方式1、继承Thread类
- 继承Thread,覆写该类中的run()方法,run()方法中即为该线程要实现的具体业务。
public class NewThread1 extends Thread{
private String title;
public NewThread1(String title){
this.title = title;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(this.title+",i="+i);
}
}
}
如何启动线程?
- 启动线程时不能直接调用run()方法
先观察一下直接调用run()方法会出现什么情况:
public class ThreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewThread1 thread1 = new NewThread1("Thread1");
NewThread1 thread2 = new NewThread1("Thread2");
NewThread1 thread3 = new NewThread1("Thread3");
thread1.run();
thread2.run();
thread3.run();
}
}
截取一部分结果,可以看出:直接调用run()方法仅仅是做了一个顺序打印,并没有使用多线程。

- 启动多线程正确的方式是调用Thread类的start()方法
public class ThreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewThread1 thread1 = new NewThread1("Thread1");
NewThread1 thread2 = new NewThread1("Thread2");
NewThread1 thread3 = new NewThread1("Thread3");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
通过观察结果,可以看出,调用start()方法才能启动线程:
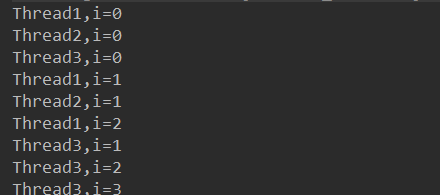
start()方法与run()方法的区别与关系:
-
调用start方法方可








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1958
1958











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








