文章目录

C++类与对象之运算符重载与const成员
运算符重载
赋值运算符重载
运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其
返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
函数名字为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号。
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
注意:
不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不 能改变其含义
作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐
藏的this
. :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。这个经常在笔试选择题中出现*
日期类的实现与运算符重载
像这种运算符重载,我们可以思考多个运算符代码到复用(在这里统一说一下const可以暂时不管,同时此处会涉及到后面的友元类,友元类就是虽然不是成员函数,就是没用this指针,但是可以访问私有成员数据)
基本实现
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
public:
Date(){}
Date(int year, int month, int day);
int Get_day()
{
return _day;
}
int Get_month()
{
return _month;
}
int Get_year()
{
return _year;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
int Getmonthday(int year,int month)
{
static int monthday[13]={0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30,31};
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return monthday[month];
}
}
Date(const Date& B)
{
_day = B._day;
_month = B._month;
_year = B._year;
}
bool operator<(const Date& x) const;
bool operator==(const Date& x) const;
bool operator<=(const Date& x) const;
bool operator>(const Date& x) const;
bool operator>=(const Date& x) const;
bool operator!=(const Date& x) const;
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day) const;
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date operator-(int day) const;
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (!(this == &d))
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
Date operator++(int)
{
Date temp(*this);
_day += 1;
return temp;
}
Date& operator++()
{
_day += 1;
return *this;
}
Date& operator--()
{
_day -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date operator--(int)
{
Date temp = *this;
_day -= 1;
return temp;
}
赋值运算符重载
-
参数类型:const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率(因为无需调用赋值构造函数)
-
返回值类型:T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值
Date A(2023,5,4); Date B(A);//赋值构造 Date C; Date D; C = D = B;//B赋值给D,同时D的赋值函数返回D的引用,将D赋给C -
检测是否自己给自己赋值
-
返回*this :要复合连续赋值的含义
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (!(this == &d))
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
比较类运算符的重载
- 参数类型:const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率
- 返回值类型:T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值
- 代码复用:可以先重载<和==,其他的复用其代码就行
- 返回bool:即判断是否正确
bool Date::operator<(const Date& x) const
{
if (_year < x._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x) const
{
return _year == x._year
&& _month == x._month
&& _day == x._day;
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x) const
{
return *this < x || *this == x;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this <= x);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this < x);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this == x);
}
二元运算符±的重载
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > Getmonthday(_year, _month))
{
_day -= Getmonthday(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
_day += Getmonthday(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day) const//日期加天数,算多少天前的日期
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const//日期减日期,算相差的天数
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
前置++和后置++重载
前置++和后置++都是一元运算符,为了让前置++与后置++形成能正确重载
C++规定:后置++重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递,编译器
自动传递
注意:后置++是先使用后+1,因此需要返回+1之前的旧值,故需在实现时需要先将this保存
一份,然后给this+1
Date operator++(int)
{
Date temp(*this);
_day += 1;
return temp;
}
Date& operator++()
{
_day += 1;
return *this;
}
同理,前置–和后置–
Date& operator--()
{
_day -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date operator--(int)
{
Date temp = *this;
_day -= 1;
return temp;
}
总体实现代码
#include"date.h"
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day > 0 && day <= Getmonthday(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& x) const
{
if (_year < x._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x) const
{
return _year == x._year
&& _month == x._month
&& _day == x._day;
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x) const
{
return *this < x || *this == x;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this <= x);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this < x);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x) const
{
return !(*this == x);
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > Getmonthday(_year, _month))
{
_day -= Getmonthday(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
_day += Getmonthday(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in,Date& d)
{
int year, month, day;
in >> year >> month >> day;
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day > 0 && day <= d.Getmonthday(year, month))
{
d._year = year;
d._month = month;
d._day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
return in;
}
const成员
const的好处
1.防止程序员犯错
就拿上面的日期减天数的代码来说
这个代码不能改变原来的日期类,只有-=才改变。如果你没有加const,你可能在写代码时犯错,不小心把原来的日期类改了
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
2.提高代码的复用性
如果-的重载没有加const
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
我们运行这个代码
const Date d1(2023,5,1);
Date d2 = d1 - 100;3
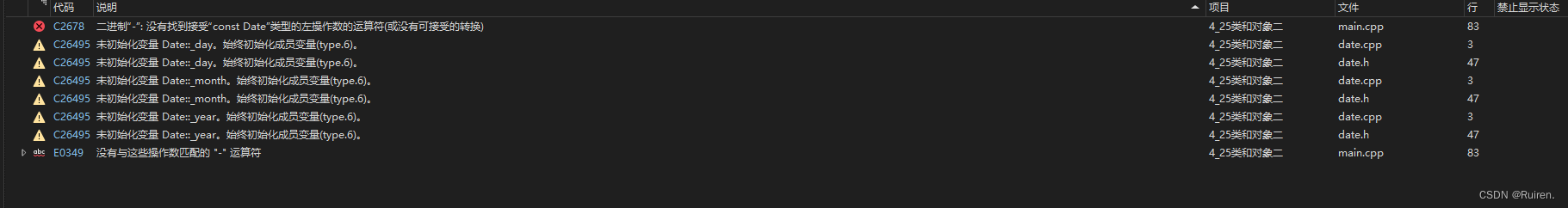
原因在于d1是 const Date类,不能改变,所以他的取地址应该是const Data*this,而系统传过去的this指针是一个普通的,这属于权限放大了(具体可以看看我前面的&(引号)的使用),而又因为this不能自己改C++添加了个在函数后面的const 的方法给this指针添加const
那么我们的const的对象就可以调用-这个函数了
const 成员与函数重载规则
能不能构成重载得看是单纯传值还是是否涉及到权限问题,比如形参是const 引用和指针,这就涉及到了权限所以能重载,而类的成员函数有this指针,也能构成,如果是传值的话,没有涉及到权限所以不构成,但以下图片中的text函数未构成函数重载的原因是const 为管控到this指针,所以未涉及到权限问题,未构成函数重载(记住只是单纯的赋值重载不行,其他都可以)
再者调用关系上,如果两个函数都实现了,那么const 类型的调const的,普通的调普通的,但如果只有const函数,那么普通的类型也可以调const类型的函数























 967
967











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










