常用的IO类
字节流
- InputStream:读取字节
- FileInputStream:从文件读取
- FileInputStream(File file)
- FileInputStream(String name)
- BufferedInputStream:加入缓存读取,更加高效
- BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
- FileInputStream:从文件读取
- OutputStream:写入字节
- FileOutputSteam:从文件写入
- FileOutputSteam(String name)
- FileOutputSteam(File file, boolean append)
- BufferedOutputStream :加入缓存写入,更加高效
- BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
字符流
- Reader:读取字符
- InputStreamReader:从流读取
- InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
- InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) 可以指定编码
- FileReader:从文件读取
- FileReader(String fileName)
- FileReader(File file)
- FileReader(String fileName)
- BufferedReader:持有特有成员方法 readLine(),从流高效读取
- BufferedReader(Reader in)
- Writer:写入字符
- InputStreamWriter
- InputStreamWriter(InputStream in)
- InputStreamWriter(InputStream in, String charsetName) 可以指定编码
- FileWriter
- FileWriter(String fileName)
- FileWriter(File file)
- FileWriter(File file, boolean append)
- FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append)
- FileWriter(File file, boolean append)
- FileWriter(File file)
- FileWriter(String fileName)
- BufferedWriter:持有特有成员方法 writeLine(),高效写入流
- BufferedWriter(Writer out)
BIO、NIO、多路复用、AIO的区别
-
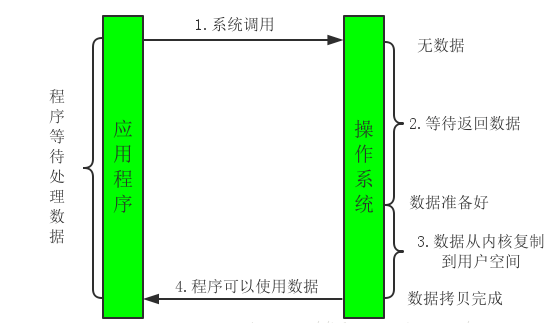
BIO
-
实现方式:基于流实现的
-
特点:同步和阻塞的,一个线程处理一个流,会阻塞,无法执行其他程序
-
适用场景:对于并发量不大的情况
-
-
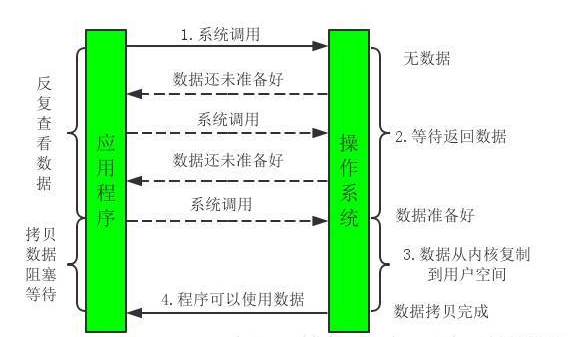
NIO
- 实现方式:基于块实现的,也就是将数据写入缓冲区中,再从缓冲区中读取
- 特点:同步非阻塞的,一个线程可以同时处理多个流,不阻塞,可以执行其他程序,但CPU回一直查看
- 适用场景:对于数据量较小的数据,有选择器,可同时打开多个通道,适用于并发量较大的情况。Netty使用该模式
-
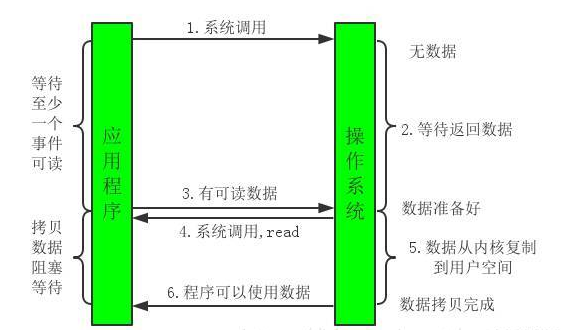
多路复用
-
实现方式:基于块实现的,也就是将数据写入缓冲区中,再从缓冲区中读取
-
特点:将NIO中反复查看的过程交给操作系统的select poll epoll等函数,当有可读数据时,收到通知,获取数据。避免了NIO中线程一直占用CPU的情况。
-
适用场景:性能较优。Redis使用该模式
-
-
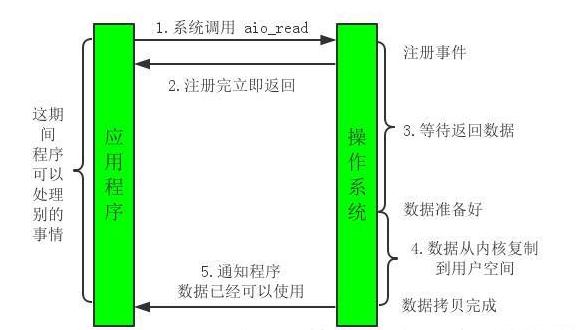
AIO:
-
实现方式:基于块实现的,在读取完成后会发送回调通知
-
特点:异步非阻塞的,一个线程可以处理多个流,且不用手动查看流是否完成,只需回调通知即可
-
适用场景:对于数据量较大的数据,且并发量较大的情况
-
NIO的实现方式
- 从通道进行数据读取 :创建一个缓冲区,然后请求通道读取数据。
- 从通道进行数据写入 :创建一个缓冲区,填充数据,并要求通道写入数据。
- 选择器:一个选择器可以管理多个通道,判断通道状态是否可读、可写,从而管理数据
public class NIOTest {
/**
* 通过通道和缓冲区复制文件
* @param srcFile
* @param destFile
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void copy(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
FileChannel inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer bf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = 0;
while ((len = inputChannel.read(bf))!=-1){
bf.flip();
fosChannel.write(bf);
bf.clear();
}
inputChannel.close();
fis.close();
fosChannel.close();
fos.close();
}
/**
* 通过文件输出通道复制文件
* @param srcFile
* @param destFile
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void copy2(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
FileChannel fisChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
fosChannel.transferFrom(fisChannel,0,fisChannel.size());
fisChannel.close();
fis.close();
fosChannel.close();
fos.close();
}
/**
* 通过文件输入通道复制文件
* @param srcFile
* @param destFile
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void copy3(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
FileChannel fisChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
fisChannel.transferTo(0,fisChannel.size(),fosChannel);
fisChannel.close();
fis.close();
fosChannel.close();
fos.close();
}
/**
* 通过选择器复制文件,伪代码,需要调试,一个选择器可管理多个通道
* @param srcFile
* @param destFile
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void copy4(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
FileChannel fisChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
Selector selector = Selector.open();
fisChannel .configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey key = fisChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
fosChannel .configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey key2 = fosChannel .register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
while(true) {
int readyChannels = selector.select();
if(readyChannels == 0) continue;
Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if(key.isAcceptable()) {
// a connection was accepted by a ServerSocketChannel.
} else if (key.isConnectable()) {
// a connection was established with a remote server.
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// a channel is ready for reading
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
// a channel is ready for writing
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
copy3("E:\\桌面\\临时\\aaa.txt","E:\\桌面\\临时\\bbb.txt");
}
}
参考
IO流和NIO总结
Java NIO系列教程
IO复用,AIO,BIO,NIO,同步,异步,阻塞和非阻塞 区别(百度)
BIO,NIO,多路复用,AIO






















 1662
1662











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








