复习题
1. 实际参数和形式参数的区别是什么?
形式参数:被定义在被调用函数中的变量。
实际参数:出现在函数调用中的值,该值被附给形式参数。
2. 根据下面各函数的描述,分别编写它们的 ANSI C 函数头。注意,只需写出函数头,不用写函数体。
a. donut()接受一个int类型的参数,打印若干(参数指定数目)个0
b. gear()接受两个int类型的参数,返回int类型的值
c. guess()不接受参数,返回一个int类型的值
d. stuff_it()接受一个double类型的值和double类型变量的地址,把第1个值储存在指定位置
a. void donut(int);
b. int gear(int, int);
c. int guess(void);
d. void stuff_it(double, double*)
3. 根据下面各函数的描述,分别编写它们的ANSI C函数头。注意,只需写出函数头,不用写函数体
a. n_to_char()接受一个int类型的参数,返回一个char类型的值
b. digit()接受一个double类型的参数和一个int类型的参数,返回一个int类型的值
c. which()接受两个可储存double类型变量的地址,返回一个double类型的地址
d. random()不接受参数,返回一个int类型的值
a. char n_to_char(int);
b. int digit(double, int);
c. double* which(double*, double*);
d. int random();
4. 设计一个函数,返回两整数之和
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
5. 如果把复习题4改成返回两个double类型的值之和,应如何修改函数?
double add(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
6. 设计一个名为alter()的函数,接受两个int类型的变量x和y,把它们的值分别改成两个变量之和以及两变量之差
void alter(int *a, int *b)
{
int sum = *a + *b;
int subtract = *a - *b;
*a = sum;
*b = subtract;
return;
}
7. 下面的函数定义是否正确?
void salami(num)
{
int num, count;
for (count = 1; count <= num; num++)
printf(" O salami mio!\n");
}
修改后:
void salami(int num)
{
int count;
for (count = 1; count <= num; count++)
printf(" O salami mio!\n");
}
8. 编写一个函数,返回3个整数参数中的最大值
int max(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a > b ? (a > c ? a : c) : (b > c ? b : c);
}
9. 给定下面的输出:
Please choose one of the following:
1) copy files 2) move files
3) remove files 4) quit
Enter the number of your choice:
a. 编写一个函数,显示一份有4个选项的菜单,提示用户进行选择(输出如上所示)。
b. 编写一个函数,接受两个int类型的参数分别表示上限和下限。该函数从用户的输入中读取整数。如果整数超出规定上下限,函数再次打印菜单(使用a部分的函数)提示用户输入,然后获取一个新值。如果用户输入的整数在规定范围内,该函数则把该整数返回主调函数。如果用户输入一个非整数字符,该函数应返回4。
c. 使用本题a和b部分的函数编写一个最小型的程序。最小型的意思是,该程序不需要实现菜单中各选项的功能,只需显示这些选项并获取有效的响应即可。
a.
void menu()
{
printf("Please choose one of the following: \n");
printf("1) copy files 2) move files \n");
printf("3) remove files 4) quit\n");
printf("Enter the number of your choice: ");
}
b.
int ul(int u, int l)
{
int num;
while(scanf("%d", &num) == 1)
{
if(num >= l && num <= u)
{
return num;
}
else
{
menu();
}
}
return 4;
}
c.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void menu()
{
printf("Please choose one of the following: \n");
printf("1) copy files 2) move files \n");
printf("3) remove files 4) quit\n");
printf("Enter the number of your choice:");
}
int ul(int u, int l)
{
int num;
while(scanf("%d", &num) == 1)
{
if(num >= l && num <= u)
{
return num;
}
else
{
menu();
}
}
return 4;
}
int main(void)
{
int u, l;
scanf("%d %d", &l, &u);
int x = ul(u, l);
printf("\nXXXX%d\n", x);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
编程练习
1. min(x, y)
设计一个函数min(x, y),返回两个double类型值的较小值。在一个简单的驱动程序中测试该函数。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
double min(double, double);
int main(void)
{
double a, b;
printf("Enter 2 values of double :");
if (scanf("%lf %lf", &a, &b) == 2)
{
printf("The smaller one in %lf and %lf is %lf\n", a, b, min(a, b));
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
double min(double x, double y)
{
return x > y ? y : x;
}
2. chline(ch, i, j)
设计一个函数chline(ch, i, j),打印指定的字符j行i列。在一个简单的驱动程序中测试该函数。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void chline(char, int, int);
int main(void)
{
char c;
int rows, cols;
printf("Enter a character: ");
scanf("%c", &c);
printf("Enter the rows and cols: ");
scanf("%d %d", &rows, &cols);
chline(c, rows, cols);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void chline(char ch, int i, int j)
{
for (int row = 0; row < j; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < i; col++)
{
putchar(ch);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
3. 打印字符
编写一个函数,接受3个参数:一个字符和两个整数。字符参数是待打印的字符,第1个整数指定一行中打印字符的次数,第2个整数指定打印指定字符的行数。编写一个调用该函数的程序。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void chline(char, int, int);
int main(void)
{
char c;
int rows, cols;
printf("Enter a character: ");
scanf("%c", &c);
printf("Enter the rows and cols: ");
scanf("%d %d", &rows, &cols);
chline(c, rows, cols);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void chline(char ch, int i, int j)
{
for (int row = 0; row < j; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < i; col++)
{
putchar(ch);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
4. 调和平均数
两数的调和平均数这样计算:先得到两数的倒数,然后计算两个倒数的平均值,最后取计算结果的倒数。编写一个函数,接受两个double类型的参数,返回这两个参数的调和平均数。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
double harmonic_average(double, double);
int main(void)
{
double a, b;
printf("Enter 2 values of double: ");
scanf("%lf %lf", &a, &b);
printf("The harmonic average of %lf and %lf is %lf\n", a, b, harmonic_average(a, b));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
double harmonic_average(double a, double b)
{
return 1 / ((1 / a + 1 / b) / 2);
}
5. larger_of()
编写并测试一个函数larger_of(),该函数把两个double类型变量的值替换为较大的值。例如, larger_of(x, y)会把x和y中较大的值重新赋给两个变量。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void large_of(double *, double *);
int main(void)
{
double a, b;
printf("Enter 2 values of double: ");
scanf("%lf %lf", &a, &b); //注意参数是指针
large_of(&a, &b);
printf("We will change both values to the larger one.\nNow, a is %lf, b is %lf.\n", a, b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void large_of(double *a, double *b)
{
*a > *b ? *b = *a : *a = *b;
}
6. 三数排序
编写并测试一个函数,该函数以3个double变量的地址作为参数,把最小值放入第1个变量,中间值放入第2个变量,最大值放入第3个变量。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
void func(double *, double *, double *);
int main(void)
{
double x, y, z;
printf("Enter 3 values of double: ");
scanf("%lf %lf %lf", &x, &y, &z);
func(&x, &y, &z);
printf("After sorting, now x is %lf, y is %lf, z is %lf.\n", x, y, z);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void func(double *a, double *b, double *c)
{
double max = *a, mid, min;
if (*b > max)
max = *b;
if (*c > max)
max = *c;
if (*a == max)
{
mid = *b > *c ? *b : *c;
min = *b > *c ? *c : *b;
}
if (*b == max)
{
mid = *a > *c ? *a : *c;
min = *a > *c ? *c : *a;
}
if (*c == max)
{
mid = *a > *b ? *a : *b;
min = *a > *b ? *b : *a;
}
*a = min;
*b = mid;
*c = max;
}
7. 读取字符
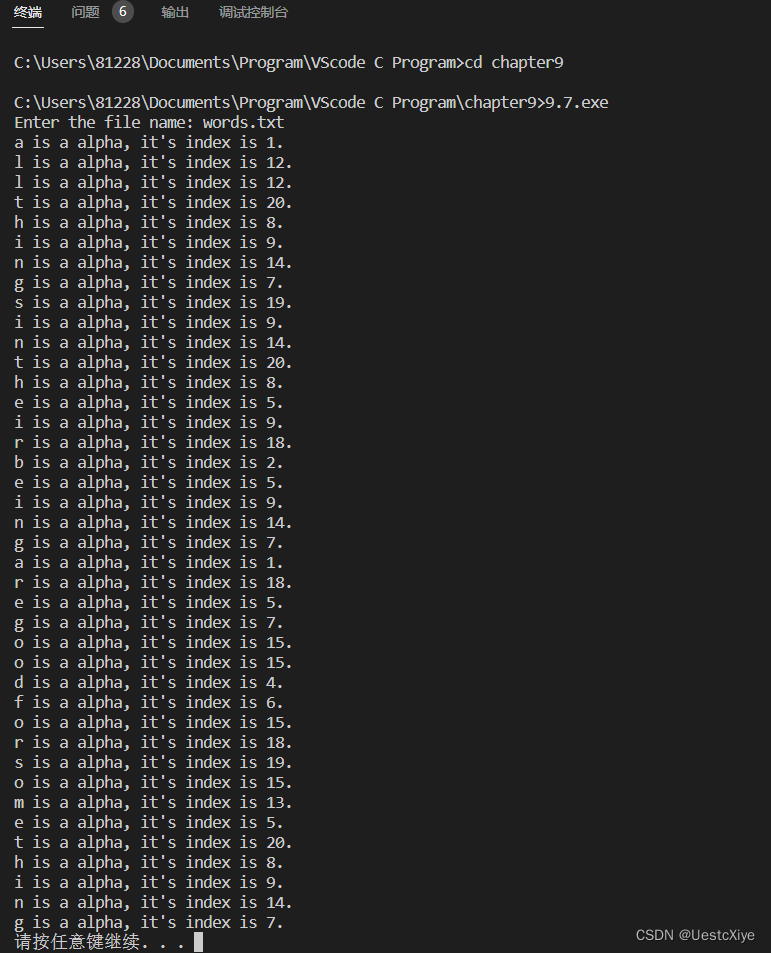
编写一个函数,从标准输入中读取字符,直到遇到文件结尾。程序要报告每个字符是否是字母。如果是,还要报告该字母在字母表中的数值位置。例如,c和C在字母表中的位置都是3。合并一个函数,以一个字符作为参数,如果该字符是一个字母则返回一个数值位置,否则返回-1。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int char_to_index(char);
int main(void)
{
FILE *fp;
char fname[50];
char ch;
printf("Enter the file name: ");
scanf("%s", fname);
fp = fopen(fname, "r"); // 只读模式打开文件
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to open file.\n");
exit(1); // 退出程序
}
// getc(fp)从打开的文件中获取一个字符
while ((ch = getc(fp)) != EOF)
{
int index;
if ((index = char_to_index(ch)) > 0)
printf("%c is a alpha, it's index is %d.\n", ch, index);
}
fclose(fp); // 关闭文件
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int char_to_index(char ch)
{
if (isalpha(ch))
{
if (isupper(ch))
return ch - 'A' + 1;
else
return ch - 'a' + 1;
}
else
return -1;
}
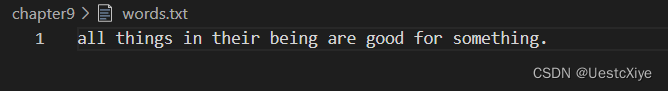
words.txt:
运行结果:
8. power()
第6章的程序清单6.20中,power()函数返回一个double类型数的正整数次幂。改进该函数,使其能正确计算负幂。另外,函数要处理0的任何次幂都为0,任何数的0次幂都为1(函数应报告0的0次幂未定义,因此把该值处理为1)。要使用一个循环,并在程序中测试该函数。
代码:
// power.c -- 计算数的整数幂
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
double power(double n, int p); // ANSI函数原型
int main(void)
{
double x, xpow;
int exp;
printf("Enter a number and the positive integer power");
printf(" to which\nthe number will be raised.Enter q");
printf(" to quit.\n");
while (scanf("%lf%d", &x, &exp) == 2)
{
if (x == 0 && exp == 0)
printf("0 to the power 0 is undefined.\n");
else
{
xpow = power(x, exp); // 函数调用
printf("%.3g to the power %d is %.5g\n", x, exp, xpow);
}
printf("Enter next pair of numbers or q to quit.\n");
}
printf("Hope you enjoyed this power trip -- bye!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
double power(double n, int p) // 函数定义
{
double pow = 1;
int i;
bool negative; // 判断p的正负
if (p == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (p < 0)
{
p = -p;
negative = true;
}
else
negative = false;
for (i = 1; i <= p; i++)
pow *= n;
if (negative)
return 1 / pow;
else
return pow;
}
9. 使用递归函数重写编程练习8
代码:
// power.c -- 计算数的整数幂
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
double power(double n, int p); // ANSI函数原型
int main(void)
{
double x, xpow;
int exp;
printf("Enter a number and the positive integer power");
printf(" to which\nthe number will be raised.Enter q");
printf(" to quit.\n");
while (scanf("%lf%d", &x, &exp) == 2)
{
if (x == 0 && exp == 0)
printf("0 to the power 0 is undefined.\n");
else
{
xpow = power(x, exp); // 函数调用
printf("%.3g to the power %d is %.5g\n", x, exp, xpow);
}
printf("Enter next pair of numbers or q to quit.\n");
}
printf("Hope you enjoyed this power trip -- bye!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
double power(double n, int p) // 函数定义
{
if (p == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (p > 0)
return n * power(n, p - 1);
else
return 1 / n * power(n, p + 1);
}
10. to_base_n()
为了让程序清单9.8中的to_binary()函数更通用,编写一个to_base_n()函数接受两个在2~10范围内的参数,然后以第2个参数中指定的进制打印第1个参数的数值。例如,to_base_n(129, 8)显示的结果为201,也就是129的八进制数。在一个完整的程序中测试该函数。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void to_base_n(unsigned long n, unsigned int x);
int main(void)
{
unsigned long number;
unsigned int base;
char prompt[] = "Enter an integer and a base(2~10):\n(Enter q to quit) ";
printf("%s", prompt);
while (scanf("%lu %hd", &number, &base) == 2)
{
printf("Equivalent: ");
to_base_n(number, base);
putchar('\n');
printf("%s", prompt);
}
printf("Done.\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void to_base_n(unsigned long n, unsigned int x) // 递归函数
{
int r;
if (x < 2 || x > 10)
{
printf("Base Error! Please try again.\n");
return;
}
r = n % x;
if (n >= x)
to_base_n(n / x, x);
printf("%d", r);
return;
}
11. fibonacci()
编写并测试Fibonacci()函数,该函数用循环代替递归计算斐波那契数
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int fibonacci(int i);
int main()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d\t\n", fibonacci(i));
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int fibonacci(int n)
{
int a = 1, b = 1, sum;
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
sum = a + b;
a = b;
b = sum;
}
return sum;
}






















 4122
4122











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










