ps是什么
ps就是最基本,同时也是非常强大的进程查看命令。使用该命令,可以确定有哪些进程正在运行以及其运行的状态、有没有僵尸进程、占用的资源信息等等。总之大部分信息都是可以通过执行该命令得到的。
- ps命令支持三种使用的语法格式
- UNIX 风格,选项可以组合在一起,并且选项前必须有“-”连字符
- BSD 风格,选项可以组合在一起,但是选项前不能有“-”连字符
- GNU 风格的长选项,选项前有两个“-”连字符
在日常生活和工作中,用的较多时前两种风格。本文后面的例子就采用前两种风格。
注意:ps命令能够给出当前系统中进程的快照(即显示某时刻的进程状态),并不是动态连续的。如果想对进程进行实时监控,请用top命令
关于ps的详细信息,请自己查看man手册,本文只介绍一些常用的参数和例子。
ps常用参数
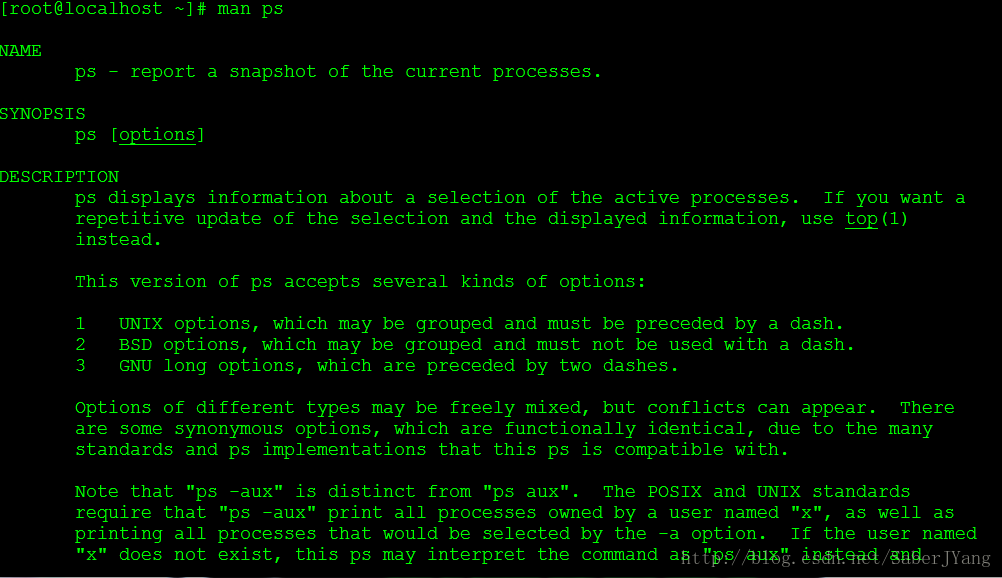
man手册部分英文描述
SIMPLE PROCESS SELECTION
a Lift the BSD-style "only yourself" restriction, which is imposed upon the
set of all processes when some BSD-style (without "-") options are used or
when the ps personality setting is BSD-like. The set of processes selected
in this manner is in addition to the set of processes selected by other
means. An alternate description is that this option causes ps to list all
processes with a terminal (tty), or to list all processes when used
together with the x option.
-A Select all processes. Identical to -e.
-a Select all processes except both session leaders (see getsid(2)) and
processes not associated with a terminal.
-d Select all processes except session leaders.
--deselect
Select all processes except those that fulfill the specified conditions
(negates the selection). Identical to -N.
-e Select all processes. Identical to -A.
g Really all, even session leaders. This flag is obsolete and may be
discontinued in a future release. It is normally implied by the a flag,
and is only useful when operating in the sunos4 personality.
-N Select all processes except those that fulfill the specified conditions
(negates the selection). Identical to --deselect.
T Select all processes associated with this terminal. Identical to the t
option without any argument.
r Restrict the selection to only running processes.
x Lift the BSD-style "must have a tty" restriction, which is imposed upon the
set of all processes when some BSD-style (without "-") options are used or
when the ps personality setting is BSD-like. The set of processes selected
in this manner is in addition to the set of processes selected by other
means. An alternate description is that this option causes ps to list all
processes owned by you (same EUID as ps), or to list all processes when
used together with the a option.
中文描述
a 显示终端上地所有进程,包括其他用户地进程
e 命令之后显示环境(如:ps -d e; ps -a e)
h 不显示标题(即第一行)
l 长格式输出
u 按用户名和启动时间的顺序来显示进程
j 用任务格式来显示进程
f 用树形格式来显示进程
a 显示所有用户的所有进程(包括其它用户)
x 显示无控制终端的进程
r 显示运行中的进程
v 以虚拟存储器格式显示
s 以信号格式显示
U username 显示该用户下的所有进程,且显示各个命令的详细路径。如:ps U zhang
-A 显示所有进程(等价于-e)
-a 显示所有终端机下执行的程序,除了session leaders
-d 显示所有进程,但省略所有的session leaders
-N 选择除满足指定条件的进程之外的所有进程(否定选择)。 等价于–deselect
-x 显示没有控制终端的进程,同时显示各个命令的具体路径。dx不可合用。
-p pid 进程使用cpu的时间
-u uid or username 选择有效的用户id或者是用户名
-g gid or groupname 显示组的所有进程。
-f 全部列出,通常和其他选项联用。如:ps -fa or ps -fx and so on.
-l 长格式(有F,wchan,C 等字段)
-j 作业格式
-o 用户自定义格式。
-w 显示加宽可以显示较多的资讯
-m 显示所有的线程
-H 显示进程的层次(和其它的命令合用,如:ps -Ha)
ps命令常用用法
man手册列举的例子
EXAMPLES
To see every process on the system using standard syntax:
ps -e
ps -ef
ps -eF
ps -ely
To see every process on the system using BSD syntax:
ps ax
ps axu
To print a process tree:
ps -ejH
ps axjf
To get info about threads:
ps -eLf
ps axms
To get security info:
ps -eo euser,ruser,suser,fuser,f,comm,label
ps axZ
ps -eM
To see every process running as root (real & effective ID) in user format:
ps -U root -u root u
To see every process with a user-defined format:
ps -eo pid,tid,class,rtprio,ni,pri,psr,pcpu,stat,wchan:14,comm
ps axo stat,euid,ruid,tty,tpgid,sess,pgrp,ppid,pid,pcpu,comm
ps -Ao pid,tt,user,fname,tmout,f,wchan
Print only the process IDs of syslogd:
ps -C syslogd -o pid=
Print only the name of PID 42:
ps -q 42 -o comm=
中文描述
1)ps a 显示现行终端机下的所有程序,包括其他用户的程序。
2)ps -A 显示所有程序。
3)ps c 列出程序时,显示每个程序真正的指令名称,而不包含路径,参数或常驻服务的标示。
4)ps -e 此参数的效果和指定”A”参数相同。
5)ps e 列出程序时,显示每个程序所使用的环境变量。
6)ps f 用ASCII字符显示树状结构,表达程序间的相互关系。
7)ps -H 显示树状结构,表示程序间的相互关系。
8)ps -N 显示所有的程序,除了执行ps指令终端机下的程序之外。
9)ps s 采用程序信号的格式显示程序状况。
10)ps S 列出程序时,包括已中断的子程序资料。
11)ps -t<终端机编号> 指定终端机编号,并列出属于该终端机的程序的状况。
12)ps u 以用户为主的格式来显示程序状况。
13)ps x 显示所有程序,不以终端机来区分。
最常用的方法是ps -aux,然后再利用一个管道符号,导向到grep去查找特定的进程,然后再对特定的进程进行操作。
ps Head标头信息
USER 用户名
UID 用户ID(User ID)
PID 进程ID(Process ID)
PPID 父进程的进程ID(Parent Process id)
SID 会话ID(Session id)
%CPU 进程的cpu占用率
%MEM 进程的内存占用率
VSZ 进程所使用的虚存的大小(Virtual Size)
RSS 进程使用的驻留集大小或者是实际内存的大小,Kbytes字节。
TTY 与进程关联的终端(tty)
STAT 进程的状态:进程状态使用字符表示的(STAT的状态码)
START: 启动进程的时间;
TIME: 进程消耗CPU的时间
COMMAND:命令的名称和参数
NI 优先级(Nice)
PRI 进程优先级编号(Priority)
WCHAN 进程正在睡眠的内核函数名称;该函数的名称是从/root/system.map文件中获得的。
FLAGS 与进程相关的数字标识
STAT信息
D 无法中断的休眠状态(通常 IO 的进程);
R 正在运行,在可中断队列中;
S 处于休眠状态,静止状态;
T 停止或被追踪,暂停执行;
W 进入内存交换(从内核2.6开始无效);
X 死掉的进程;
Z 僵尸进程不存在但暂时无法消除;
W: 没有足够的记忆体分页可分配
WCHAN 正在等待的进程资源;
<: 高优先级进程
N: 低优先序进程
L: 有记忆体分页分配并锁在记忆体内 (即时系统或捱A I/O),即,有些页被锁进内存
s 进程的领导者(在它之下有子进程);
l 多进程的(使用 CLONE_THREAD, 类似 NPTL pthreads);
+位于后台的进程组
ps命令举例
环境有2个用户root和saber。root登录两个,saber登录三个,一个执行了man ps命令,一个执行了vim test.txt命令。
1. ps a -a au等例子
[root@localhost ~]# ps a
PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND
2193 tty1 Ss+ 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4 -verbose -auth /run/gdm/auth-for-gdm-
2696 pts/0 Ss+ 0:00 -bash
16510 pts/1 Ss 0:00 -bash
17911 pts/2 Ss 0:00 -bash
20682 pts/2 S+ 0:00 man ps
20693 pts/2 S+ 0:00 less -s
21192 pts/3 Ss+ 0:00 -bash
21588 pts/4 Ss 0:00 -bash
21671 pts/4 S+ 0:00 vim test.txt
22438 pts/1 R+ 0:00 ps a
[root@localhost ~]# ps -a
PID TTY TIME CMD
20682 pts/2 00:00:00 man
20693 pts/2 00:00:00 less
21671 pts/4 00:00:00 vim
22439 pts/1 00:00:00 ps
[root@localhost ~]# ps au
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 2193 0.0 0.7 191040 14044 tty1 Ss+ 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4
root 2696 0.0 0.1 116688 3548 pts/0 Ss+ 10:36 0:00 -bash
root 16510 0.0 0.1 120800 3348 pts/1 Ss 11:19 0:00 -bash
saber 17911 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/2 Ss 12:07 0:00 -bash
saber 20682 0.0 0.1 119496 2244 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 man ps
saber 20693 0.0 0.0 110276 1240 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 less -s
saber 21192 0.0 0.1 116556 3204 pts/3 Ss+ 14:52 0:00 -bash
saber 21588 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/4 Ss 15:03 0:00 -bash
saber 21671 0.0 0.2 153392 4880 pts/4 S+ 15:03 0:00 vim test.txt
root 22440 0.0 0.0 139492 1636 pts/1 R+ 15:47 0:00 ps au
[root@localhost ~]# ps -au
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 2193 0.0 0.7 191040 14044 tty1 Ss+ 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4
root 2696 0.0 0.1 116688 3548 pts/0 Ss+ 10:36 0:00 -bash
root 16510 0.0 0.1 120800 3352 pts/1 Ss 11:19 0:00 -bash
saber 17911 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/2 Ss 12:07 0:00 -bash
saber 20682 0.0 0.1 119496 2244 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 man ps
saber 20693 0.0 0.0 110276 1240 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 less -s
saber 21192 0.0 0.1 116556 3204 pts/3 Ss+ 14:52 0:00 -bash
saber 21588 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/4 Ss 15:03 0:00 -bash
saber 21671 0.0 0.2 153392 4880 pts/4 S+ 15:03 0:00 vim test.txt
root 22441 0.0 0.0 139492 1636 pts/1 R+ 15:48 0:00 ps -au
[root@localhost ~]# ps auf
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
saber 21588 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/4 Ss 15:03 0:00 -bash
saber 21671 0.0 0.2 153392 4880 pts/4 S+ 15:03 0:00 \_ vim test.txt
saber 21192 0.0 0.1 116556 3204 pts/3 Ss+ 14:52 0:00 -bash
saber 17911 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/2 Ss 12:07 0:00 -bash
saber 20682 0.0 0.1 119496 2244 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 \_ man ps
saber 20693 0.0 0.0 110276 1240 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 \_ less -s
root 16510 0.0 0.1 120800 3352 pts/1 Ss 11:19 0:00 -bash
root 22442 0.0 0.0 139488 1604 pts/1 R+ 15:48 0:00 \_ ps auf
root 2696 0.0 0.1 116688 3548 pts/0 Ss+ 10:36 0:00 -bash
root 2193 0.0 0.7 191040 14044 tty1 Ss+ 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4
[root@localhost ~]# ps al
F UID PID PPID PRI NI VSZ RSS WCHAN STAT TTY TIME COMMAND
4 0 2193 1091 20 0 191040 14044 poll_s Ss+ tty1 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -au
4 0 2696 2692 20 0 116688 3548 n_tty_ Ss+ pts/0 0:00 -bash
4 0 16510 16507 20 0 120800 3352 wait Ss pts/1 0:00 -bash
0 1000 17911 17910 20 0 116556 3184 wait Ss pts/2 0:00 -bash
0 1000 20682 17911 20 0 119496 2244 wait S+ pts/2 0:00 man ps
0 1000 20693 20682 20 0 110276 1240 n_tty_ S+ pts/2 0:00 less -s
0 1000 21192 21189 20 0 116556 3204 n_tty_ Ss+ pts/3 0:00 -bash
0 1000 21588 21585 20 0 116556 3184 wait Ss pts/4 0:00 -bash
0 1000 21671 21588 20 0 153392 4880 poll_s S+ pts/4 0:00 vim test.txt
4 0 22547 16510 20 0 137372 1272 - R+ pts/1 0:00 ps al
[root@localhost ~]# ps aw
PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND
2193 tty1 Ss+ 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4 -verbose -auth /run/gdm/auth-for-gdm-vlnJ2G/database
2696 pts/0 Ss+ 0:00 -bash
16510 pts/1 Ss 0:00 -bash
17911 pts/2 Ss 0:00 -bash
20682 pts/2 S+ 0:00 man ps
20693 pts/2 S+ 0:00 less -s
21192 pts/3 Ss+ 0:00 -bash
21588 pts/4 Ss 0:00 -bash
21671 pts/4 S+ 0:00 vim test.txt
22572 pts/1 R+ 0:00 ps aw
[root@localhost ~]#2. 显示当前所有进程
这个命令的结果或许会很长。为了便于查看,可以结合less命令和管道来使用。
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | less
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.2 123256 3896 ? Ss 10:34 0:03 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 21
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [kworker/u256:0]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [migration/0]
root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcu_bh]
root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/0]
root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/1]
root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/2]
root 12 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/3]
root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/4]
root 14 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/5]
root 15 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/6]3. 通过cpu和内存使用来过滤进程
默认的结果集是未排好序的。可以通过 - -sort命令来排序,根据CPU使用率来升序排序。
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux --sort -pcpu | less
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 820 0.1 0.3 317552 6324 ? Ssl 10:35 0:21 /usr/bin/vmtoolsd
root 1 0.0 0.2 123256 3896 ? Ss 10:34 0:03 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 21
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [kworker/u256:0]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [migration/0]
root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcu_bh]
root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/0]
root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/1]
root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:34 0:00 [rcuob/2]根据内存使率来升序排序
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux --sort -pmem | less
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
gdm 2448 0.0 6.2 1393792 117116 ? Sl 10:35 0:06 gnome-shell --mode=gdm
root 2856 0.0 1.2 323580 23272 ? Ssl 10:36 0:00 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid
gdm 2417 0.0 1.0 1091488 19088 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gnome-settings-daemon
gdm 2518 0.0 0.9 787076 18172 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/goa-daemon
root 1081 0.0 0.8 553048 16328 ? Ssl 10:35 0:03 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/tuned -l -P
root 865 0.0 0.8 110524 15828 ? S 10:35 0:00 /sbin/dhclient -d -q -sf /usr/libexec/nm-dhcp-helper -pf /var/run/dhclient-eno16777736.pid -lf /var/lib/NetworkManager/dhclient-f35d0a44-99d4-4dca-b595-3303ed1ffd09-eno16777736.lease -cf /var/lib/NetworkManager/dhclient-eno16777736.conf eno16777736
root 1085 0.0 0.7 555492 14736 ? Ssl 10:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/libvirtd
root 2193 0.0 0.7 191040 14044 tty1 Ss+ 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4 -verbose -auth /run/gdm/auth-for-gdm-vlnJ2G/database -seat seat0 -nolisten tcp vt1
polkitd 22967 0.0 0.6 526464 12124 ? Ssl 16:10 0:00 /usr/lib/polkit-1/polkitd --no-debug4. 通过进程名过滤
使用 -C 参数,后面跟你要找的进程的名字。比如想显示一个名为bash的进程的信息,就可以使用下面的命令:
[root@localhost ~]# ps -f -C bash
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 2696 2692 0 10:36 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 16510 16507 0 11:19 pts/1 00:00:00 -bash
saber 17911 17910 0 12:07 pts/2 00:00:00 -bash
saber 21192 21189 0 14:52 pts/3 00:00:00 -bash
saber 21588 21585 0 15:03 pts/4 00:00:00 -bash
[root@localhost ~]#5. 根据线程来过滤进程
如果我们想知道特定进程的线程,可以使用-L 参数,后面加上特定的PID。
[root@localhost ~]# ps u -L 2562
USER PID LWP %CPU NLWP %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
gdm 2562 2562 0.0 2 0.1 312512 3296 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gvfs-mtp-volume-monitor
gdm 2562 2564 0.0 2 0.1 312512 3296 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gvfs-mtp-volume-monitor
[root@localhost ~]# ps u -L 2566
USER PID LWP %CPU NLWP %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
gdm 2566 2566 0.0 3 0.2 421780 5172 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gvfs-afc-volume-monitor
gdm 2566 2575 0.0 3 0.2 421780 5172 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gvfs-afc-volume-monitor
gdm 2566 2577 0.0 3 0.2 421780 5172 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gvfs-afc-volume-monitor
[root@localhost ~]#6. 树形显示进程
有时候我们希望以树形结构显示进程,可以使用 f 参数,或pstree命令
[root@localhost ~]# ps auf
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
saber 21588 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/4 Ss 15:03 0:00 -bash
saber 21671 0.0 0.2 153392 4880 pts/4 S+ 15:03 0:00 \_ vim test.txt
saber 21192 0.0 0.1 116556 3204 pts/3 Ss+ 14:52 0:00 -bash
saber 17911 0.0 0.1 116556 3184 pts/2 Ss 12:07 0:00 -bash
saber 20682 0.0 0.1 119496 2244 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 \_ man ps
saber 20693 0.0 0.0 110276 1240 pts/2 S+ 14:29 0:00 \_ less -s
root 16510 0.0 0.1 120800 3352 pts/1 Ss 11:19 0:00 -bash
root 23431 0.0 0.0 139488 1608 pts/1 R+ 16:30 0:00 \_ ps auf
root 2696 0.0 0.1 116688 3548 pts/0 Ss+ 10:36 0:00 -bash
root 2193 0.0 0.7 191040 14044 tty1 Ss+ 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4
[root@localhost ~]# pstree
systemd─┬─ModemManager───2*[{ModemManager}]
├─NetworkManager─┬─dhclient
│ └─2*[{NetworkManager}]
├─2*[abrt-watch-log]
├─abrtd
├─accounts-daemon───2*[{accounts-daemon}]
├─alsactl
├─at-spi-bus-laun─┬─dbus-daemon
│ └─3*[{at-spi-bus-laun}]
├─at-spi2-registr───{at-spi2-registr}
├─atd
├─auditd─┬─audispd─┬─sedispatch
│ │ └─{audispd}
│ └─{auditd}
├─avahi-daemon───avahi-daemon
├─caribou───2*[{caribou}]
├─colord───2*[{colord}]
├─crond
├─cupsd
├─2*[dbus-daemon]
├─dbus-launch
├─dconf-service───2*[{dconf-service}]
├─dnsmasq───dnsmasq
├─firewalld───{firewalld}
├─gdm─┬─Xorg
│ ├─gdm-session-wor─┬─gnome-session─┬─gnome-settings-───4*[{gnome-settings-}]
│ │ │ ├─gnome-shell─┬─ibus-daemon─┬─ibus-dconf───3*[{ibus-dconf}]7. 显示安全信息
如果想要查看现在有谁登入了你的服务器。可以使用ps命令加上相关参数:
-o 参数控制输出。Pid,User,Args显示PID,运行应用的用户,该应用。
[root@localhost ~]# ps -ao pid,user,args
PID USER COMMAND
20682 saber man ps
20693 saber less -s
21671 saber vim test.txt
23642 root ps -ao pid,user,args
[root@localhost ~]# ps -ao "%U,%P,%a"
USER , PPID,COMMAND
saber , 17911,man ps
saber , 20682,less -s
saber , 21588,vim test.txt
root , 16510,ps -ao %U,%P,%aman手册列出的参数列表如下:
AIX FORMAT DESCRIPTORS
This ps supports AIX format descriptors, which work somewhat like the formatting
codes of printf(1) and printf(3). For example, the normal default output can be
produced with this: ps -eo "%p %y %x %c". The NORMAL codes are described in the
next section.
CODE NORMAL HEADER
%C pcpu %CPU
%G group GROUP
%P ppid PPID
%U user USER
%a args COMMAND
%c comm COMMAND
%g rgroup RGROUP
%n nice NI
%p pid PID
%r pgid PGID
%t etime ELAPSED
%u ruser RUSER
%x time TIME
%y tty TTY
%z vsz VSZ8. 使用PS实时监控进程状态
ps 命令会显示你系统当前的进程状态,但是这个结果是静态的。
当有一种情况,我们需要像上面第三条提到的通过CPU和内存的使用率来筛选进程,并且我们希望结果能够每5秒刷新一次。为此,我们可以将ps命令和watch命令结合起来。我们可以使用head -20命令来限制输出,只输出前20行。
[root@localhost ~]# watch -n 5 'ps -aux --sort -pmem,-pcpu | head -20'
Every 5.0s: ps -aux --sort -pmem,-pcpu | head -20 Sat Apr 8 16:54:27 2017
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
gdm 2448 0.0 6.2 1393792 117116 ? Sl 10:35 0:06 gnome-shell --mode=gdm
root 2856 0.0 1.2 323580 23272 ? Ssl 10:36 0:00 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --
gdm 2417 0.0 1.0 1091488 19088 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/gnome-settings-daemon
gdm 2518 0.0 0.9 787076 18172 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/goa-daemon
root 1081 0.0 0.8 553048 16328 ? Ssl 10:35 0:03 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/tuned -l -P
root 865 0.0 0.8 110524 15828 ? S 10:35 0:00 /sbin/dhclient -d -q -sf /usr/libexec/nm-dhcp-helpe
root 1085 0.0 0.7 555492 14736 ? Ssl 10:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/libvirtd
root 2193 0.0 0.7 191040 14044 tty1 Ss+ 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/Xorg :0 -background none -noreset -audit 4
polkitd 22967 0.0 0.6 526644 12344 ? Ssl 16:10 0:02 /usr/lib/polkit-1/polkitd --no-debug
root 811 0.0 0.5 449240 10448 ? Ssl 10:34 0:00 /usr/sbin/NetworkManager --no-daemon
gdm 2497 0.0 0.5 469948 9360 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/ibus-x11 --kill-daemon
root 2508 0.0 0.4 487080 9240 ? Ssl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/packagekitd
gdm 2393 0.0 0.4 562672 8924 ? Ssl 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/gnome-session --autostart /usr/share/gdm/g
gdm 2489 0.0 0.4 469996 7668 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 ibus-daemon --xim --panel disable
gdm 2503 0.0 0.3 395740 7412 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/mission-control-5
gdm 2504 0.0 0.3 575016 7000 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/caribou
root 820 0.1 0.3 317552 6332 ? Rsl 10:35 0:24 /usr/bin/vmtoolsd
gdm 2459 0.0 0.3 526680 6204 ? S<l 10:35 0:00 /usr/bin/pulseaudio --start --log-target=syslog
gdm 2574 0.0 0.3 334440 6092 ? Sl 10:35 0:00 /usr/libexec/goa-identity-service结论
你也许每天都会使用ps命令来监控你的Linux系统。但是事实上,你可以通过ps命令的参数来生成各种你需要的报表。
ps命令的另一个优势是ps是各种 Linux系统都默认安装的,因此你只要用就行了。
不要忘了通过 man ps来查看更多的参数。(由于 ps 命令古老而重要,所以它在不同的 UNIX、BSD、Linux 等系统中的参数不尽相同,因此如果你用的不是 Linux 系统,请查阅你的文档了解具体可用的参数。)






















 544
544

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








