文件IO/系统调用IO
文件IO操作
open( )、close( )、read( )、write( )、lseek( )
标准IO中的文件操作都是依赖于文件IO
文件描述符(fd)
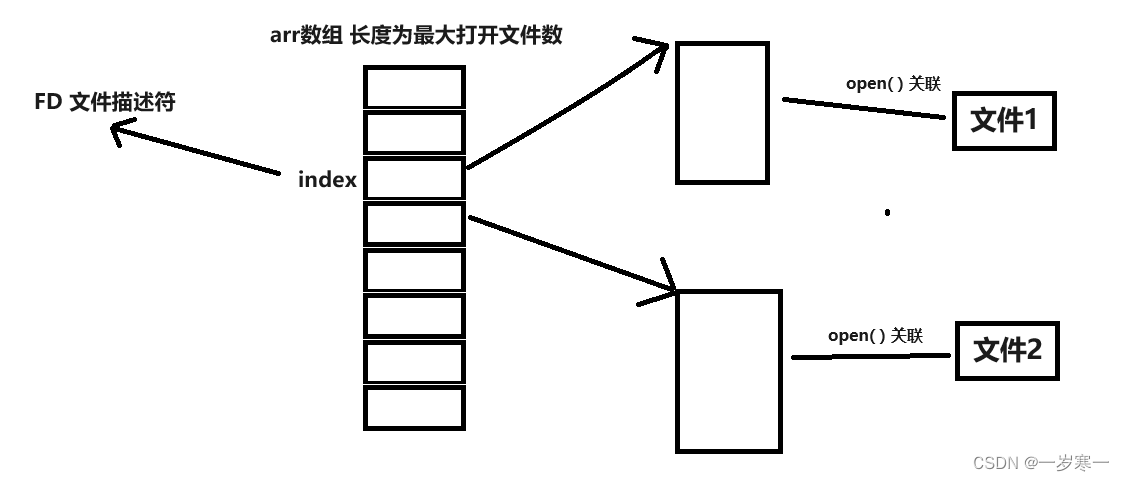
- fd本质是一个整型数,表示数组的下标
- 优先使用当前可用范围内最小的
open
函数原型:
int open(const char* pathname,int flags);
int open(const char* pathname,int flags,mode_t mode);变参实现,并非重载实现 open() 变参函数
close
函数原型:
int close(int fd);
read/write
函数原型:
ssize_t read(int fd,void* buf,size_t count);
ssize_t write(int fd,const void* buf,size_t count);
lseek
函数原型:
off_t lseek(int fd,off_t offest,int whence);
实现mycopy
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define BUFSIZE 1024
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int sfd,dfd;
int ch,len,ret,pos = 0;
char buf[BUFSIZE];
if (argc < 3)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Usage : %s <source_filename> <dest_filename>\n",argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
sfd = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
if (sfd < 0)
{
perror("open()");
exit(1);
}
dfd = open(argv[2],O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0600);
if (dfd < 0)
{
close(sfd);
perror("open()");
exit(1);
}
while (1)
{
/*len read 10 byte*/
len = read(sfd,buf,BUFSIZE);
if (len<0)
{
perror("read()");
break;
}
if (len == 0)
{
break;
}
pos = 0;
/*判断len是否全部填入*/
while (len > 0)
{
/*from buf read len byte to dfd*/
ret = write(dfd,buf+pos,len);
if (ret < 0 )
{
perror("write()");
exit(1);
}
/*计算下一个写入的位置*/
pos += ret;
/*计算剩下的没填入的字节数*/
len -= ret;
}
}
close(dfd);
close(sfd);
exit(0);
}
文件IO和标准IO
标准IO有缓冲机制,吞吐量大
文件IO无缓冲机制,响应速度快,实时效率高
标准IO与文件IO不可混用
int fileno(FILE* stream); 通过标准IO --> 文件IO
FILE* fdopen(int fd,const char* mode); 通过文件IO --> 标准IO
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main(){
putchar('a');
write(1,"b",1);
putchar('a');
write(1,"b",1);
putchar('a');
write(1,"b",1);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main(){
putchar('a');
write(1,"b",1);
putchar('a');
write(1,"b",1);
putchar('a');
write(1,"b",1);
return 0;
}
输出结果为: bbbaaa
文件共享
多个任务共同操作一个文件或者协同完成任务
删除一个文件的第10行
思路:
- 方法一:一个文件在一个进程中以不同的方式打开两次进行操作
- 方法二:两个线程或进程以不同的方式打开同一个文件进行操作
原子操作/文件重定向
原子操作
不可分割的操作,用于解决竞争和冲突
文件重定向
dup、dup2
函数原型:
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd,int newfd);
同步操作
sync
函数原型:
void sync(void);
fsync/fdatasync
函数原型:
int fsync(int fd);
int fdatasync(int fd);
其它操作
fcntl
函数原型:
int fcntl(int fd,int cmd, ..../*arg*/);
作用:
针对文件描述符进行一些列操作
ioctl
函数原型:
int ioctl(int d,int request, ....);
作用:
设备相关内容的操作
/dev/fd/ 目录
是一个虚目录,显示的是当前进程的文件描述符信息






















 2031
2031











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








