文章目录
一 、简述
在程序中,数据是以流的方式进行传输和保存的。在java.io包中有字节流 、字符流两大类。
字节流 : 输出数据使用 OutputStream 类 ,输入数据使用 InputStream 类
字符流 : 输出数据使用 Writer 类 ,输入数据使用 Reader 类
二 、字节流
1 、字节输出流:OutputStream

public class OutputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1、定义文件,将数据输出保存到此文件里面
//文件不存在将会自动创建新的文件
File file = new File("e:" + File.separator + "test.txt");
try {
//2、通过子类实例化父类对象
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
//3、进行写入操作
String str = "Hello World!";
byte[] strBytes = str.getBytes();
out.write(strBytes);
//4、关闭输出流
out.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
程序运行结果:
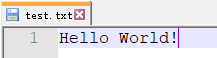
以上的写入每次执行都会覆盖文件内容,如果需要在文件原来内容的基础上写入内容,代码如下:
FileOutputStream 有以下一个构造方法:

public class OutputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1、定义文件,将数据输出保存到此路径下的文件里面
//文件不存在将会自动创建新的文件
File file = new File("e:" + File.separator + "test.txt");
try {
//2、通过子类实例化父类对象,传入布尔值,表示追加写入内容
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
//3、进行写入操作
String str = "Append Hello World!";
byte[] strBytes = str.getBytes();
out.write(strBytes);
//4、关闭输出流
out.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
程序运行结果:
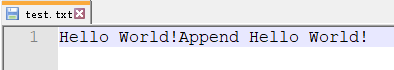
2 、字节输入流:InputStream
public class InputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("e:" + File.separator + "test.txt");
try {
InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] b = new byte[(int) file.length()]; //根据文件字节大小开辟空间
input.read(b);
input.close();
System.out.println("文件内容:" + new String(b));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
程序运行结果:

三、字符流
1 、字符输出流:Writer
public class WriterDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1、定义文件,将数据输出保存到此路径下的文件里面
File file = new File("e:" + File.separator + "writerTest.txt");
try {
//2、通过子类实例化父类对象
Writer writer = new FileWriter(file);
//3、进行写入操作
String str = "Hello World!";
writer.write(str);
//4、关闭输出流
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
与字节流操作没有太大区别,直接输出字符串,不需要将字符串转为byte数组之后再输出,追加内容代码如下:
public class WriterDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1、定义文件,将数据输出保存到此路径下的文件里面
File file = new File("e:" + File.separator + "writerTest.txt");
try {
//2、通过子类实例化父类对象
Writer writer = new FileWriter(file,true);
//3、进行写入操作
String str = "Writer Append Hello World!";
writer.write(str);
//4、关闭输出流
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2 、字符输入流:Reader
public class ReaderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("e:" + File.separator + "writerTest.txt");
try {
Reader reader = new FileReader(file);
char[] c = new char[(int) file.length()];
reader.read(c);
reader.close();
System.out.println("文件内容:" + new String(c));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
四、实际开发中使用字节流还是字符流比较合适?
在实际开发中使用字节流比较合适。因为文件在硬盘或是传输时都是以字节的方式进行的,包括图片等都是以字节的方式存储的,而字符一般在内存中才会形成,所以在开发中,使用字节流比较合适。
























 793
793











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








