目录
44.sar 主要帮助我们掌握系统资源的使用情况,特别是内存和CPU的使用情况
48.objdump 反汇编工具 告诉我们可执行程序是有地址的
一、基础操作指令
1.man
an interface to the on-line reference manuals
1 Executable programs or shell commands
2 System calls (functions provided by the kernel)
3 Library calls (functions within program libraries)
4 Special files (usually found in /dev)
5 File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd
6 Games
7 Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7)
8 System administration commands (usually only for root)
9 Kernel routines [Non standard]
2.ls(list)
list directory content
-l use a long list format
-a all
3.mkdir
make directories
mkdir -p dir1/dir2 #创建一连串路径
4.rmdir
remove empty directories
5. touch
update the access and modification times of each FILE to the current time
6.type
命令可以用来查看 shell 命令的类型,即它是内置命令还是外部命令。命令类型有如下几种:
alias:表示是别名。keyword:关键字,shell 保留字。function:函数,shell 函数。builtin:内置命令。file:文件,外部命令。- :空表示没找到。
Linux命令之查看命令类型type_type命令-CSDN博客 具体type用法
7.cd
cd .. #返回上一层
cd ~ #返回当前用户的家目录
cd / #返回根目录
cd - #返回上一个路径
cd + 绝对路径/相对路径8.pwd
print name of working directory
9.rm
remove files or directories
-r : recurive
-rf : recurive force
-i : prompt before every removal
*通配结构 (*.c 表示所有.c文件)(*表示所有文件)
10.nano
a small ,free and friendly editor
11.cp
copy files or directories
-rf : recurive force
12.mv
move(rename) files
13.cat/tac
concatenate files and print on the standard output

Linux中的13个基本Cat命令示例 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
14.echo
diaplay a line of text
>:输出重定向(覆盖式的写入)
echo aaa > test.txt # 1.创建没有的文件 2.将本该输出到显示器的内容输出到了文件里
>>:追加重定向(追加式的写入)
<:输入重定向,本该从键盘中输入改为从文件中输入
echo $? // 获取最近一个进程执行完毕的退出码
15.tree
list contents of directories in a tree-like format
tree root
16.stat
display file or file system status
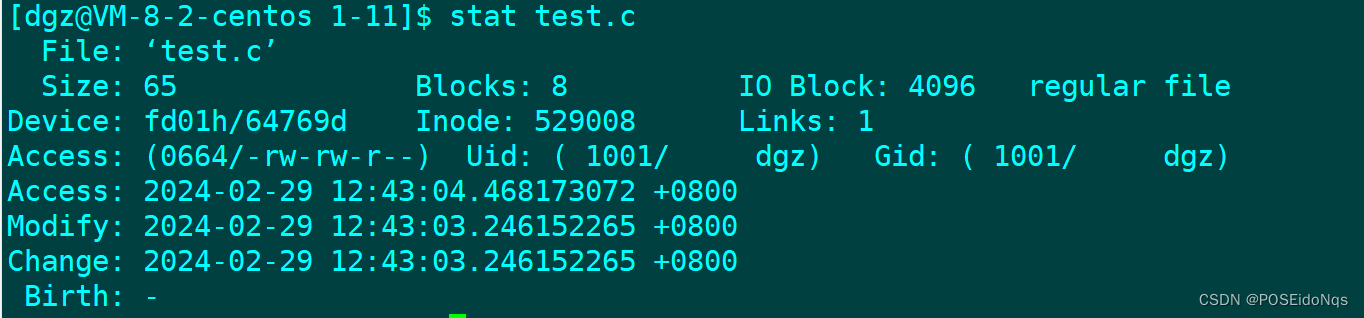
Modification time (mtime):当该文件的『内容数据』变更时,就会更新这个时间! 『内容数据』指的是文件中记录的内容,而不包括文件属性和权限等!
Change time (ctime):当该文件的『状态 (status)』改变时,就会更新这个时间,举例来说, 像是文件权限、属性、inode号等被更改了,都会更新这个时间。
Access time (atime):当我们访问该文件时,就会更新这个时间为最后一次访问该文件的时间 。 当我们使用 cat 、more、less等命令读取文件信息的时候,就会更新 atime 了。
17.more
可以把一个文件内容打印至屏幕占满,用于阅读长文本,需要逐行阅读,只能向前移动
more -5 xxx #打印前五行
18.less
与more相似,但可以前后移动,重新回到开始,输入g
19.head
output the first part of files
head -30 xxx
20.tail
output the last of files
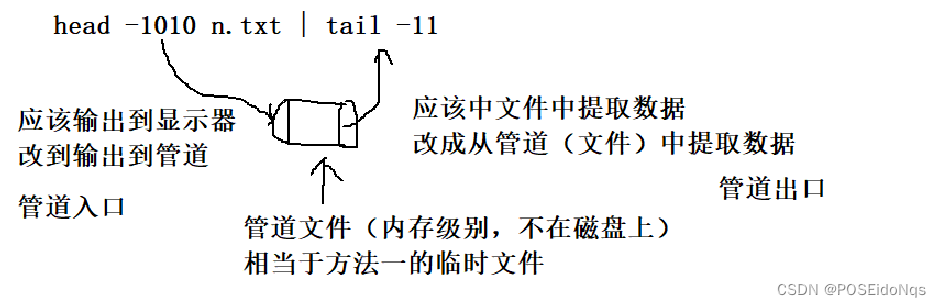
提取999-1009行
1.利用临时文件
2.利用管道
head -1010 n.txt | tail -11
 21.grep
21.grep
print lines maching a pattern
行文本过滤器,比less和more功能更强大
grep大小写敏感
-i 不区分大小写
-v 不显示xxx
grep -E ^a test.txt #找到文件test.txt含有以a字母为行开头的内容
-E选项可以用来扩展选项为正则表达式
$表示匹配文件末尾,字符需要在$之前表示以字符结尾 a$表示以a结尾
^表示匹配文件起始,字符需要在^之后表示以字符起始 ^a表示以a起始
22.wc
print newline,word and bype counts of each file
wc -l #计算文件行数
23.xargs
build and excute command lines from standard input

24.date
date +%Y:%m:%d-%H:%M:%S
date +%Y:%m:%d-%H:%M:%S +@xxx # xxx为时间戳
 25.cal
25.cal
display a calendar
26.find
search for files in a directory hierachy
find常用选项很多,先了解按name寻找文件
find ~ -name xxx #在~家目录下找名字为xxx的文件
find . -name "*.c" -maxdepth 1 | xargs rm
find . -name "*.c" -maxdepth 1 找到当前目录下.*结尾的文件,目录深度为1
xargs是一个强有力的命令,它能够捕获一个命令的输出,然后传递给另外一个命令,用于很多不支持|管道来传递参数的命令
相当于将前边命令的执行结果,也就是查找到的文件名,传递给后边的rm指令进行删除
find . -name "*.c" | xargs rm 没有进行深度控制,删除的不仅是当前目录下的文件,会将子目录下的文件也删除
27.which
show the full path of (shell) commands
只有设置了环境变量才可以搜索到
28.whereis
locate binary, source and manual page files for a command
寻找特定文件,只能用于查找二进制文件、源代码文件和man手册页
29.alias
给一条命令起别名,只能在当前有效
30.zip/unzip
package and compress(archive) files
zip name.zip xxx -r #将目录里所有文件或目录压缩,不加-r只能压缩xxx
unzip name.zip -d 要解压的路径
31.tar
32.uname
print system information




33.ln
make links between files
ln -s xxx name.link
34.mkfifo
make FIFOs(name pipes)
mkfifo f
35.su
run a command with substitute user and group ID
su + usr #切换到用户
su #切换到root
36.yum
yum list
yum install
yum remove [-y]
37.ldd + filename (查看文件的动态库)
38.file + filename (查看文件属性)
39.readelf
40.ps (查看当前终端下对应的进程)
ps axj #查看当前系统中所有的进程
ps axj | head 1 && ps axj | grep 'myproc'
41.top (相当于任务管理器)
42.ls /proc (用文件的方式查看进程)
43.vmstat(CPU监控命令)
报告关于内核线程、虚拟内存、磁盘、陷阱和 CPU 活动的统计信息
44.sar 主要帮助我们掌握系统资源的使用情况,特别是内存和CPU的使用情况
45.netstat 查看网络连接状态
46.free 查看内存资源状态
47.df 查看磁盘分区资源状态
48.objdump 反汇编工具 告诉我们可执行程序是有地址的
49.ipcs 查看众多ipc资源
ipcs -m 查看共享内存
ipcrm -m shmid 删除id为shmid的共享内存
50.ulimit 命令
ulimit -a 查看所有相关命令
改变Shell进程的Resource Limit允许core文件最大为1024K: $ ulimit -c 1024
51.rpm
rpm -qa 查询所有rpm包
52.systemctl
systemctl start mysqld.service
二、几个重要的热键
























 81
81











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








