1、链表的基础知识
关于链表的基础知识还有不熟悉的,请查看链表的实现(基于动态内存分配)
2、使用链表实现稀疏多项式,也是基于上述的链表来实现的。
稀疏多项式可以当作一种链表结构,所以,可以直接从上述的链表派生过来。在派生之前应该考虑清楚稀疏多项式的结构,稀疏多项式的基本单元由系数和指数构成,所以构成该类的模板需要两个参数,声明为如下的形式:
template<typename T,typename S>
class CPolynomialtemplate <typename T>
class List
{
protected:
class Node
{
public:
Node *pNext;
T m_data;
Node()
{
memset(&m_data, 0, sizeof(m_data));
pNext = NULL;
}
};
//typedef Node * Link_List;
int m_Lenth;
public:
List();
List(const List &m_List);
~List();
const List&operator=(const List &m_List);
bool List_IsEmpty();
int List_Lenth();
void List_Insert(T num);
void List_Delete(int nPos);
void List_Destroy();
void List_Clear();
void List_Display();
Node * List_GetHead() const;
bool List_FindElem(T num);
void List_Modify(T num, int nPos);
protected:
//Link_List pHead;
Node *pHead;
typedef Node* Position;
};
#endiftemplate<typename T,typename S>
class Item
{
public:
T coeff;
S index;
Item()
{
coeff = 0;
index = 0;
}
Item(const Item& item)
{
coeff = item.coeff;
index = item.index;
}
Item & operator = (const Item& item)
{
coeff = item.coeff;
index = item.index;
return *this;
}
bool operator == (const Item& item)
{
return coeff == item.coeff&& index == item.index;
}
};1、该实例类需要和CPolynomial中的指数和系数对应
2、该实例化类的对象之间存在赋值,拷贝,判断相等的操作
到目前,构建该多项式类的基本工作已经完成了,下面需要来实际构建该类:
<pre name="code" class="cpp">template<typename T,typename S>
class CPolynomial :public List<Item<T,S>>
{
public:
CPolynomial();
CPolynomial(const CPolynomial& poly);
~CPolynomial();
//操作符重载
const CPolynomial &operator =(const CPolynomial &polyn);
//friend CPolynomial operator+(const CPolynomial &polyn);
//①friend CPolynomial operator+<>(const CPolynomial<T,S>& polynLeft,const CPolynomial<T,S> &polynRight);
template<typename T,typename S>
friend CPolynomial<T, S> operator+(const CPolynomial<T, S>&, const CPolynomial<T, S>&);
template<typename T,typename S>
friend CPolynomial<T,S> operator-(const CPolynomial<T,S>& polynLeft,const CPolynomial<T,S> &polynRight)
{
CPolynomial<T, S> polynTemp = polynLeft;
polynTemp.PolynSubstract(polynRight);
return polynTemp;
}
friend CPolynomial operator*(const CPolynomial &polyn)
{
}
void PolynInsert(const Item<T,S> & item);
void PolynRemove(const Item<T,S> & item);
bool PolynSearch(const Item<T,S> &item,int &nPos);
bool PolynSearchIndex(const S& index,Position *pos = NULL);
bool PolynModify(Position pos);
bool PolynIsEmpty();
void PolynClear();
void PolynDestroy();
void PolynPrint();
void PolynAdd(const CPolynomial &polynSecond);
void PolynSubstract(CPolynomial polynSecond);
void PolynMultiply(CPolynomial polynFirst, CPolynomial polynSecond);
public:
int m_nLenth;
List<Item<T,S>> m_List;
};
<pre name="code" class="cpp">#include "List.h"
#include "List.cpp"
#include "Polynomial.h"
#include "Polynomial.cpp"
void main()
{
List<int> myList;
for(int i=0;i<12;i++)
{
myList.List_Insert(i);
}
myList.List_Insert(15);
cout<<"**myList:"<<myList.List_Lenth()<<endl;
myList.List_Display();
List<int> newList = myList;
cout<<"**newList:"<<newList.List_Lenth()<<endl;
newList.List_Display();
myList.List_Insert(-2);
List<int> newOpList;
newOpList = myList;
cout<<"**newOpList:"<<newOpList.List_Lenth()<<endl;
newOpList.List_Display();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
newOpList.List_Delete(1);
cout<<"**newOpList:"<<newOpList.List_Lenth()<<endl;
newOpList.List_Display();
newOpList.List_Destroy();
Item<double, int> item;
CPolynomial<double, int> m_Polyn;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++)
{
item.coeff = i*3.14;
item.index = i;
m_Polyn.PolynInsert(item);
}
m_Polyn.PolynPrint();
CPolynomial<double, int> m_PolynSecond;
for (int i = 3; i < 8; i++)
{
item.coeff = i*i;
item.index = i;
m_PolynSecond.PolynInsert(item);
}
cout << "Second:" << endl;
m_PolynSecond.PolynPrint();
m_Polyn.PolynAdd(m_PolynSecond);
cout << "Add:" << endl;
m_Polyn.PolynPrint();
CPolynomial<double, int> m_PolynThird;
m_PolynThird = m_Polyn + m_PolynSecond;
cout << "+:" << endl;
m_PolynThird.PolynPrint();
CPolynomial<double, int> m_PolynForth;
m_PolynForth = m_PolynThird - m_PolynSecond;
cout << "Forth:" << endl;
m_PolynForth.PolynPrint();
system("pause");
}
最终程序的输出如下所示:
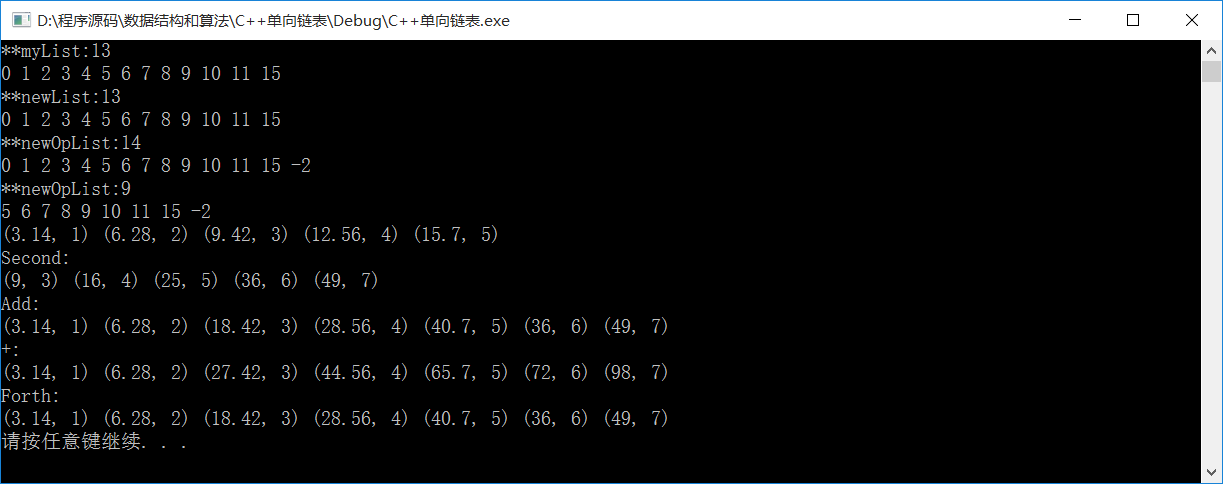
至此,多项式的构建完成了。通过类模板和继承来实现了稀疏多项式,并且实现了操作符的重载。






















 283
283











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








