一 、线程的状态
二 、线程操作的相关方法

1 、取得和设置线程的名称
在线程操作中,如果没有为一个线程指定一个名称,则系统在使用会自动为线程分配一个名称,格式为 Thread-xx
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("当前执行的线程名称是" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public class ThreadNameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
new Thread(mt,"线程-A").start();
new Thread(mt,"线程-B").start();
new Thread(mt).start();
new Thread(mt,"线程-C").start();
new Thread(mt).start();
}
}
程序运行结果:

修改以上的代码,观察其运行结果:
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("当前执行的线程名称是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public class ThreadNameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
new Thread(mt,"线程").start();
mt.run();
}
}
程序运行结果:

从结果中发现,主方法可以直接通过 Runnable 接口的子类对象调用 run() 方法,实际上,主方法也是一个线程。
提问:Java 程序每次运行至少启动几个线程?
回答:至少启动两个线程。一个是 main 线程,另一个是垃圾收集线程。
2 、判断线程是否启动
在Java中通过 isAlive() 方法判断线程是否已经启动而且仍然在启动
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("当前执行的线程名称是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public class ThreadNameDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt,"线程");
System.out.println("线程开始执行之前--->" + t.isAlive()); //判断是否启动
t.start(); //启动线程
System.out.println("线程开始执行之后--->" + t.isAlive()); //判断是否启动
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
System.out.println("main方法运行" + i);
}
//以下输出结果不确定
System.out.println("代码执行之后--->" + t.isAlive()); //输出结果不确定
}
}
程序运行结果(可能的一种结果):

由于线程操作的不确定性,如果线程率先执行完成,则最后结果为false,如果主线程先执行完成,那么其它线程也不会收到影响,并不会随着主线程的结束而结束,所以最后为 true
3 、线程的强制运行
在线程操作中,可以使用 join() 方法让一个线程强制运行,线程强制运行期间,其它线程无法运行,必须等待其它线程完成之后才可以继续执行
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i=0; i<5; i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行--->" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadJoinDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt,"线程");
t.start();
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
if(i>5){
try {
t.join(); //强制运行线程t
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("main 线程运行" + i);
}
}
}
程序运行结果:
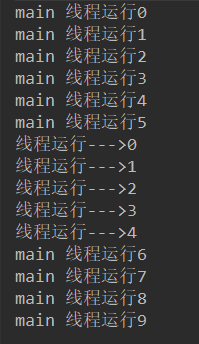
4 、线程的休眠
在程序中,可以使用 Thread.sleep() 方法实现线程休眠
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i=0; i<5; i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(500); //线程睡眠500毫秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行--->" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadJoinDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt,"线程");
t.start();
}
}
程序运行结果:

以上程序在执行时,每次的输出都会间隔 500 ms, 达到延迟操作的效果
5 、中断线程
interrupt() 方法可以中断线程运行
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("1、执行run()方法");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(10000); //休眠10秒钟
System.out.println("2、线程完成休眠");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("3、休眠被中断");
return;
}
System.out.println("4、run()方法正常执行结束");
}
}
}
public class ThreadInterruptDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt,"线程");
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); //稍停2秒钟后中断线程
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t.interrupt(); //中断线程执行
}
}
程序运行结果:
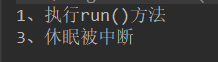
6、线程的优先级
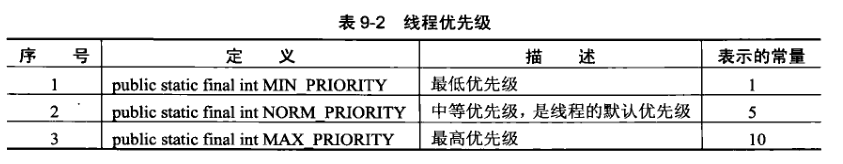
在Java中,所有线程在运行前都会保持在就绪状态,此时,哪个线程的优先级高,哪个线程就有可能会被先执行。
使用 setPriority()方法可以设置一个线程的优先级,在Java的线程中,一共有3种优先级
class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i=0; i<3; i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(500); //休眠10秒钟
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行,i = " + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadPriorityDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程B");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程C");
t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //设置线程优先级最低
t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //设置线程优先级最高
t3.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); //设置线程优先级中等
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
程序运行结果:
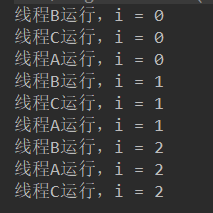
值得注意的是,并非优先级越高就一定先执行,哪个线程先执行由CPU调度决定























 204
204











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








