一、什么是链表
链表在内存中的位置不一定是连续的,如下图所:数据元素随机存储在内存中,通过指针维系数据之间一对一的逻辑关系,这样的存储结构就是链表;

链表由多个节点组成,每个节点又是由值和指向下一个节点的地址组成,所以链表在内存中存储的位置不一定是连续的,节点之间的关联是通过节点中存储的地址进行关联。
对于单链表,如果知道了第一个元素,就可以通过遍历的方式访问整个链表,因此第一个节点最重要,称之为头节点。
二、如何构造链表
链表的节点是由值和指向下一个节点的地址组成,所以在定义实体类时,需要最基本的两个属性,如下所示,val用来存储数据,next用来存储指向下一个节点的地址;
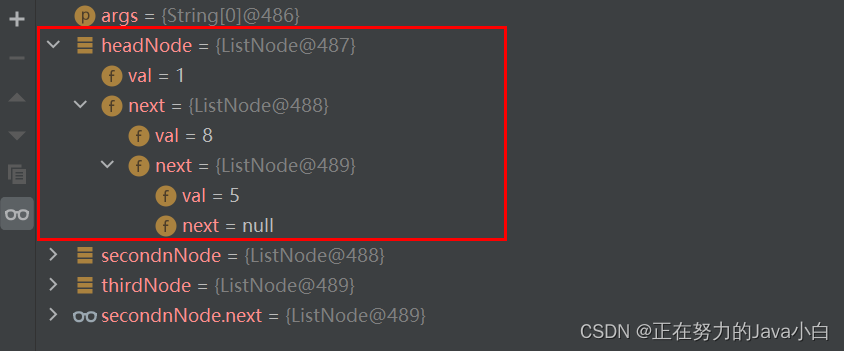
下面代码中创建了三个对象,headNode(头节点),secondnNode,thirdNode。其中secondnNode赋值给了headNode中的next属性,thirdNode赋值给了secondnNode中的next属性。
/**
* 在算法中最常用的链表定义方式
*/
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode headNode=new ListNode(1);
ListNode secondnNode=new ListNode(8);
ListNode thirdNode=new ListNode(5);
headNode.next = secondnNode;
secondnNode.next = thirdNode;
System.out.println(headNode);
}
}
通过Debug可以看出,整体代码执行后,三个节点组成了一个简单的线性访问,可以通过headNode节点逐个向后访问。
三、链表的基本操作
3.1遍历链表
/**
* 获取链表长度
*
* @param headNode 表头
* @return
*/
private static void getListLength(ListNode headNode) {
int length = 0;
ListNode node = headNode;
while (node != null) {
node = node.next;
length++;
}
System.out.println(length);
}
3.2插入链表
1)插入节点位置在第一个:直接将插入节点的next指向头节点t即可;
2)插入节点位置非第一个:则只需要遍历到插入节点的前一个元素,然后将插入节点的next指向遍历当前节点的next,当前节点的next指向插入节点的next即可;
/**
* 插入操作
*
* @param headNode 表头
* @param nodeInsert 插入节点
* @param position 插入位置
* @return
*/
private static ListNode insertNode(ListNode headNode, ListNode nodeInsert, int position) {
if (headNode == null) {
return nodeInsert;
}
int listLength = getListLength(headNode);
if (position > listLength + 1 || position < 1) {
System.out.println("下标越界");
return headNode;
}
if (position == 1) {
nodeInsert.next = headNode;
return nodeInsert;
}
int i = 1;
ListNode node = headNode;
while (i < position - 1) {
i++;
node = node.next;
}
nodeInsert.next = node.next;
node.next = nodeInsert;
return headNode;
}
3.3删除链表
1)删除节点位置在第一个:直接返回headNode.next即可;
2)插入节点位置非第一个:则只需要遍历到删除的前一个元素,然后将当前节点的next指向下个节点的next即可;
/**
* 删除节点
*
* @param headNode 表头
* @param position 删除节点位置
* @return
*/
private static ListNode deleteNode(ListNode headNode, int position) {
int listLength = getListLength(headNode);
if (position > listLength || position < 0) {
System.out.println("下标越界");
return headNode;
}
int i = 1;
ListNode node = headNode;
while (i < position - 1) {
i++;
node = node.next;
}
if (position == 1) {
return node.next;
}
node.next = node.next.next;
return headNode;
}
























 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








