Go语言是一个极容易上手的语言,而且Go程序的优化套路基本上被大家莫得清清楚楚的,如果你有心,可以在互联网上搜出很多Go程序优化的技巧,有些文章可能只介绍了几个优化点,有些文章从CPU的架构到Slice预分配,再到通过pprof找性能的瓶颈点等等全面介绍Go程序的优化,所以说可见的手段基本上被大家摸得门清,最近老貘出了一道题,如下所示,可以看到大家对Go语言的优化已经摸的多深了。
const N = 1000
var a [N]int
//go:noinline
func g0(a *[N]int) {
for i := range a {
a[i] = i // line 12
}
}
//go:noinline
func g1(a *[N]int) {
_ = *a // line 18
for i := range a {
a[i] = i // line 20
}
}Go 官方也没闲着。虽然Go语言创立之初也并没有目标要和C++语言打平性能,但是Go团队对Go语言的编译和运行时优化也一直在进行着。
最近,Go语言也正在新加两个性能优化的特性,一个是cmd/compile: profile-guided optimization[1], 这个提案[2]已经被接受, 后续功能初步成型后我们再介绍。另外一个增加memory arena[3]。
除了大家常见的通用语言的优化外,影响Go程序性能最大的问题之一就是垃圾回收,所以使用C++、Rust开发的程序员diss Go程序的原因之一。不过这也是垃圾回收编程语言无法绕开的特性,基本上无可避免的带有STW的开销,即使没有STW,垃圾回收时也会耗资源进行对象的便利和检查,所以理论上来说Go性能相比较C+/Rust语言性能总会差一些,除非你禁用垃圾回收、纯粹做CPU计算。
Debian的 benchmark's game网站测试和公布了好多语言的一些场景的性能比较,比如下面这个是Rust和Go的几个实现版本的性能比较:
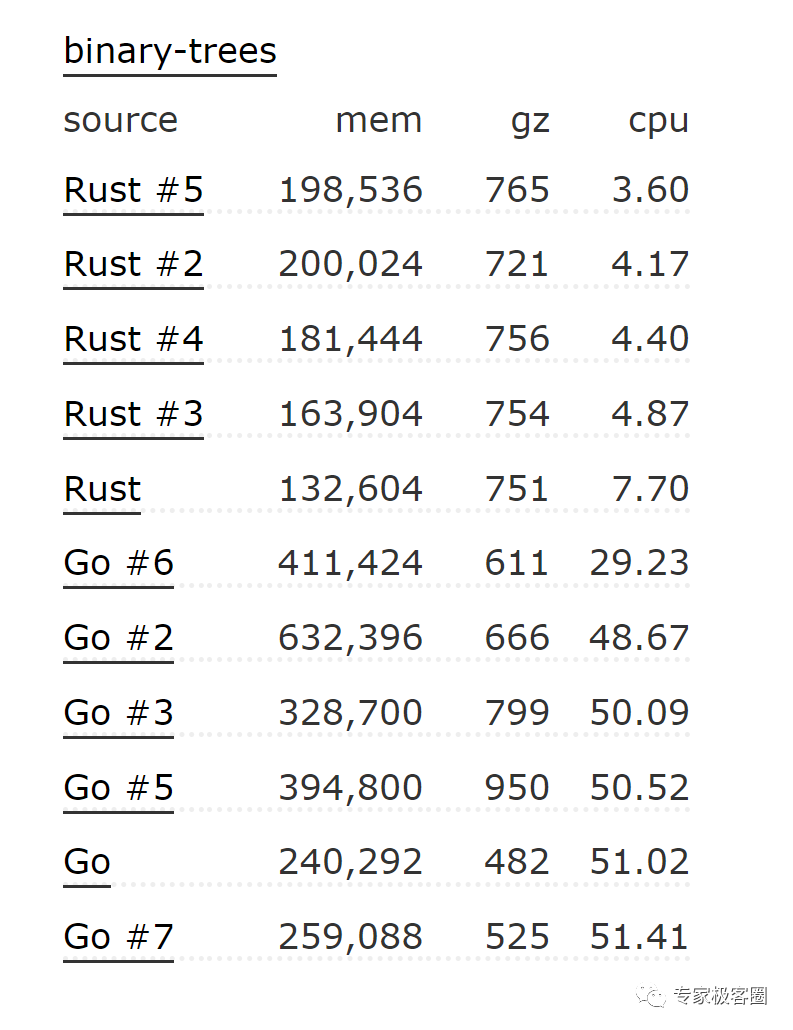
可以看到在这个二叉树的场景下Go的性能比Rust的也差很多。不过性能最好的Rust实现使用arena的内存分配:
use bumpalo::Bump;
use rayon::prelude::*;
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Clone, Copy)]
struct Tree<'a> {
left: Option<&'a Tree<'a>>,
right: Option<&'a Tree<'a>>,
}
fn item_check(tree: &Tree) -> i32 {
if let (Some(left), Some(right)) = (tree.left, tree.right) {
1 + item_check(right) + item_check(left)
} else {
1
}
}
fn bottom_up_tree<'r>(arena: &'r Bump, depth: i32) -> &'r Tree<'r> {
let tree = arena.alloc(Tree { left: None, right: None });
if depth > 0 {
tree.right = Some(bottom_up_tree(arena, depth - 1));
tree.left = Some(bottom_up_tree(arena, depth - 1));
}
tree
}
...arena是一个内存池的技术,一般来说arena会创建一个大的连续内存块,该内存块只需要预先分配一次,在这块内存上的创建和释放都是手工执行的。
Go语言准备新加入 arena 的功能,并在标准库提供一个新的包: arena。当前这个提案[4]还是holding的状态,但是相关的代码已经陆陆续续地提到master分支了,所以说配批准也基本跑不了了,应该在Go 1.20,也就是明年春季的版本中尝试使用了。(当然也有开发者对Go的这种做法不满,因为外部开发者提出这种想法基本上被驳回或者不被关注,而Go团队的人有这想法就可以立马实现,甚至提案还没批准)。
包arena当前提供了几个方法:
NewArena(): 创建一个Arena, 你可以创建多个Arena, 批量创建一批对象,统一手工释放。它不是线程安全的。
Free(): 释放Arena以及它上面创建出来的所有的对象。释放的对象你不应该再使用了,否则可能会导致意想不到的错误。
New[T any](a *Arena "T any") *T:创建一个对象
MakeSlice[T any](a *Arena, len, cap int "T any") []T: 在Arena创建一个Slice。
Clone[T any](s T "T any"): 克隆一个Arena上对象,只能是指针、slice或者字符串。如果传入的对象不是在Arena分配的,直接原对象返回,否则脱离Arena创建新的对象。
当前还没有实现MakeMap、MakeChan这样在Arena上创建map和channel的方法,后续可能会加上。
arena的功能为一组Go对象创建一块内存,手工整体一次性的释放,可以避免垃圾回收。毕竟,我们也提到了,垃圾回收是Go程序的最大的性能杀手之一。
官方建议在批量创建大量的Go对象的时候,每次能以Mib分配内存的场景下使用更有效,甚至他们找到了一个场景:protobuf的反序列化。
因为涉及到垃圾回收、内存分配的问题,所以这个功能实现起来也并不简单,涉及到对运行时代码的改造。不考虑垃圾回收对arena的处理, arena主要的实现在在运行时的arena.go[5]中。因为这个功能还在开发之中,或许这个文件还会有变更。
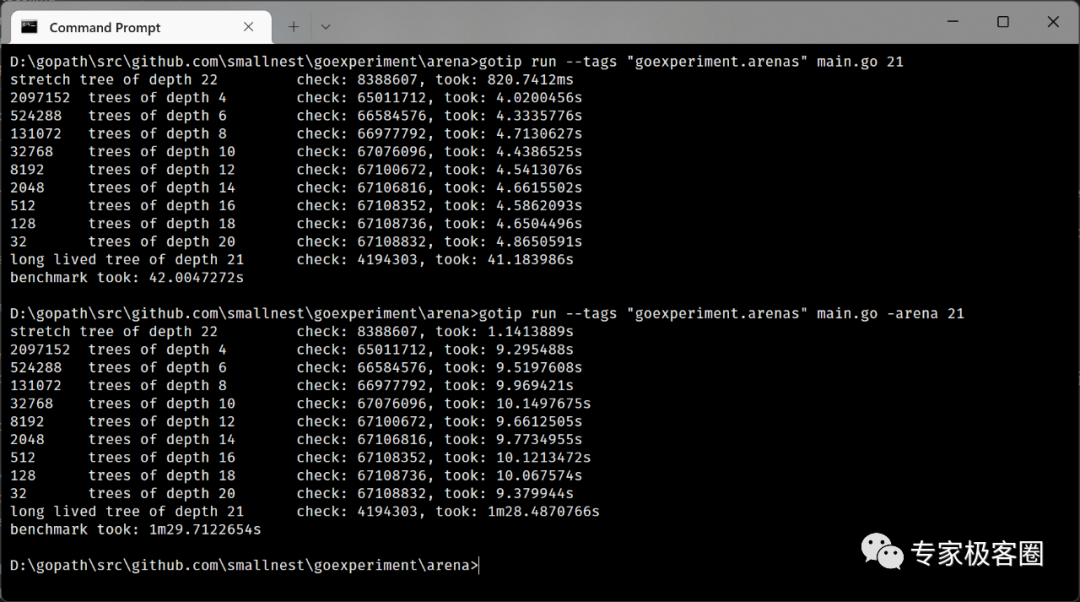
接下来,我们使用debian benchmark's game的二叉树的例子,对使用arena和不使用arena的情况下做一个比较:
package main
import (
"arena"
"flag"
"fmt"
"strconv"
"time"
)
// gotip run -tags "goexperiment.arenas" main.go -arena 21
// GOEXPERIMENT=arenas gotip run main.go -arena 21
var n = 0
type Node struct {
left, right *Node
value []byte
}
func bottomUpTree(depth int) *Node {
if depth <= 0 {
return &Node{}
}
return &Node{bottomUpTree(depth - 1), bottomUpTree(depth - 1), make([]byte, 128, 128)}
}
func bottomUpTreeWithArena(depth int, a *arena.Arena) *Node {
node := arena.New[Node](a "Node")
node.value = arena.MakeSlice[byte](a, 128, 128 "byte")
if depth <= 0 {
return node
}
node.left = bottomUpTreeWithArena(depth-1, a)
node.right = bottomUpTreeWithArena(depth-1, a)
return node
}
func (n *Node) itemCheck() int {
if n.left == nil {
return 1
}
return 1 + n.left.itemCheck() + n.right.itemCheck()
}
const minDepth = 4
var useArena = flag.Bool("arena", false, "use arena")
func main() {
flag.Parse()
if flag.NArg() > 0 {
n, _ = strconv.Atoi(flag.Arg(0))
}
appStart := time.Now()
defer func() {
fmt.Printf("benchmark took: %v\n", time.Since(appStart))
}()
if *useArena {
maxDepth := n
if minDepth+2 > n {
maxDepth = minDepth + 2
}
stretchDepth := maxDepth + 1
a := arena.NewArena()
start := time.Now()
check := bottomUpTreeWithArena(stretchDepth, a).itemCheck()
a.Free()
fmt.Printf("stretch tree of depth %d\t check: %d, took: %v\n", stretchDepth, check, time.Since(start))
a = arena.NewArena()
longLiveStart := time.Now()
longLivedTree := bottomUpTreeWithArena(maxDepth, a)
defer a.Free()
for depth := minDepth; depth <= maxDepth; depth += 2 {
iterations := 1 << uint(maxDepth-depth+minDepth)
check = 0
start := time.Now()
for i := 1; i <= iterations; i++ {
a := arena.NewArena()
check += bottomUpTreeWithArena(depth, a).itemCheck()
a.Free()
}
fmt.Printf("%d\t trees of depth %d\t check: %d, took: %v\n", iterations, depth, check, time.Since(start))
}
fmt.Printf("long lived tree of depth %d\t check: %d, took: %v\n", maxDepth, longLivedTree.itemCheck(), time.Since(longLiveStart))
} else {
maxDepth := n
if minDepth+2 > n {
maxDepth = minDepth + 2
}
stretchDepth := maxDepth + 1
start := time.Now()
check := bottomUpTree(stretchDepth).itemCheck()
fmt.Printf("stretch tree of depth %d\t check: %d, took: %v\n", stretchDepth, check, time.Since(start))
longLiveStart := time.Now()
longLivedTree := bottomUpTree(maxDepth)
for depth := minDepth; depth <= maxDepth; depth += 2 {
iterations := 1 << uint(maxDepth-depth+minDepth)
check = 0
start := time.Now()
for i := 1; i <= iterations; i++ {
check += bottomUpTree(depth).itemCheck()
}
fmt.Printf("%d\t trees of depth %d\t check: %d, took: %v\n", iterations, depth, check, time.Since(start))
}
fmt.Printf("long lived tree of depth %d\t check: %d, took: %v\n", maxDepth, longLivedTree.itemCheck(), time.Since(longLiveStart))
}
}这段程序中我们使用-arena参数控制要不要使用arena。首先你必须安装或者更新gotip到最新版(如果你已经安装了gotip, 执行gotip downloamd,如果还未安装,请先go install golang.org/dl/gotip@latest)。
启用
-arena: 运行GOEXPERIMENT=arenas gotip run -arena main.go 21不启用
-arena: 运行GOEXPERIMENT=arenas gotip run -arena=false main.go 21
不过这个特性还在开发之中,功能还不完善。
我在MacOS上测试,使用arena性能会有明显的提升,而在windows下测试,性能反而下降了。
参考资料
[1]
cmd/compile: profile-guided optimization: https://github.com/golang/go/issues/55022#
[2]提案: https://github.com/golang/proposal/blob/master/design/55022-pgo-implementation.md
[3]memory arena: https://github.com/golang/go/issues/51317
[4]提案: https://github.com/golang/go/issues/51317
[5]arena.go: https://github.com/golang/go/blob/26b48442569102226baba1d9b4a83aaee3d06611/src/runtime/arena.go
2022 GopherChina大会报名火热进行中!
扫描下方二维码即可报名参与哦~大会合作、现场招聘及企业购票等事宜请联系微信:18516100522
戳这里 Go !




















 135
135











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








