1 MyBatis的快速入门
1.1配置环境
- 在maven中的 pom.xml 添加依赖 主要是mybatis
<dependencies>
<!-- mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql 驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.40</version>
</dependency>
<!--测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加slf4j日志api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.20</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加logback-classic依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加logback-core依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.2 在XML中构件SqlSessionFactory
- 数据库连接信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 配置数据库环境信息 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置数据库连接的4个基本信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://001.001.001.001:3306/demo01"/>
<property name="username" value="demo01"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!--
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!–数据库连接信息–>
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///001.001.001.001:3306/demo01?useSSl=false"/>
<property name="username" value="demo01"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
-->
</environments>
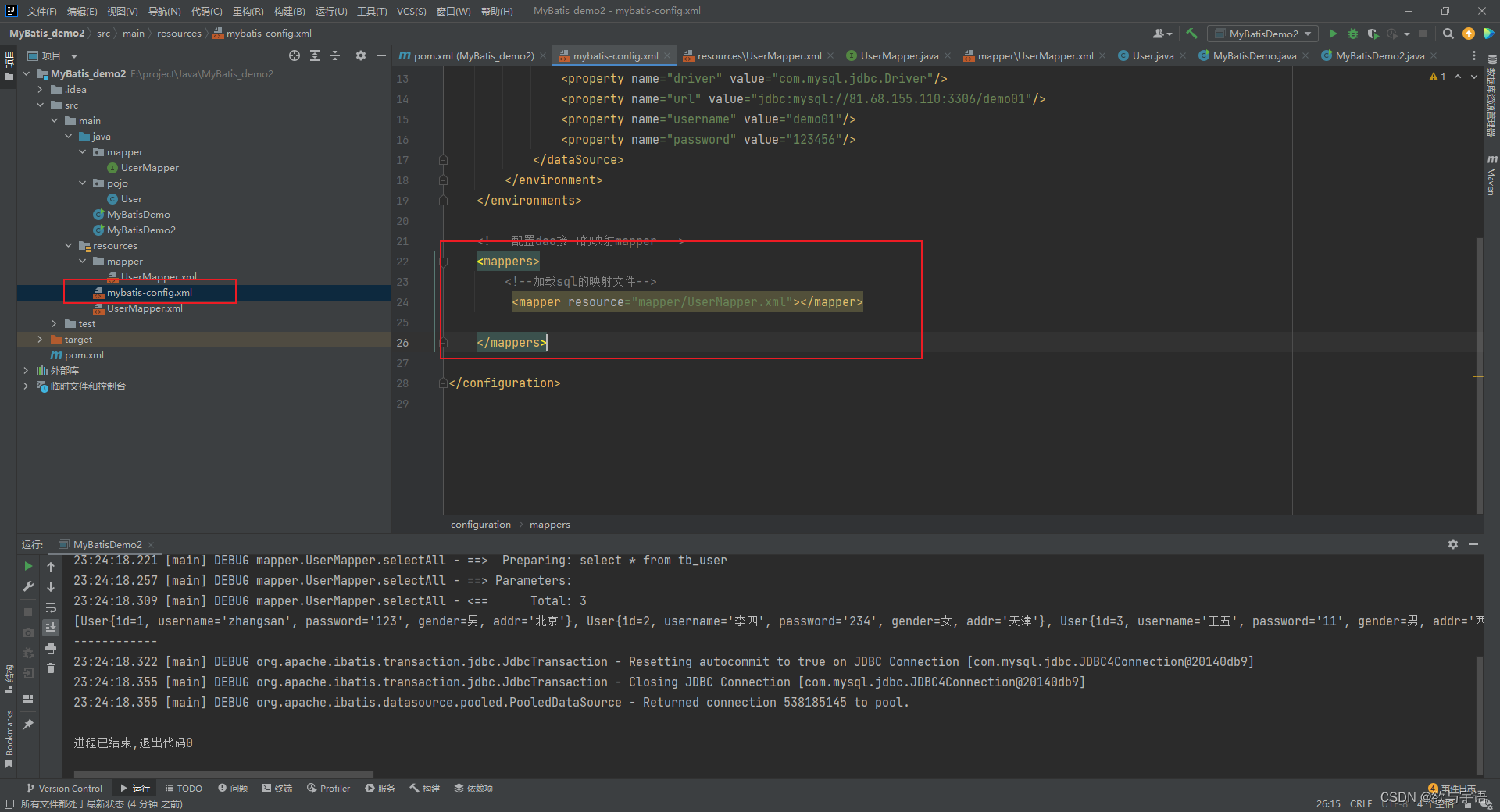
<!-- 配置dao接口的映射mapper -->
<mappers>
<!--加载sql的映射文件-->
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 创建xml文件
- UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
namespace:名称空间
-->
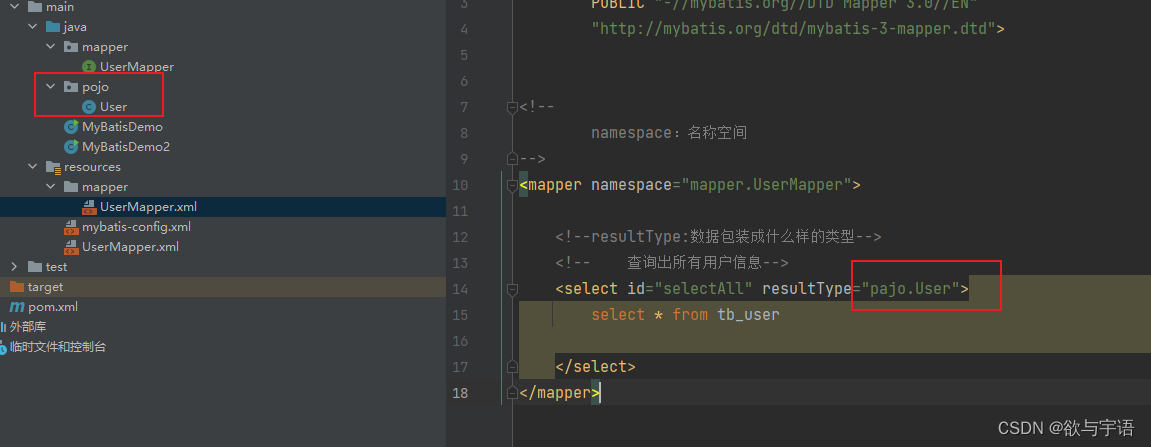
<mapper namespace="test">
<!--resultType:数据包装成什么样的类型-->
<select id="selectAll" resultType="pojo.User">
select * from tb_user
</select>
<select id="getUserById" resultType="pojo.User">
select * from tb_user where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- <!– create user–>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.it.mapper.UserMapper">
insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})
</insert>-->
</mapper>
- user类
package pojo;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private char gender;
private String addr;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", gender=" + gender +
", addr='" + addr + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
1.3 测试
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import pojo.User;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class mybatisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象,用它来执行sql
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 执行sql
//这个在UserMapper.xml拿到唯一标识的Id 名称空间+唯一标识
List<User> users = sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll");
System.out.println(users);
//4. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
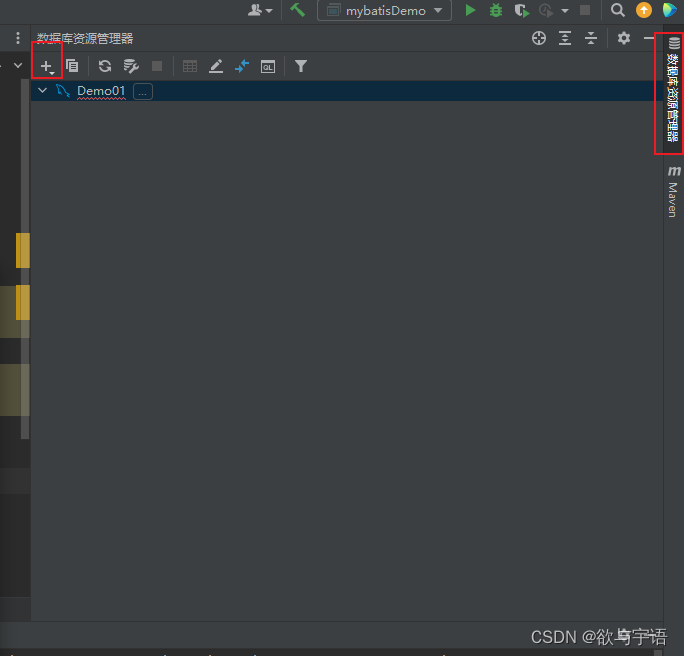
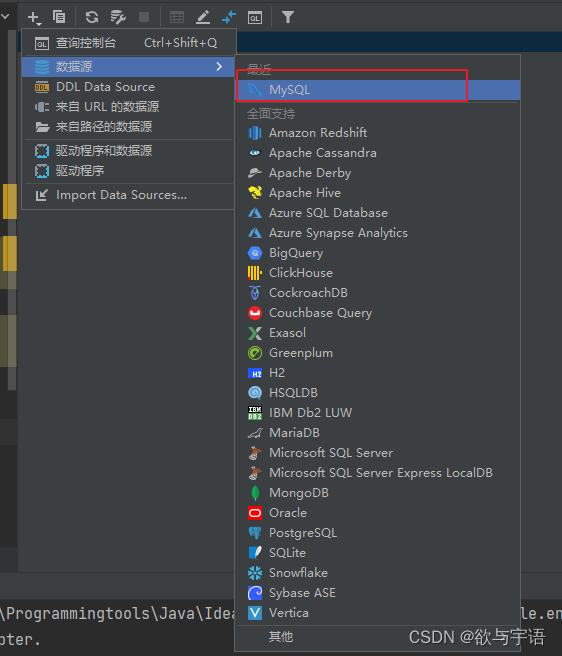
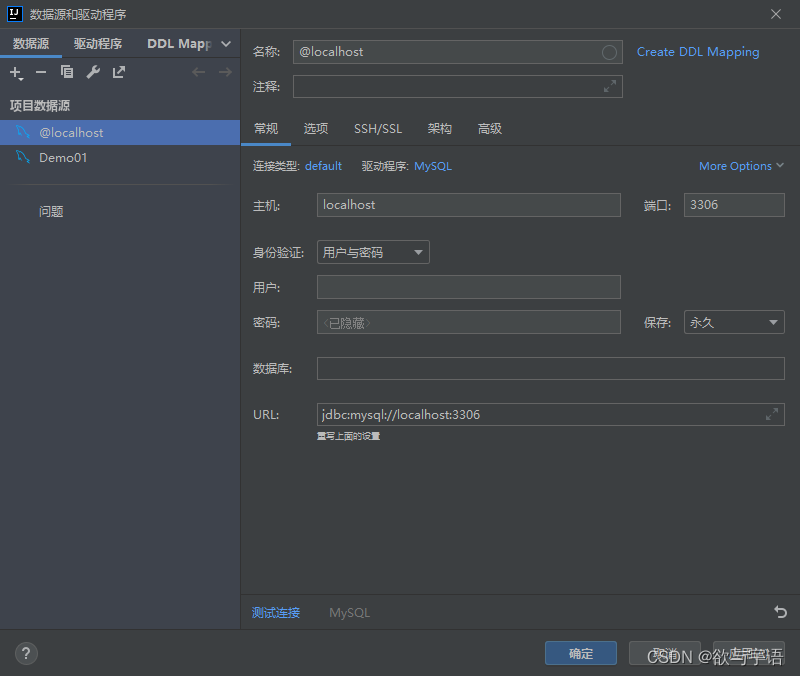
1.4 idea连接数据库
- 从数据库中选择然后将其添加
- 将内容输入
2 优化
2.1 Mapper代理开发
因为通过mapper每次都要用Id去访问太麻烦了可以通过Mapper代理开发
- 需要定义一个与SQl映射文件同名的Mapper接口,并且将Mapper接口和SQL映射文件放置在同一个目录下
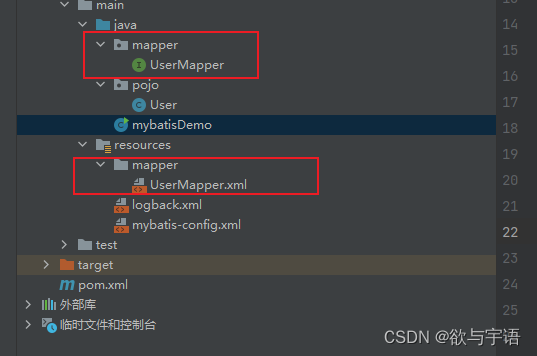
- 设置sql映射文件的namespace属性为Mapper接口全限定名:即就是以前的命名空间改成你创建的那个接口的
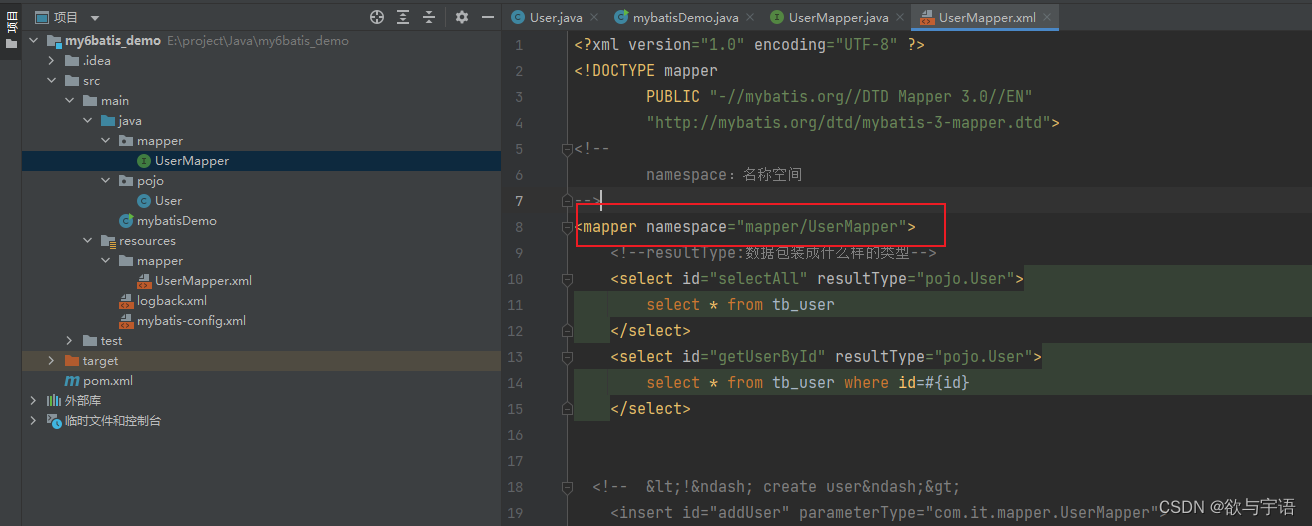
- 在mapper接口中定义方法
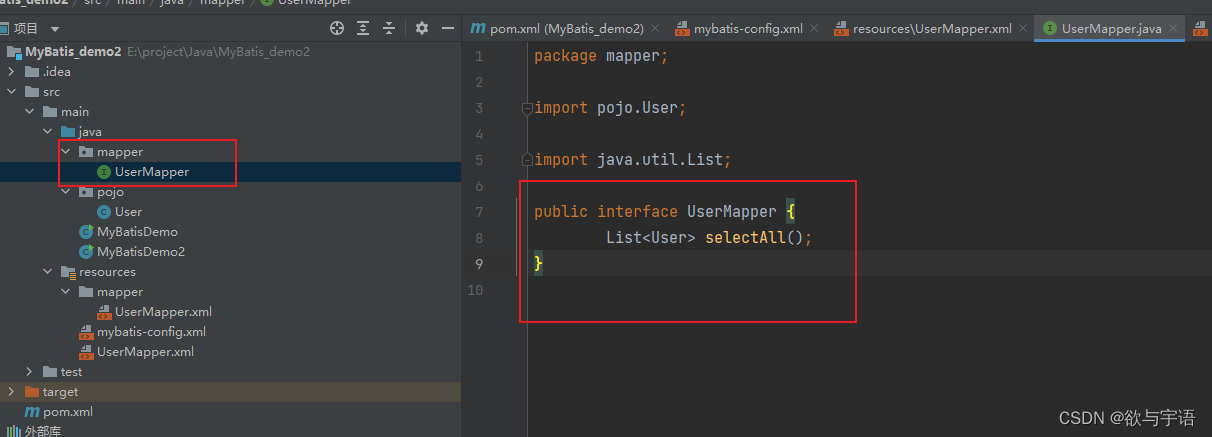
- sql的映射文件也要改
2.2 测试
public class MyBatisDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象,用它来执行sql
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 执行sql
//将其获取接口
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User>users=mapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(users);
System.out.println("------------");
//4. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
3 小知识
3.1 < typeAliases >的用法
<typeAliases>
//name输入上级目录的
<package name="pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
当在mybatic_config中配置了这个的话则可以将其pajo.User直接写成User
3.2 在sql查询的妙招
3.2.1 问题(一)背景
问题情况:
假设说你的数据库表里的字段名和你定义的类名不一致的情况下会导致出你的数据查询不出来
比如:
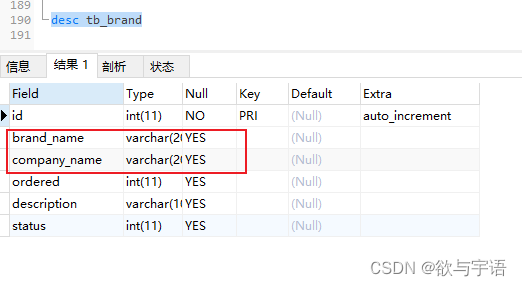
-
数据库中定义的表如下:
-
类定义的如下:

-
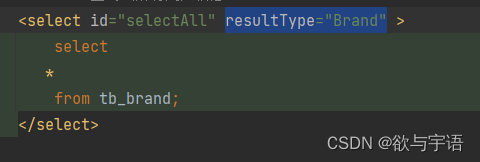
sql查询语句如下
-
查询的结果如图所示:
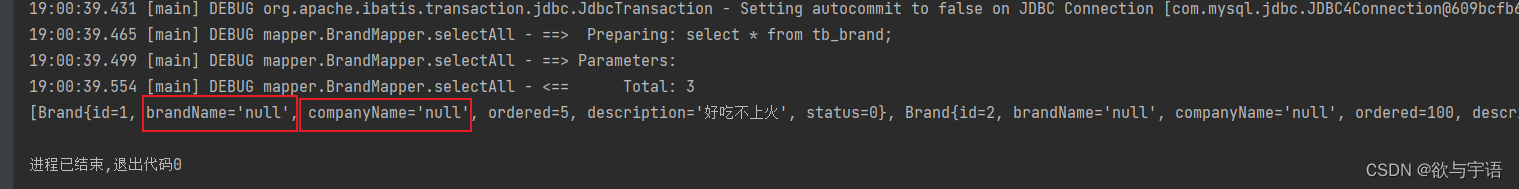
会导致查出来的结果不一样
3.2.2 问题(一)解决方案
- 第一种解决方案:可以直接在查询中通过使用重命名的方法
- 即直接将查询语句改为
<select id="selectAll" resultType="Brand">
select
id,brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
from tb_brand;
</select>
- 第二种方法:发现上面的方法太过于复杂 因为每次查询的时候都要自己去重命名这些字段则是不是可以将其抽出来重命名
- 使用sql片段
<!--先定义一个sql片段-->
<sql id="brand_column">
id,brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="Brand" >
select
<!--在查询中进行调用-->
<include refid="brand_column"></include>
from tb_brand;
</select>
- 第三种方法 发现上面这个方法每次都要调用这个字段 并且可能有时候查询出的字段是不相同的就需要查询去定义一个新的字段
- 可以使用 映射方法
<!--映射-->
<!--
id:完成主键字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
result:完成一般字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
-->
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="brand">
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>
<!--需要将返回值修改一下-->
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap" >
select
*
from tb_brand;
</select>
3.2.3 问题(二)
问题情况:
sql语句的书写时里面的占位符有哪些,有什么区别,并且在输入 < 号或者 <= 号不支持这样子的格式怎么办
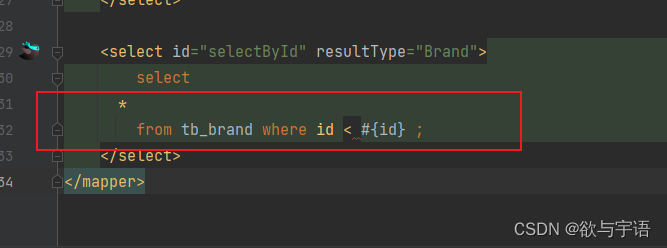
3.2.3 问题(二)解决方案:
sql语句中里面的占位符分为两种:#{} 和 ${}
- 使用 #{} 占位符时

- 会发现会将其替换为 ? 再将值输入进去

- 会发现会将其替换为 ? 再将值输入进去
- 使用 ${} 占位符时
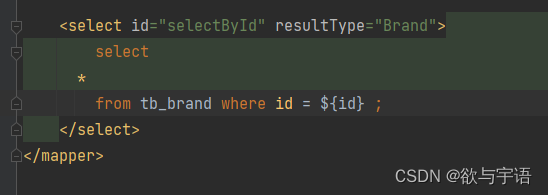
- 是直接将其的值替换过去

- 是直接将其的值替换过去
区别:
- 参数占位符:
- #{}:会将其替换为 ?,为了防止SQL注入
- ${}:拼sql。会存在SQL注入问题
- 使用时机:
- 参数传递的时候:#{}
- 表名或者列名不固定的情况下:${} 会存在SQL注入问题
- 参数类型:parameterType:可以省略
- 如何解决< 号的问题:
- 转义字符:通过直接书写 <小于号的转移字符如:& lt;
- CDATA区:
<select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where id
<![CDATA[
<
]]>
#{id};
</select>
3.3 条件查询
3.3.1 散装参数
散装参数:如果方法中有多个参数,需要使用@Param(“SQL参数占位符名称”)
- BrandMapper.class:
/**
* 条件查询
* @param status 状态
* @param companyName 公司名
* @param brandName 品牌名
* @return
*/
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status") int status , @Param("companyName") String companyName, @Param("brandName") String brandName);
- BrandMapper.xml:
<!--条件查询-->
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from tb_brand
where status = #{status}
and company_name like #{companyName}
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</select>
- Test
@Test
public void testSelectByCondition() throws IOException {
//1、获取sqlSessionFactory
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
int status=0;
String companyName="公司";
String brandName="三";
companyName="%"+companyName+"%";
brandName="%"+brandName+"%";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2。获取对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3获取map对象
BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
List<Brand> brandList=mapper.selectByCondition(status,conmpanyName,brandName);
System.out.println(brandList);
sqlSession.close();
}
3.3.2 对象参数
散装参数:参数通过一个对象进行传递
注意:对象的属性名称要和参数占位符名称一致
- BrandMapper.class:
/**
* 条件查询
* @param status 状态
* @param companyName 公司名
* @param brandName 品牌名
* @return
*/
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status") int status , @Param("companyName") String companyName, @Param("brandName") String brandName);
- BrandMapper.xml:
<!--条件查询-->
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from tb_brand
where status = #{status}
and company_name like #{companyName}
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</select>
- Test
@Test
public void testSelectByCondition() throws IOException {
//1、获取sqlSessionFactory
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
int status=0;
String companyName="公司";
String brandName="三";
companyName="%"+companyName+"%";
brandName="%"+brandName+"%";
Brand brand =new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2。获取对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3获取map对象
BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
List<Brand> brandList=mapper.selectByCondition(brand);
System.out.println(brandList);
sqlSession.close();
}
3.3.3 Map集合参数
Map集合参数:参数通过一个Map集合进行传递
注意:SQL中的参数名要和Map集合中的键的名字对呀上
- BrandMapper.class:
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
- BrandMapper.xml:
<!--条件查询-->
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from tb_brand
where status = #{status}
and company_name like #{companyName}
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</select>
- Test
@Test
public void testSelectByCondition() throws IOException {
//1、获取sqlSessionFactory
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
int status=0;
String companyName="公司";
String brandName="三";
companyName="%"+companyName+"%";
brandName="%"+brandName+"%";
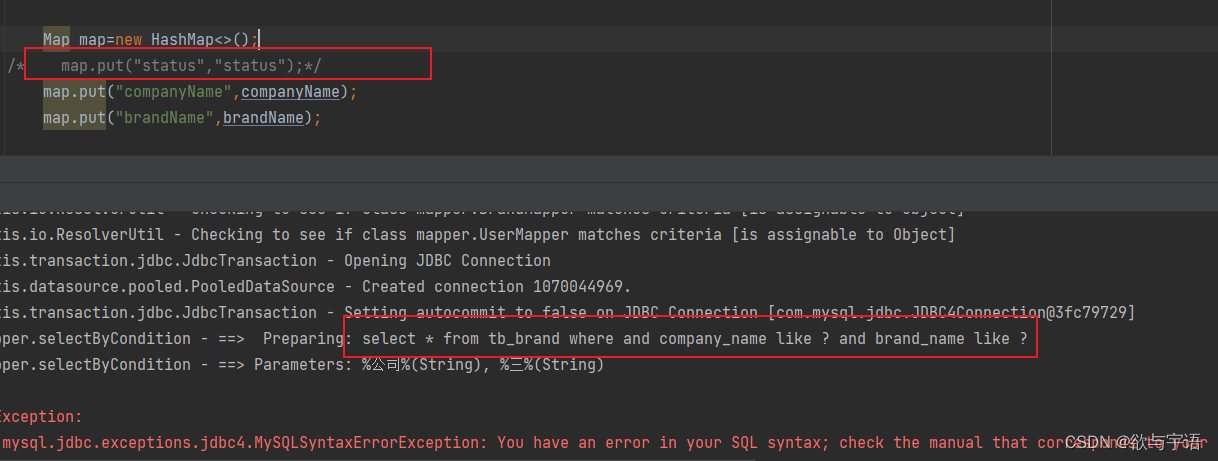
Map map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("status",status);
map.put("companyName",companyName);
map.put("brandName",brandName);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2。获取对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3获取map对象
BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
List<Brand> brandList=mapper.selectByCondition(map);
System.out.println(brandList);
sqlSession.close();
}
3.3.4 动态Sql
背景:上面三种发现还是有Bug,因为必须要三个条件都填写的情况下才会输入,所以是否要将其进行筛选,将其Sql语句动态变化
- 使用 if 判断 当输入值了的情况下则将其条件加入进去
<!--
动态条件查询
* if: 条件判断
* test:逻辑表达式
* 问题:
* 恒等式
* <where> 替换 where 关键字
-->
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from tb_brand
where
<if test="status != null">
status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName!=''">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName!= null and brandName!=''">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</select>
问题:假设第一个条件没传递的话那么sql语句中第二个会直接显示一个 and 条件
解决方案;
- 恒等式:在where条件中加一个恒等式然后后面全用and拼接
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where 1 = 1
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</select>
- 替换 where 关键字
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
/* where 1 = 1*/
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</where>
</select>
- 单条件查询:里面有类似swich查询比如说一个下拉框可以让你选择通过状态查询还是通过品牌名还是公司名查询从中选择一个的话可以用这种方式(< /otherwise>是因为避免一个条件都没有选择)
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where
<choose><!--相当于switch-->
<when test="status != null"><!--相当于case-->
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "><!--相当于case-->
company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''"><!--相当于case-->
brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
<otherwise> <!--相当于default-->
1 = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
- 假设想省略掉 < /otherwise>
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<choose><!--相当于switch-->
<when test="status != null"><!--相当于case-->
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "><!--相当于case-->
company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''"><!--相当于case-->
brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
3.4 Mybatis增删改
3.4.1 添加功能
-
添加功能会将其改为手动提交事务所以在执行完之后需要自己提交
觉得麻烦的话可以将其定义的时候赋值为true- Mybatis事务
- openSession():默认开启事务,进行增删改操作后需要使用 sqlSession.commit(); 手动提交事务
- openSession(true):可以设置为自动提交事务(关闭事务)
-
主键返回:
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
- BrandMapper.class:
void addBrand(Brand brand);
- BrandMapper.xml:
<insert id="addBrand">
insert into tb_brand(brand_name,company_name,ordered,description,status)
value (#{brandName},#{companyName},#{ordered},#{description},#{status});
</insert>
- Test
@Test
public void testAdd() throws IOException {
//1、获取sqlSessionFactory
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
int status=0;
String companyName="博导手机";
String brandName="博导";
String description="好手机好品质";
int orderd=100;
Brand brand =new Brand();
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setOrdered(orderd);
brand.setStatus(status);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2。获取对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//假设觉得每次要手动提交的麻烦的情况下可以将其创建的时候传递一个true
//SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3获取map对象
BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
mapper.addBrand(brand);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭
sqlSession.close();
}
3.4.2 修改功能
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
- BrandMapper.class:
/**
* 修改功能
* @param brand 参数类型:Brand
* @return 返回类型:int 影响的行数
*/
int updateBrand(Brand brand);
- BrandMapper.xml:
<!--修改功能-->
<update id="updateBrand">
update tb_brand
<set>
<if test="brandName!=null and brandName !='' ">
brand_name= #{brandName},
</if>
<if test="companyName!=null and companyName !='' ">
company_name= #{companyName},
</if>
<if test="ordered!=null and ordered !='' ">
ordered= #{ordered},
</if>
<if test="description!=null and description !='' ">
description= #{description},
</if>
<if test="status!=null ">
status=#{status}
</if>
</set>
where id= #{id};
</update>
- Test
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws IOException {
//1、获取sqlSessionFactory
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
int status=0;
String companyName="博导手机1222222222";
String brandName="博导1111111111";
String description="好手机好品质1";
int orderd=200;
Integer id=5;
Brand brand =new Brand();
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
/* brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setOrdered(orderd);
brand.setStatus(status);*/
brand.setId(id);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2。获取对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//假设觉得每次要手动提交的麻烦的情况下可以将其创建的时候传递一个true
// SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3获取map对象
BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//修改功能
int count = mapper.updateBrand(brand);
System.out.println(count);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭
sqlSession.close();
}
3.4.2 删除功能
删除功能分为:
- 单个删除
- 批量删除
通过下面代码解释
-
单个删除:
-
BrandMapper.class:
/** * 单个删除 * @param id 参数类型:int Id * @return 返回类型:int 影响的行数 */ int deleteForId (int id); -
BrandMapper.xml:
<delete id="deleteForId"> delete from tb_brand where id = #{id}; </delete> -
Test
@Test public void testDeleteById() throws IOException { int id =6; //1、获取sqlSessionFactory //1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2。获取对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //3获取map对象 BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); int count = mapper.deleteForId(id); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.close(); }
-
-
批量删除:
需要用到foreach元素来遍历数组属性 说明 item 表示集合中每一个元素进行迭代时的别名 index 指 定一个名字,用于表示在迭代过程中,每次迭代到的位置 open 表示该语句以什么开始 separator 表示在每次进行迭代之间以什么符号作为分隔符 close 表示以什么结束。 -
BrandMapper.class:
/** * 批量删除 * @param ids 参数类型:int[] * @return 返回类型:int 影响的行数 */ int deleteByIds(@Param("ids") int[] ids); -
BrandMapper.xml:
<delete id="deleteByIds"> delete from tb_brand where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")"> #{id} </foreach> </delete> -
Test
@Test public void testDeleteByIds() throws IOException { int[]ids ={1,2}; //1、获取sqlSessionFactory //1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2。获取对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //3获取map对象 BrandMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); int count = mapper.deleteByIds(ids); System.out.println(count); sqlSession.close(); }
-
3.5 Mybatis 传参
- MyBatis 参数封装:
- 单个参数:
- POJO类型:直接使用,属性名 和 参数占位符名称 一致
- Map集合:直接使用,键名 和 参数占位符名称 一致
- Collection:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put(“arg0”,collection集合);
map.put(“collection”,collection集合); - List:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put(“arg0”,list集合);
map.put(“collection”,list集合);
map.put(“list”,list集合); - Array:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put(“arg0”,数组);
map.put(“array”,数组); - 其他类型:直接使用
- 多个参数:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
- 当不写 :
第一个参数的键名叫做 arg0或param1
第二个参数的键名叫做 arg1或param2
map.put(“arg0”,参数值1)
map.put(“param1”,参数值1)
map.put(“param2”,参数值2)
map.put(“agr1”,参数值2)User select(String username,String password); - 当写 :
第一个参数的键名叫做 username或param1(因为第一个参数使用@Param注解了所以为 username)
第二个参数的键名叫做 arg1或param2(因为没有使用@Param注解)
---------------@Param(“username”)
map.put(“username”,参数值1)
map.put(“param1”,参数值1)
map.put(“param2”,参数值2)
map.put(“agr1”,参数值2)User select(@Param("username") String username,String password);
- 当不写 :
- 单个参数:
建议:尽量以后都是用使用@Param注解来修改Map集合中默认的键名,并使用修改后的名称来获取值,这样可读性更高!
3.6 Mybatis 注解开发
注解开发: 使用注解来映射简单语句会使代码显得更加简洁,但对于稍微复杂一点的语句,Java注解不仅力不从心,还会让你本就复杂的 SQL语句更加混乱不堪。因此,如果你需要做一些很复杂的操作,最好用XML 来映射语句。
- 优点:可以省略掉XML直接书写,使用于简单的Sql语句
- 缺点:对于复杂的操作不方便
| 说明 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| 查询 | @Select |
| 添加 | @Insert |
| 修改 | @Updatet |
| 删除 | @Delete |
如何使用:
/**
* 查询
*/
@Select(value = "select * from tb_user where id = #{id}")
public User select(int id);
/**
* 添加
*/
@Insert (
value=" insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status) values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status}); ")
void addBrand(Brand brand);
/**
* 修改
*/
@Updatet(value=" update tb_brandset brand_name= #{brandName},company_name= #{companyName},ordered=#{ordered},description= #{description}, status=#{status} where id= #{id};")
int updateBrand(Brand brand);
/**
* 删除
*/
@Delete(value = " delete from tb_brand where id = #{id};")
int deleteForId (int id);






















 629
629











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








