#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Stack
{
private:
int len;
int count = 0;
int *stack;
public:
Stack():len(10) //无参构造
{
stack = new int[len];
stack[len] = {0};
}
Stack(int len):len(len) //有参构造
{
stack = new int[len];
stack[len] = {0};
}
Stack(Stack &other):len(other.len) //拷贝构造函数
{
stack = new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
stack[i] = other.stack[i];
}
}
Stack &operator=(const Stack &other) //拷贝赋值函数
{
if(this != &other)
{
this->count = other.count;
this->len = other.len;
int *newstack = new int[this->len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
newstack[i] = other.stack[i];
}
delete [] stack;
stack = newstack;
}
return *this;
}
~Stack() //析构函数
{
delete [] stack;
}
int top();
bool empty();
int size();
int push(int n);
void expand();
void show();
int pop();
};
int Stack::top()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"error" <<endl;
return -1;
}
return stack[count-1];
}
bool Stack::empty()
{
return count == 0;
}
int Stack::size()
{
return count;
}
int Stack::push(int n)
{
if(count == len)
{
expand();
}
stack[count++] = n;
return 0;
}
void Stack::expand()
{
len = len * 2;
int *newstack = new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
newstack[i] = stack[i];
}
delete [] stack;
stack = newstack;
}
void Stack::show()
{
for(int i=count-1;i>=0;i--)
{
cout<<stack[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int Stack::pop()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"error"<<endl;
return -1;
}
stack[--count] = 0;
return 0;
}
class Queue
{
private:
int len;
int count = 0;
int *queue;
public:
Queue():len(10)
{
queue = new int[len];
queue[len] = {0};
};
Queue(int n):len(n)
{
queue = new int[len];
queue[len] = {0};
};
Queue(Queue &other):len(other.len)
{
queue = new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
queue[i] = other.queue[i];
}
};
Queue &operator=(const Queue &other) //拷贝赋值函数
{
if(this != &other)
{
this->count = other.count;
this->len = other.len;
int *newqueue = new int[this->len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
newqueue[i] = other.queue[i];
}
delete [] queue;
queue = newqueue;
}
return *this;
}
~Queue()
{
delete []queue;
};
int front();
int back();
bool empty();
int size();
int push(int n);
void pop();
void expand();
void show();
};
int Queue::front()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"error"<<endl;
return -1;
}
return queue[count-1];
}
int Queue::back()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"error"<<endl;
return -1;
}
return queue[0];
}
bool Queue::empty()
{
return count == 0;
}
int Queue::size()
{
return count;
}
int Queue::push(int n)
{
if(count == len)
{
expand();
}
queue[count++] = n;
return 0;
}
void Queue::pop()
{
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
queue[i] = queue[i+1];
}
count--;
}
void Queue::expand()
{
len = len * 2;
int *newqueue = new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
newqueue[i] = queue[i];
}
delete [] queue;
queue = newqueue;
}
void Queue::show()
{
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
cout<<queue[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
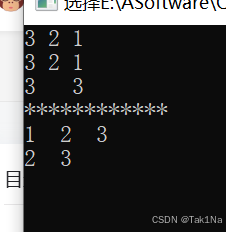
Stack s1(3);
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(3);
s1.pop();
Stack s2;
s2 = s1;
s1.show();
s2.show();
cout<<s2.top()<<" "<<s2.size()<<endl;
cout<<"************"<<endl;
Queue q1(3);
q1.push(1);
q1.push(2);
q1.push(3);
q1.show();
q1.pop();
q1.show();
return 0;
}






















 1076
1076

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








