边依次判断要不要插入(如果a[i] > b[i]就要插入)
代码
i是遍历a数组看要不要插入,j是a[i]对应的b数组下标
总之把后移操作换成了移下标,i没动j后移说明a[i]对应的数还在后面,需要后移,答案加一
(我在说什么
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 105;
int a[N], b[N];
int main()
{
int T, n;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> b[i];
int ans = 0;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n)
{
while (j < n && a[i] > b[j])
{
j++;
ans++;
}
i++, j++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B. Coin Games
题意
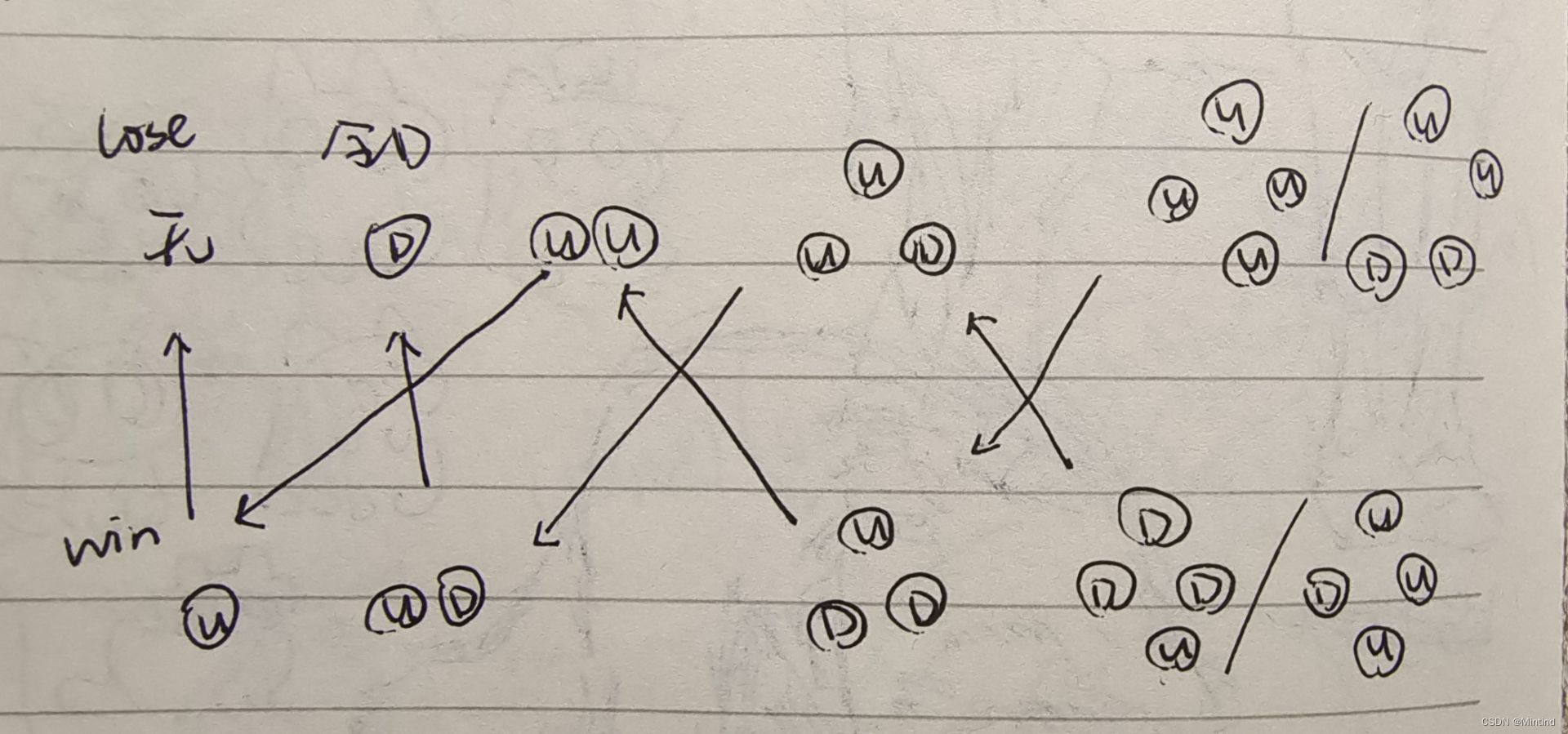
n个硬币,每个硬币有U或者D两个状态(朝上朝下),操作:选一个硬币取走,并把周围两个硬币翻面,玩家A和B依次操作,无法操作判输
思路
列了一些必赢必输的情况,然后发现这不U单数就必赢吗
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 105;
int a[N], b[N];
int main()
{
int T, n;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n;
string str;
cin >> str;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == 'U') cnt++;
}
if (cnt & 1) cout << "yes\n";
else cout <<"no\n";
}
return 0;
}
C. Permutation Counting
题意
对i(1…n),你手头有a[i]张写着i的卡,你可以再任意买k张卡(1…n),问最终你手头的卡最多能凑出多少1-n的排列
思路
贪心,首先尽凑出尽可能多套[1-n]
也就是k要先补给数量少的卡 -> 排序,补前边的
枚举要凑出的[1-n]数,判断是否可行 -> 二分答案
假设最多能凑出x个[1-n],先把他们按同样的顺序(这个顺序好像有讲究但是反正不用输出)依次摆开,这样就有x * n - n + 1个排列了
有多的卡(指最后数量>= x + 1)摆在两边,每个数只能摆一次,每摆一个答案加一(总有一个排列顺序↑满足这点),所以答案要加上本来数量就>= x+1的卡 + k补完x个[1-n]后还剩的部分
(剩下的k肯定拿去买数量不够x+1的了,这样答案最大化,而且够不到的卡数一定大于剩下的k,因为小于等于的话都可以再凑一波[1-n]了)
代码
答应我技艺不精就全用long long好吗,在这de半天(给自己一拳
二分,lower_bound,upper_bound我一生之敌
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
ll a[N], sum[N];
int n;
ll k;
ll cal(ll x)//如果要凑出x个[1-n],需要补多少卡
{
int p = lower_bound(a + 1, a + n + 1, x) - a - 1;
return x * p - sum[p];
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);//排序!
sum[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];//前缀和!好算!
ll l = a[1], r = a[1] + k;
while (l < r)
{
ll mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (cal(mid) <= k) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
//printf("l %lld\n", l);
k = k - cal(l);
int p = upper_bound(a + 1, a + n + 1, l) - a - 1;//这里要求第一个本来数量就>= x+1的卡的下标(实际上是p + 1),所以要用upper_bound
ll res = l * n - n + 1 + k + n - p; //l个[1-n]的 + 剩下的k + 本来就>= x+1的卡数
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D1. Reverse Card (Easy Version)
思路
设d = gcd(a, b),a = x * d, b = y * d
b * d | a + b
b | x + y
y * d | x + y
y | x
故有gcd(a, b) = b,设a = k * b
b * b | k * b + b
b | k + 1
设k + 1 = k' * b,则a = (k' * b - 1) * b = k' * b * b - b
对于每个b,有(n + b) / b * b个k’满足a在n范围内
枚举b,算a的个数
(好绕啊…写个博客重推一遍还是没懂思路
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e6 + 5;
int main()
{
ll T, n, m;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n >> m;
ll ans = n;
for (ll i = 2; i <= m; i++)
{
ll t = i * i;
ans += (n + i) / t;
//if (n/t) cout << i << ' ' << n / t << endl;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D2. Reverse Card (Hard Version)
思路
设d = gcd(a, b),a = x * d, b = y * d
a + b | b * d
x + y | y * d
由(x, y) = 1,得(x + y, y) = 1,故有x + y | d
枚举x、y,a = x * k * (x + y),b = y * k * (x + y),判断让a、b都落在合法区间内有多少个k,加到答案中
代码
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= sqrt(n); i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= sqrt(m); j++)
{
if (__gcd(i, j) == 1)
{
res += min(n / (i + j) / i, m / (i + j) / j);
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}






















 938
938











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








