03-树3 Tree Traversals Again(25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
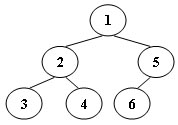
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1import java.util.Scanner;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
/**
*
*
结题思路:
根据输入,构建二叉树。
每当一行读入为Push,就在new一个节点给父节点对应的儿子。
每当一行读入为Pop ,就返回null给父节点对应的儿子。
*/
public class Main {
static Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
private static int n;
private static int count = 0;
private static StringBuffer resultBuffer = new StringBuffer();
public static void postorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
resultBuffer.append(root.val + " ");
}
}
//创建一棵树,然后返回它的根节点
public static TreeNode buildTree() {
TreeNode node = null;
if (count < 2 * n) {
String line = input.nextLine().trim();
if (line.startsWith("Push")) {
int value = Integer.parseInt(line.split(" ")[1]);
node = new TreeNode(value);
count++;
} else {
count++;
return null;
}
node.left = buildTree();
node.right = buildTree();
}
return node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当nextint和nextlne一起用的时候会出错,全部都用nextline
n = Integer.parseInt(input.nextLine().trim());
TreeNode rootNode = buildTree();
postorder(rootNode);
System.out.println(resultBuffer.toString().trim());
}
} 





















 6837
6837

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








