序言:
在传统Ajax 时代,进行 API 等网络请求都是通过XMLHttpRequest或者封装后的框架进行网络请求,然而配置和调用方式非常混乱,对于刚入门的新手并不友好。今天我们介绍的Fetch提供了一个更好的替代方法,它不仅提供了一种简单,合乎逻辑的方式来跨网络异步获取资源,而且可以很容易地被其他技术使用;fetch是web提供的一个可以获取异步资源的api,它提供的api返回的是Promise对象;
与传统Ajax对比:
Ajax代码如下:
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', url/file,true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(xhr.readyState==4){
if(xhr.status==200){
var data=xhr.responseText;
console.log(data);
}
};
xhr.onerror = function() {
console.log("Oh, error");
};
xhr.send();
//同样,我们用fetch的方式来请求获取数据......
fetch(url).then(response => response.json())//解析为可读数据
.then(data => console.log(data))//执行结果是 resolve就调用then方法
.catch(err => console.log("Oh, error", err))//执行结果是 reject就调用catch方法
简单示例:
demo:直接通过fetch方法请求接口数据,将获得的数据渲染到html上
//index.html文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>fetch</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box"></div>
<script src="./index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
//index.js文件
async function getData(){ //这里用到了async/await的语法
const responce = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts'); //fetch方法的第一个参数是url,第二个参数是一个配置对象,这里默认不传,这里的url是一个专门获取json数据的测试网址链接
const data= await responce.json();
const root =document.getElementById('box');
const ul =document.createElement('ul');
data.forEach(item=>{
const li =document.createElement('li');
const a =document.createElement('a');
a.appendChild(document.createTextNode(item.title));
a.setAttribute('href',`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${item.id}`);
li.appendChild(a);
ul.appendChild(li)
});
root.appendChild(ul)
}
getData();
最终效果如下:(渲染一个ul列表)

优缺点:
优点:
- 语法简单
- 可以被使用到更多地应用场景中
- 加强了代码的可维护性
- 避免回调地狱(Callback Hell)问题
缺点:
- fetch只对网络请求报错,对400,500都当做成功的请求(解决方案,自己配置)
fetch('https://www.haha.com/test.js')
.then(response => {
if (response.ok) {
return response.json()
} else {
return Promise.reject({
status: response.status,
statusText: response.statusText
})
}
})
.catch(error => {
if (error.status === 404) {
// do something about 404
}
})
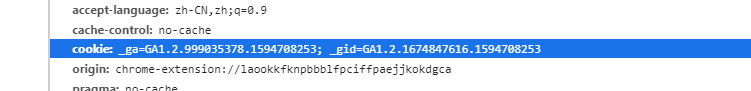
- fetch 默认不会发送 cookies,如果要想发送的话,则需要将 credentials设置为include或者same-origin,例如:credentials: ‘include’,设置完后你再次请求,会发现在请求头中会多出一个cookie项
参数
fetch() 支持传二个参数,第一个是请求的地址,第二个是可以控制不同配置的 init 对象
function postData(url, data) {
// Default options are marked with *
return fetch(url, {
body: JSON.stringify(data), // HTTP请求正文
cache: 'no-cache', // *default, no-cache, reload, force-cache, only-if-cached
credentials: 'same-origin', //身份验证凭据模式,默认:"omit"
//"omit" -请求中不包含身份验证凭据(例如Cookie)
//"same-origin" -在对同一网站的请求中包含凭据
//"include" -在对所有站点的请求中包括凭据
headers: { //可以直接写多个头部项如果传的是变量,这个变量通过 new Headers()创建,然后通过 //append()/set()来新增头部项,具体见第4点
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/4.0 MDN Example',
'content-type': 'application/json'
},
method: 'POST', // *GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.
mode: 'cors', // no-cors, cors, *same-origin
redirect: 'follow', // manual, *follow, error
referrer: 'no-referrer', // *client, no-referrer
})
.then(response => response.json()) // parses response to JSON
}
fetch的几种请求情景
- fetch请求本地文本数据
//本地有一个test.txt文档,通过以下代码就可以获取其中的数据,并且显示在页面上。
document.getElementById('button1').addEventListener('click',getText);
function getText(){
fetch("test.txt")
.then((res) => res.text())//注意:此处是res.text()
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
document.getElementById('output').innerHTML = data;
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
- fetch请求本地JSON数据
//本地有个posts.json数据,与请求本地文本不同的是,得到数据后还要用forEach遍历,最后呈现在页面上。
document.getElementById('button2').addEventListener('click',getJson);
function getJson(){
fetch("posts.json")
.then((res) => res.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
let output = '';
data.forEach((post) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
})
document.getElementById('output').innerHTML = output;
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
- fetch请求网络接口
document.getElementById('button3').addEventListener('click',getExternal);
function getExternal(){
// https://api.github.com/users
fetch("https://api.github.com/users")
.then((res) => res.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
let output = '';
data.forEach((user) => {
output += `<li>${user.login}</li>`;
})
document.getElementById('output').innerHTML = output;
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










