目录
1.2.2operator*() && operator->()
1.2.5operator==() && operator!=()
二、如何用哈希表搭配unordered_map和unordered_set(仿函数)
三、哈希表封装unordered_map和unordered_set(简易版)
3.2unordered_map的模拟实现(My_Unordered_Map.h)
3.3unordered_set的模拟实现(My_Unordered_Set.h)
上一篇章,学习了unordered系列容器的使用,以及哈希结构,那么这一篇章将通过哈希结构来封装unordered系列容器,来进一步的学习他们的使用以及理解为何是如此使用。其实,哈希表的封装方式和红黑树的封装方式形式上是差不多的,如果有了红黑树的封装理解经验,我相信在理解哈希封装的过程会减少负担的。当然,在使用哈希结构中采用的是更具代表的哈希桶,接下来进行封装。
一、改造哈希表
1.1模板参数列表的改造
同理模板参数列表的改造跟红黑树的改造差不多。
K:关键码类型
V:不同容器v的容器类型不同,如果是unordered_map,v代表一个键值对,如果是unordered_set,v为k
KeyOfT:因为v的类型不同,通过keyOfT取key的方式就不同 。
Hash:哈希函数仿函数对象类型,哈希函数使用除留余数法,需要将字符串类型转化为整形数字才能取模。
1.2增加哈希表迭代器操作
1.2.1哈希表迭代器框架
//前置声明,迭代器中才能定义HashTable对象
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K,class T,class Ref,class Ptr,class KeyOfT,class hash = HashFunc<K>>
struct _HTIterator
{
typedef _HTIterator<K,T, Ref, Ptr,KeyOfT,hash> Self;//方便作为接收迭代器操作的返回值的类型
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
PNode _node;//定义节点指针,方便访问其成员来完成迭代器的操作
HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, hash>* _ht;//定义哈希表指针,方便使用其成员来完成迭代器的操作
size_t _hashi;//记录迭代器访问的位置
_HTIterator(PNode node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, hash>* ht,size_t hashi)
:_node(node)
,_ht(ht)
,_hashi(hashi)
{}
//....
};1.2.2operator*() && operator->()
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}1.2.3operator++()
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//下一个元素不为空
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
/*hash hs;
KeyOfT oft;
int hashi = hs(oft(this->_data) % _tables.size());*/
//寻找下一个不为空的桶
++_hashi;
while(_hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[_hashi] != nullptr)
{
_node = _ht->_tables[_hashi];
break;
}
++_hashi;
}
//到末尾还没有找到不为空的桶
if(_hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}1.2.4operator--()
Self operator--()
{
PNode cur = _ht->_tables[_hashi];
//当前节点就是第一个节点
if (cur->_next == nullptr)
{
//寻找上一个非空桶
--_hashi;
while (_hashi)
{
//寻找该非空桶的最后一个元素
if (_ht->_tables[_hashi])
{
cur = _ht->_tables[_hashi];
while (cur->_next)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
_node = cur;
break;
}
_hashi--;
}
}
else
{
while (cur->_next != _node)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
_node = cur;
}
return *this;
}1.2.5operator==() && operator!=()
bool operator==(const Self& x)
{
return _node == x._node;//由于没有重复的元素,直接比较节点的地址
}
bool operator!=(const Self& x)
{
return _node != x._node;
}
二、如何用哈希表搭配unordered_map和unordered_set(仿函数)
我们可以用两张哈希表分别封装一份unordered_map和一份unordered_set,但是这样做的效果就带来了代码冗余。为了减少代码冗余,模拟跟库保持用一张哈希表封装unordered_map和unordered_set,但是该如何做到套用一张表呢,我们来进一步分析。
首先对于unordered_map而言,其存放的节点值是pair,而对于unordered_set存放的是key,这对于哈希表节点的实现到是没啥问题,但是对于哈希表内部的构造,是需要查询插入的位置,就需要进行比较,若将比较实现成key的比较,那么对于pair类型又该如何比较,虽然知道比较的也是pair中的key,但是如何做到既满足unordered_set中的key类型比较,又满足pair类型中的key比较,总不能干两份代码吧。这个时候,我们的仿函数又派上用场了,对于unordered_set和unordered_map中都构造一个仿函数,分别表示取到unordered_set的key,和unordered_map中pair中的key,那么哈希表中的比较,就可以换成仿函数的比较,当往unordered_set中插入元素进行比较,调用的就是unordered_set的仿函数,当往unordered_map中插入元素进行比较,调用的就是unordered_map的仿函数从而达到回调。用一张图来进行表示,如图:

三、哈希表封装unordered_map和unordered_set(简易版)
3.1哈希表的实现(HashTable.h)
//哈希桶/链地址法
namespace Hash_Bucket
{
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode(const T& data)
:_next(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{}
HashNode<T>* _next;
T _data;
};
//前置声明,迭代器中才能定义HashTable对象
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K,class T,class Ref,class Ptr,class KeyOfT,class hash = HashFunc<K>>
struct _HTIterator
{
typedef _HTIterator<K,T, Ref, Ptr,KeyOfT,hash> Self;
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
PNode _node;
HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, hash>* _ht;
size_t _hashi;
_HTIterator(PNode node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, hash>* ht,size_t hashi)
:_node(node)
,_ht(ht)
,_hashi(hashi)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
/*hash hs;
KeyOfT oft;
int hashi = hs(oft(this->_data) % _tables.size());*/
++_hashi;
while(_hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[_hashi] != nullptr)
{
_node = _ht->_tables[_hashi];
break;
}
++_hashi;
}
if(_hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator--()
{
PNode cur = _ht->_tables[_hashi];
//当前节点就是第一个节点
if (cur->_next == nullptr)
{
//寻找上一个非空桶
--_hashi;
while (_hashi)
{
//寻找该非空桶的最后一个元素
if (_ht->_tables[_hashi])
{
cur = _ht->_tables[_hashi];
while (cur->_next)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
_node = cur;
break;
}
_hashi--;
}
}
else
{
while (cur->_next != _node)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
_node = cur;
}
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
bool operator==(const Self& x)
{
return _node == x._node;//由于没有重复的元素,直接比较节点的地址
}
bool operator!=(const Self& x)
{
return _node != x._node;
}
};
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT,class hash>
class HashTable
{
//声明友元,迭代器方可访问该类中的私有成员
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT,class hash>
friend struct _HTIterator;
public:
typedef _HTIterator<K, T,T&, T*, KeyOfT,hash> iterator;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, hash> const_iterator;
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
HashTable(size_t size = 10)
{
_tables.resize(size);
}
iterator begin()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i] != nullptr)
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr,this,-1);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i] != nullptr)
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
return end();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT oft;
hash hs;
int hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();
PNode cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if(hs(oft(cur->_data)) == hs(key))
return iterator(cur, this, hashi);
cur = cur->_next;
}
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
pair<iterator,bool> Insert(T data)
{
hash hs;
KeyOfT oft;
iterator it = Find(oft(data));
if (it != end())
return make_pair(it,false);
//扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
vector<PNode> _newHT(_tables.size()*2);
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
PNode cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
PNode next = cur->_next;
int hashi = hs(oft(_tables[i]->_data)) % _newHT.size();
//元素一直在变,所以不能用_tables[i]做代表
/*_tables[i]->_next = nullptr;
_newHT[hashi] = _tables[i];*/
cur->_next = nullptr;
_newHT[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(_newHT);
}
//头插
PNode newnode =new Node(data);
int hashi = hs(oft(data)) % _tables.size();
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this, hashi),true);
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT oft;
iterator it = Find(key);
if (it == end())
return false;
hash hs;
int hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();
PNode cur = _tables[hashi];
PNode parent = nullptr;
while (hs(oft(cur->_data)) != hs(key))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
if (parent)
{
delete cur;
parent->_next = nullptr;
}
else
{
delete cur;
_tables[hashi] = nullptr;
}
return true;
}
~HashTable()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
PNode cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
PNode next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
//另外加的,为了测试用
void Some()
{
size_t bucketSize = 0;
size_t maxBucketLen = 0;
size_t sum = 0;
double averageBucketLen = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
++bucketSize;
}
size_t bucketLen = 0;
while (cur)
{
++bucketLen;
cur = cur->_next;
}
sum += bucketLen;
if (bucketLen > maxBucketLen)
{
maxBucketLen = bucketLen;
}
}
averageBucketLen = (double)sum / (double)bucketSize;
printf("all bucketSize:%d\n", _tables.size());
printf("bucketSize:%d\n", bucketSize);
printf("maxBucketLen:%d\n", maxBucketLen);
printf("averageBucketLen:%lf\n\n", averageBucketLen);
}
private:
vector<HashNode<T>*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}3.2unordered_map的模拟实现(My_Unordered_Map.h)
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace Hash_Bucket
{
template<class K,class V,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
public:
struct KeyOfTMap
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& data)
{
return data.first;
}
};
typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, KeyOfTMap, Hash>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, KeyOfTMap, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _hs.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _hs.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _hs.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _hs.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& data)
{
return _hs.Insert(data);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _hs.Insert(make_pair(key,V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _hs.Erase(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _hs.Find(key);
}
private:
HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, KeyOfTMap, Hash> _hs;
};
void test_map()
{
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", ""));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", ""));
dict.insert(make_pair("insert", ""));
for (auto& kv : dict)
{
//kv.first += 'x';
kv.second += 'x';
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string arr[] = { "你", " ","好", " ", "吗", " ", "你", "吃", " ", "了", "饭", "吗", "?" };
unordered_map<string, int> count_map;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
count_map[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : count_map)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
3.3unordered_set的模拟实现(My_Unordered_Set.h)
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace Hash_Bucket
{
template<class K,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
public:
struct KeyOfTSet
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
typedef typename HashTable<K, const K, KeyOfTSet, Hash>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashTable<K, const K, KeyOfTSet, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _hs.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _hs.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _hs.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _hs.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _hs.Insert(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _hs.Erase(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _hs.Find(key);
}
void some()
{
_hs.Some();
}
private:
HashTable<K, const K, KeyOfTSet, Hash> _hs;
};
void test_set()
{
unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(5);
us.insert(15);
us.insert(52);
us.insert(3);
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
//*it += 5;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : us)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
us.some();
}
}
3.4测试(test.cpp)
#include "My_Unordered_Map.h"
#include "My_Unordered_Set.h"
int main()
{
Hash_Bucket::test_map();
Hash_Bucket::test_set();
return 0;
}输出结果:
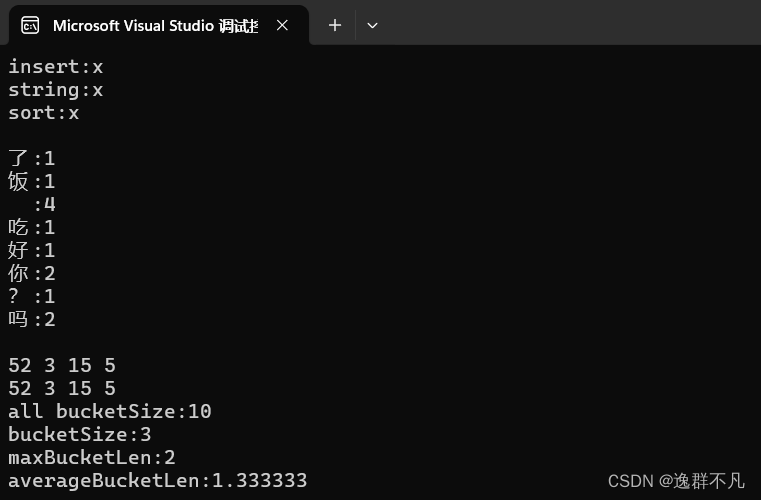






















 3101
3101











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








