目录
为什么要使用文件
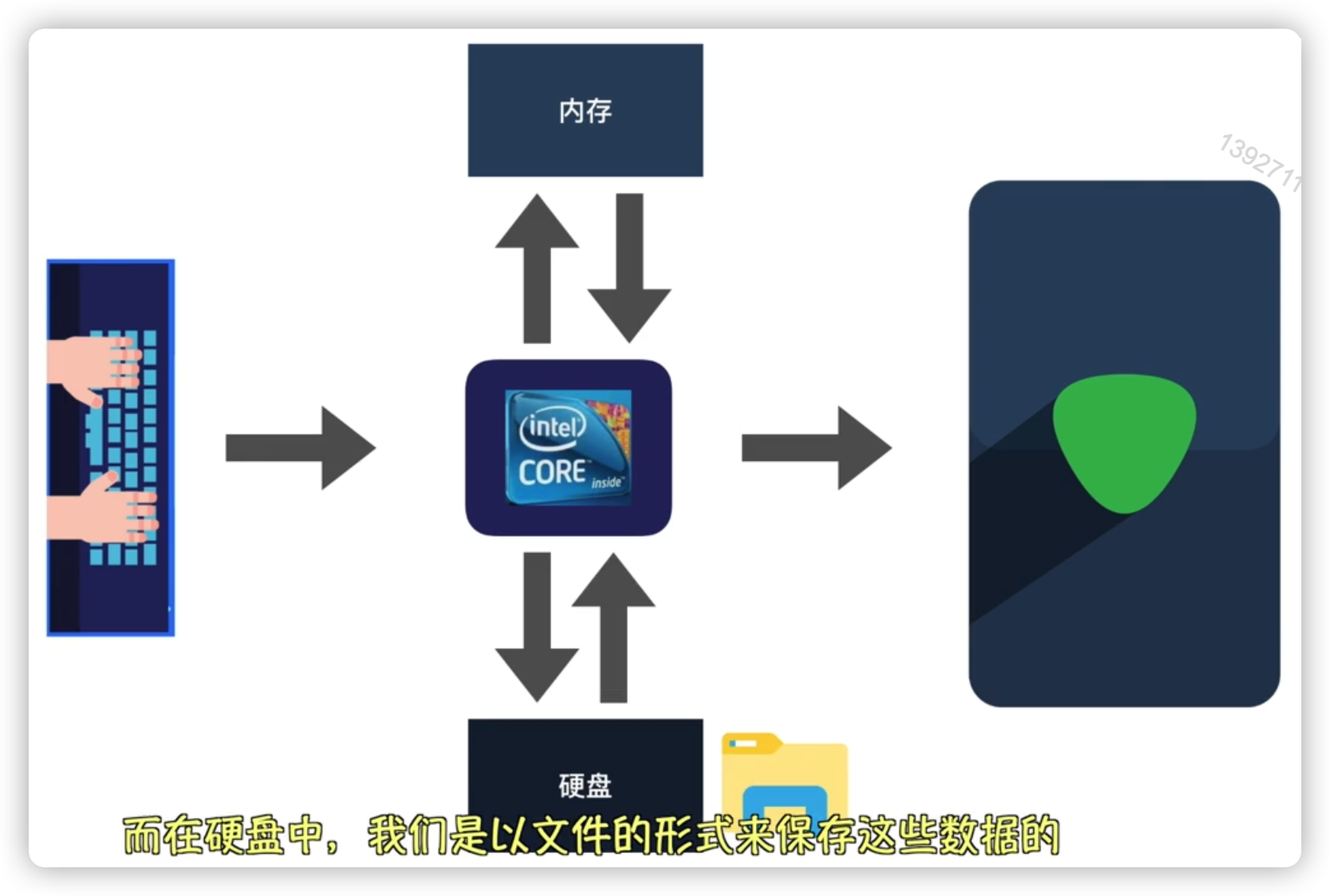
内存:程序的运行和交换,CPU将所有程序在内存中运行,把结果返回给输出设备显示屏
硬盘:一块存储空间,以文件形式保存
字节byte问题:从来没见过电脑上有010100吧,以二进制表示就是以字节byte来展示,汉字在utf-8编码下占3个字节,英文字符占1个字节,是其本身
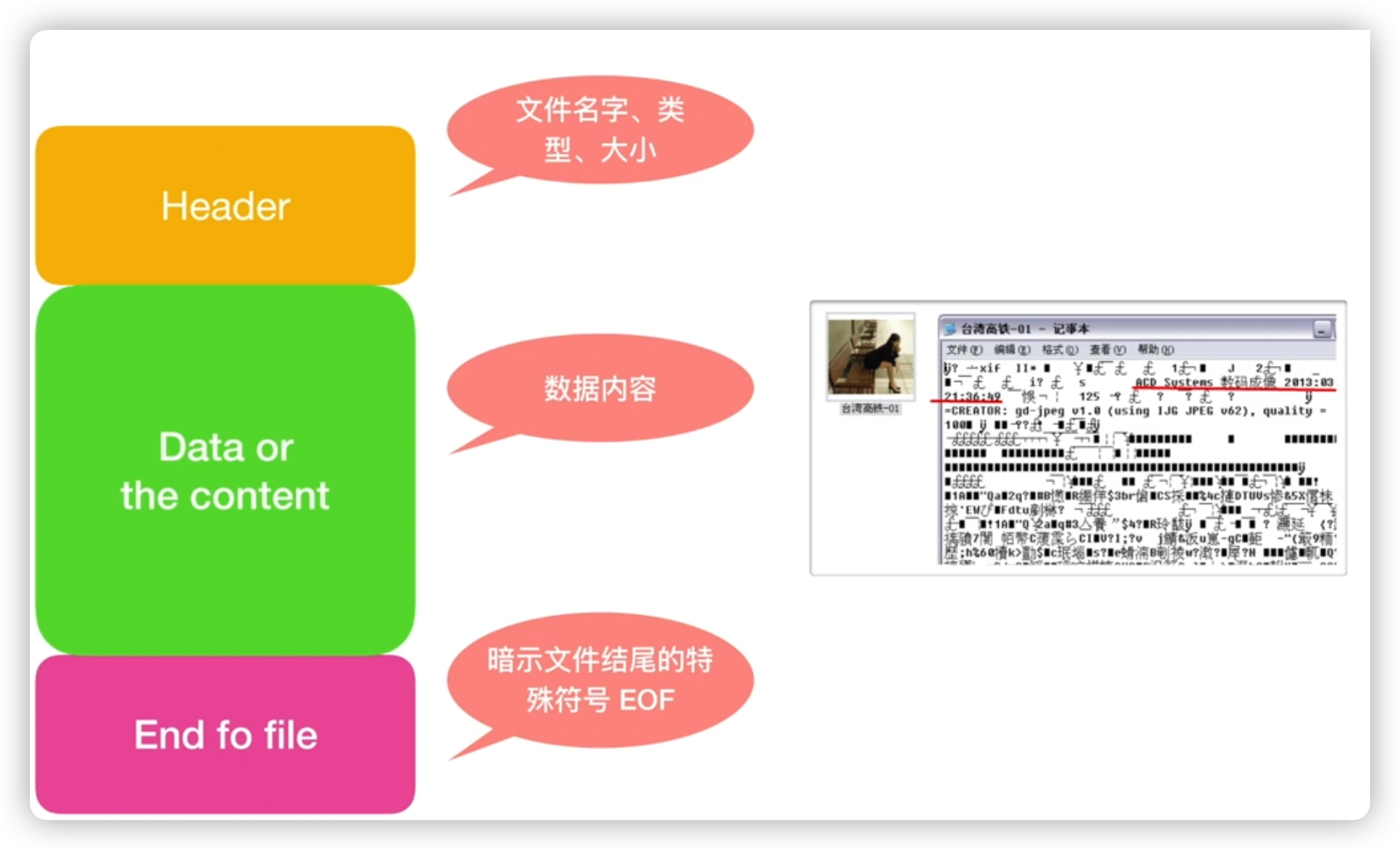
文件的结构:
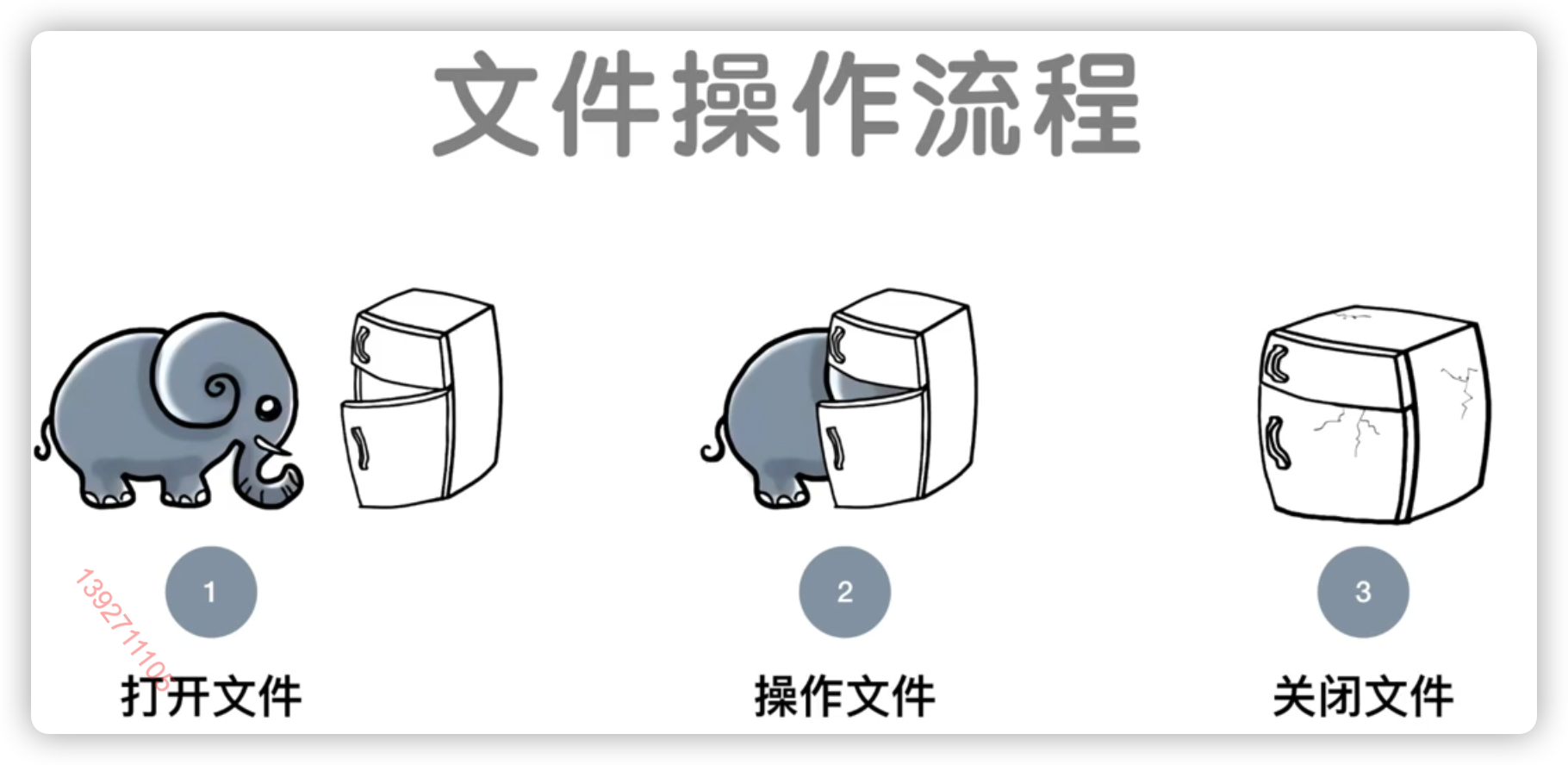
文件的操作流程
操作文件:包含读、写等等
一、打开文件概述

换行符
window:\r\n
linux:\n
mac:\n (以前是\r)
mode:
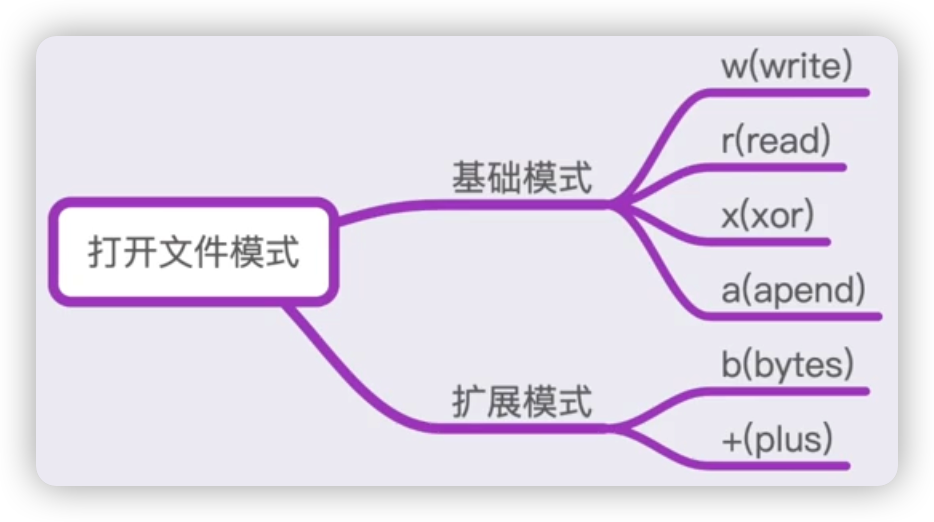
一、打开文件模式 - r
功能一: 当文件不存在时报错
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt', 'r')
# 操作文件
# 关闭文件
file.close()
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'zen.txt'
功能二: 读取txt文件中内容
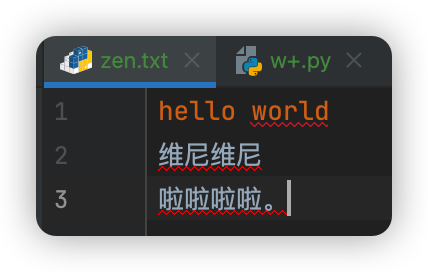
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt', 'r') # r模式:当文件不存在时报错
# 操作文件
content = file.read()
print(content)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
hello world
维尼维尼
啦啦啦啦。
一、打开文件模式 - w
功能一: 当文件不存在时,会自动创建一个文件
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','w')
# 操作文件
# 关闭文件
file.close()
功能二: 删除原内容,写进新内容
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','w')
# 操作文件
file.write("hello")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','w')
# 操作文件
file.write("wo")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
一、打开文件模式 - x
如果文件不存在,自动创建一个文件;
如果文件存在,报错
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.py','x')
# 操作文件
# 关闭文件
file.close()
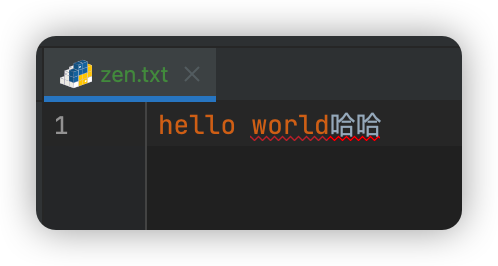
一、打开文件模式 - a
如果原文件中有内容,会追加到原文件后面
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','a')
# 操作文件
file.write('hello world')
# 关闭文件
file.close()
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','a')
# 操作文件
file.write('哈哈')
# 关闭文件
file.close()
一、打开文件模式 - wb
不能单独使用,以二进制形式展示
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','wb')
# 操作文件
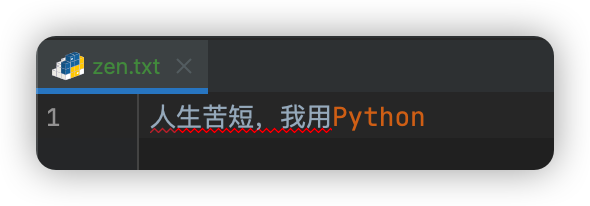
file.write(bytes('人生苦短,我用Python', encoding='utf-8'))
# 关闭文件
file.close()
一、打开文件模式 - rb
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','rb')
# 操作文件
content = file.read()
print(content)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
b'\xe4\xba\xba\xe7\x94\x9f\xe8\x8b\xa6\xe7\x9f\xad\xef\xbc\x8c\xe6\x88\x91\xe7\x94\xa8Python'
英文字幕由ASC码来编写,所以字符还是其本身
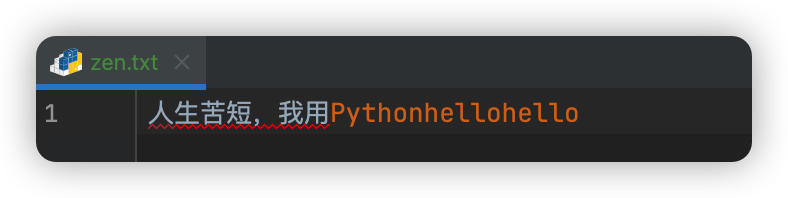
一、打开文件模式 - ab
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','ab') # b模式:不能单独使用,以二进制形式展示
# 操作文件
file.write(bytes('hellohello', encoding='utf-8'))
# 关闭文件
file.close()
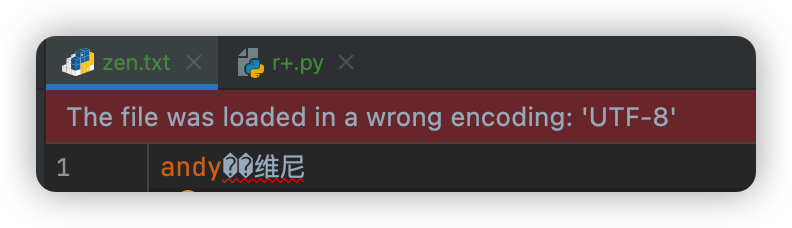
一、打开文件模式 - r+
可以用来write,是字节覆盖型write
在utf-8编码下
汉字:占3个字节
英文字母:占1个字节,是其本身
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','r+')
# 操作文件
file.write("维尼维尼")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','r+')
# 操作文件
file.write("andy")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
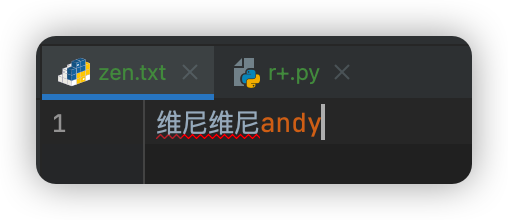
一、打开文件模式 - a+
可以用来write,追加型write
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','a+')
# 操作文件
file.write("维尼维尼")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','a+')
# 操作文件
file.write("andy")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
一、打开文件模式 - w+
写 :清空原来内容,写新的
读 :无内容,设计文件指针
# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt','w+')
# 操作文件
# file.write("hello world")
content = file.read()
print(content)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
无内容
二、操作文件指针的两种方法
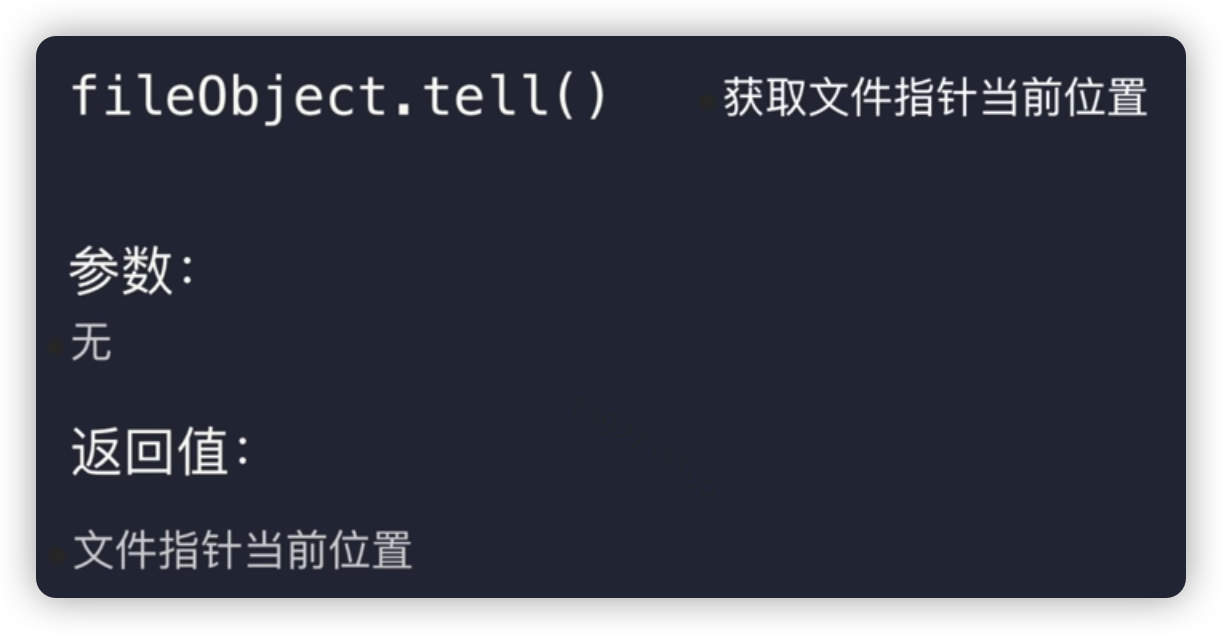

# 打开文件
file = open('zen.txt', 'w+')
# 操作文件
print(file.tell())
file.write('人生苦短,我用python.') # 写完后指针指在末尾后一个位置
print(file.tell())
file.seek(21, 0)
print(file.tell())
content = file.read()
print(content)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
0
28
21
python.
二、操作文件 – 写入文件的2种方法

1. write
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'w')
# 写入文件
file.write("人生苦短 我用Python")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短 我用Python
2. write + 换行符
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'w')
# 写入文件
file.write("人生苦短,\n我用Python")
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短,
我用Python
3. writelines
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'w')
# 写入文件
seq = ['人生苦短', '我用Python']
file.writelines(seq)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短我用Python
4. writelines + 换行符
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'w')
# 写入文件
seq = ['人生苦短\n', '我用Python\n', 'hi\n', 'andy']
file.writelines(seq)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
5. writelines + 换行符 + 简写
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'w')
# 写入文件
seq = ['人生苦短', '我用Python', 'hi', 'andy']
file.writelines('\n'.join(seq))
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
二、操作文件 – 读取文件的3种方式

1. read
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt','r')
# 操作文件
content = file.read()
print(content)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
2. read + 索引
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt','r')
# 操作文件
content = file.read(5) # 前5个字(包括换行符);难以判断位置,所以用的很少
print(content)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短
3. readline
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt','r')
# 操作文件
line = file.readline()
print(line)
line = file.readline()
print(line)
line = file.readline()
print(line)
line = file.readline()
print(line)
line = file.readline() # 读完了 再输也不报错
print(line)
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
4. readline + while循环
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'r')
# 操作文件
line = file.readline()
while line != '':
print(line, end='') # 可取消换行符
line = file.readline()
# 关闭文件
file.close()
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
5. readlines
# 打开文件
file = open('text.txt', 'r')
# 操作文件
lines = file.readlines()
print(lines)
for line in lines:
print(line, end='') # 可取消换行符
# 关闭文件
file.close()
['人生苦短\n', '我用Python\n', 'hi\n', 'andy']
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
三、关闭文件
虽然python可以自动回收文件,但为了防止一些情况,还是要主动关闭文件,比如:
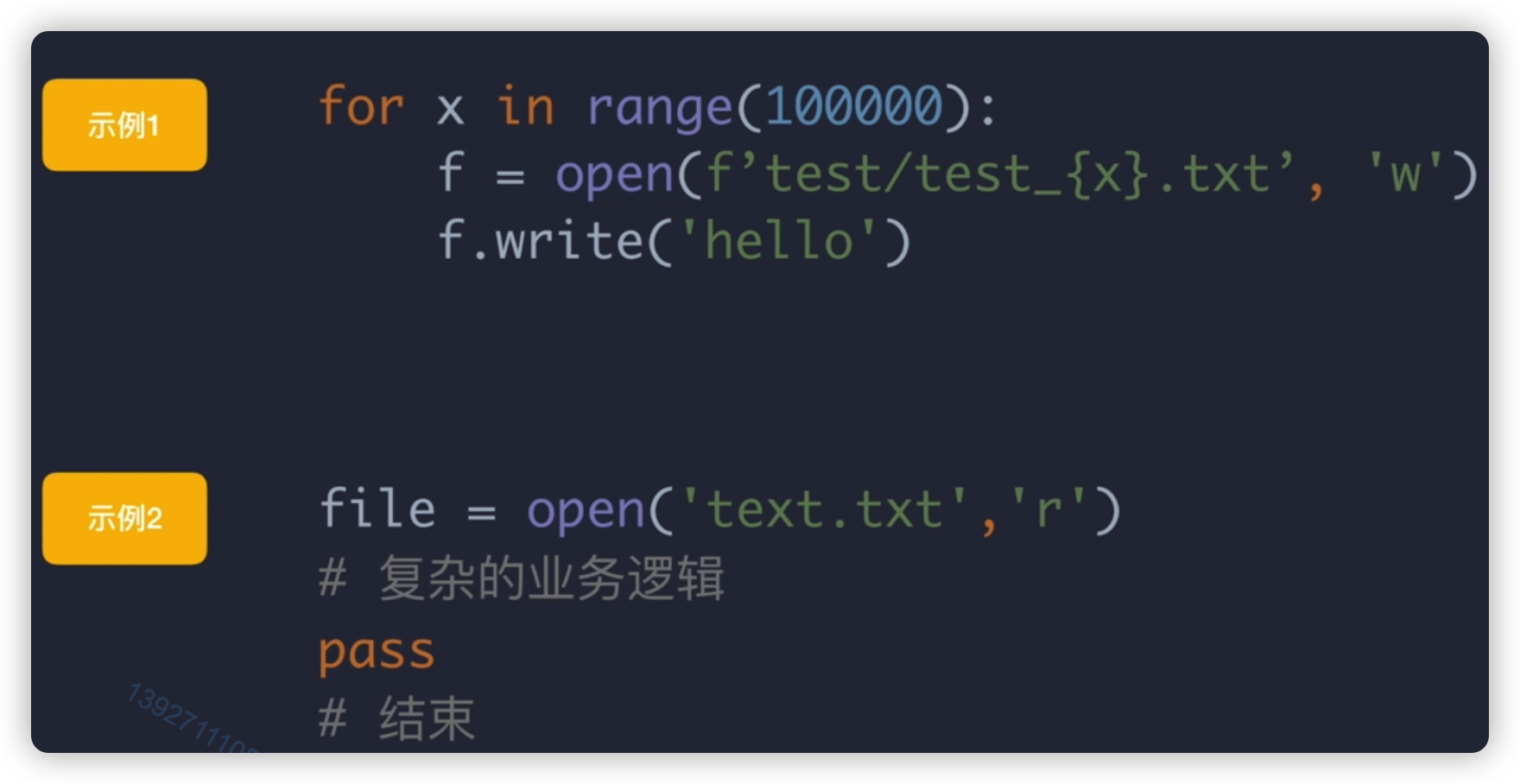
示例1:打开太多文件,导致系统卡死
示例2:打开文件后,一直没有关去执行其他的业务,业务执行的很长时间内,文件资源一直占用
try:
# 打开文件
reader = open('test.txt','r')
# 操作文件
content = reader.read()
print(content)
except Exception:
print(Exception)
finally:
# 关闭文件
reader.close()
四、with语句 – 不用close – 上下文处理器
自动关闭,不用想着加close去关闭文件
with open('test.txt','r') as reader:
content = reader.read()
print(content)
一行一行读
with open('test.txt','r') as reader:
for line in reader:
print(line)
手搓上下文处理器
class FileManager(object):
def __init__(self, name, mode):
print("调用__init__方法")
self.name = name
self.mode = mode
self.file = None
def __enter__(self):
print("调用__enter__方法")
self.file = open(self.name, self.mode)
return self.file
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
print("调用__exit__方法")
if self.file:
self.file.close()
with FileManager('test.txt','r') as file:
print("准备读取文件")
content = file.read()
print(content)
调用__init__方法
调用__enter__方法
准备读取文件
人生苦短
我用Python
hi
andy
调用__exit__方法
五、目录及文件的相关操作 – os模块
目录:文件夹
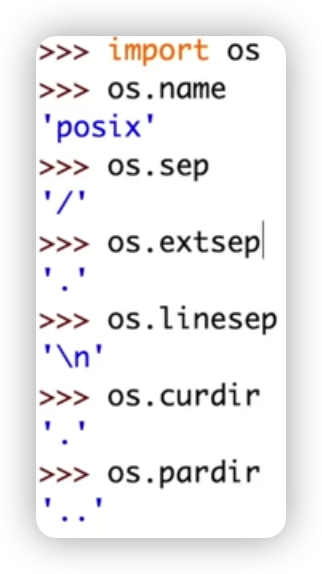
OS模块常用变量:

命令行操作:
五、查看目录和文件
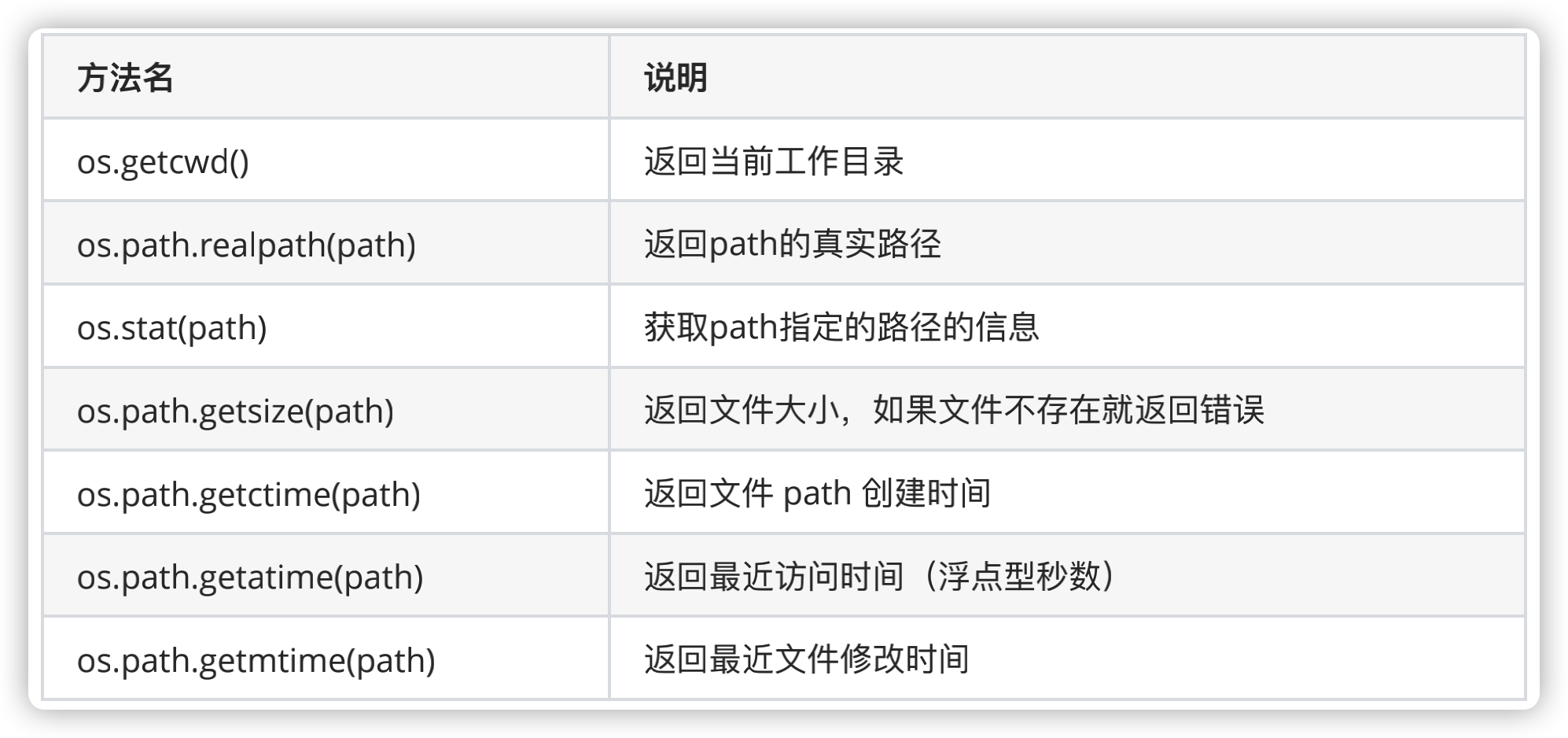

print(os.getcwd()) # 查看当前目录
print(os.stat('/Users/xxx/PycharmProjects/python/chapter14(文件操作与目录)')) # 获取指定路径的信息
print(os.path.abspath('zen.txt')) # 获取当前路径的绝对路径
print(os.path.getsize('zen.txt'))
print(os.path.getctime('zen.txt')) # 获取创建时间
print(os.path.getatime('zen.txt')) # 获取访问时间
print(os.path.getmtime('zen.txt')) # 获取修改时间
/usr/local/bin/python3.9 /Users/xxx/PycharmProjects/python/chapter14(文件操作与目录)/handle_directory.py
/Users/xxx/PycharmProjects/python/chapter14(文件操作与目录)
os.stat_result(st_mode=16877, st_ino=10898133, st_dev=16777234, st_nlink=21, st_uid=501, st_gid=20, st_size=672, st_atime=1648883039, st_mtime=1648883063, st_ctime=1648883063)
/Users/xxx/PycharmProjects/python/chapter14(文件操作与目录)/zen.txt
28
1648804358.466486
1648804358.867274
1648804358.466486
五、创建目录和文件
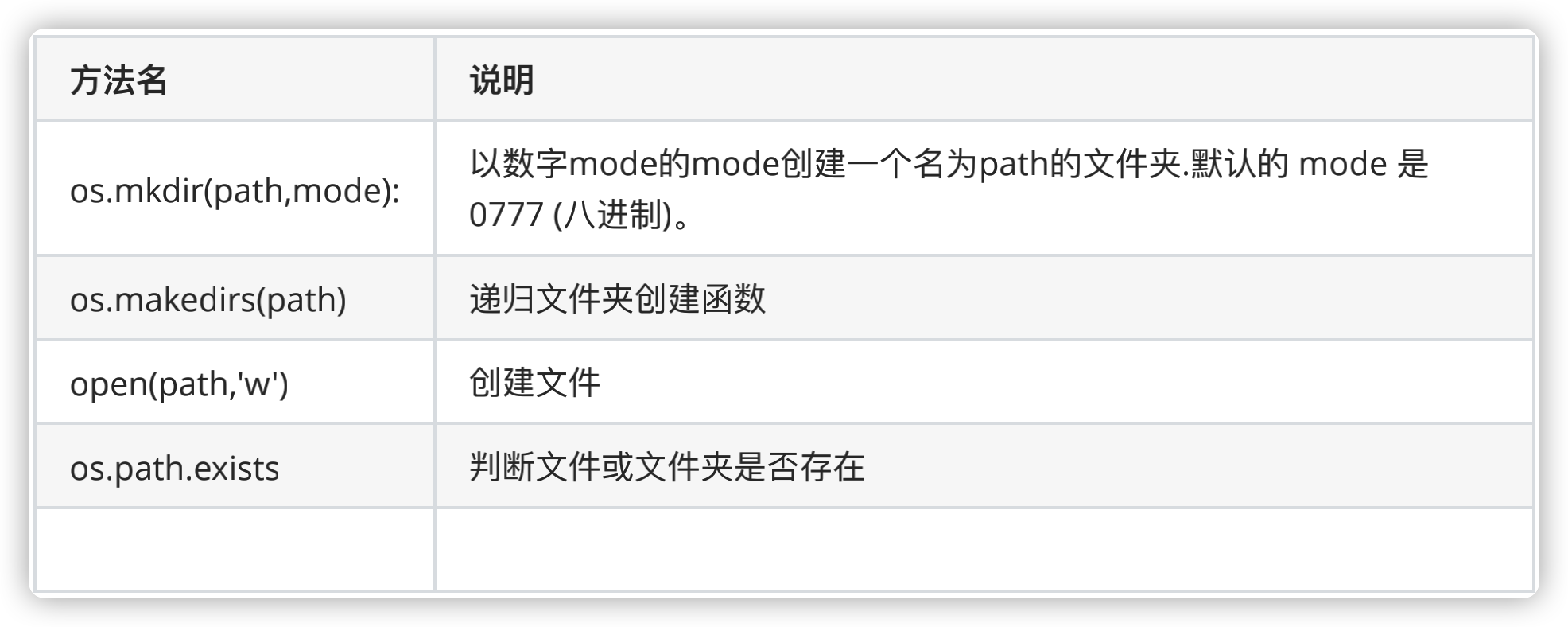
# 创建目录和文件
os.mkdir('test1.txt') # 创建一个文件夹📂,如果存在,则报错。
os.mkdir('test1/test2') # 在已有test1文件夹📂情况下,创建test2文件夹📂
os.makedirs('python1/python2') # 递归创建目录📂,如果存在,则报错。
with open('test.py', 'w') as f: # open函数创建文件📃
pass
if os.path.exists('test_test.py'): # 判断目录是否存在
print('文件已存在')
else:
print('文件不存在')
五、删除目录和文件

# 删除目录
os.rmdir('python1/python2') # 只能删除空文件
os.removedirs('python1/python2') # 可以递归删除,只能删除空文件,python2必须是空文件
# 删除文件 两个方法一样
os.remove('python1/test.py') # 删不存在的文件,会报错,经常先用os.path.exists判断是否存在
os.unlink('python1/test.py') # 删不存在的文件,会报错,经常先用os.path.exists判断是否存在
五、修改目录和文件

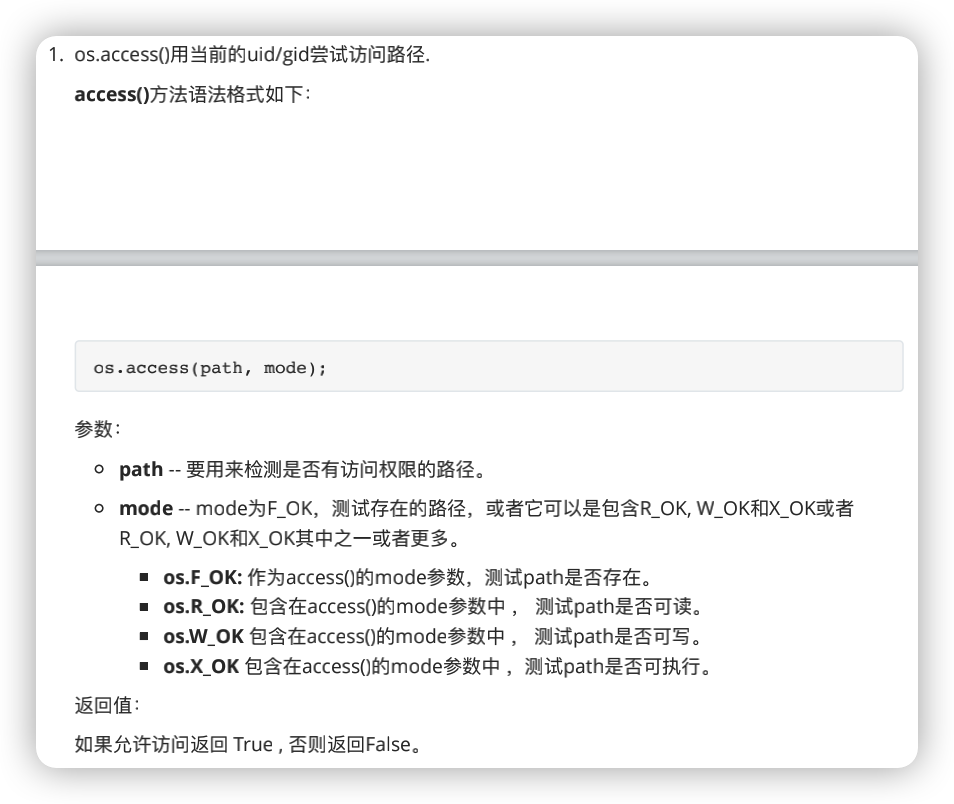

os.mkdir('log.txt',mode=0o755)
print(oct(os.stat('log.txt').st_mode))
print(os.access('log.txt',os.X_OK))
os.chmod('log.txt',0o777) # stat.S_I
print(oct(os.stat('log.txt').st_mode))
print(os.stat('log.txt'))
os.chown('log.txt',uid=2000,gid=2000)
os.rename('log','python1/log')
print(os.getcwd())
os.chdir('python1/log')
print(os.getcwd())
























 6万+
6万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










