本文分析一下Reactor模式的实现,关键是三个类:Channel、Poller、EventLoop。
事件分发类 Channel
Channel 是 selectable IO channel,负责注册与响应IO事件,包括注册给Poller的 fd 及其监听的事件,以及事件发生了所调的回调函数。
每个Channel对象自始至终只负责一个 fd 的事件分发,封装了一系列该 fd 对应的操作,使用了回调函数,包括可读、可写、关闭和错误处理四个。
首先给定Channel所属的 loop,及其要处理的 fd;接着注册 fd 上需要监听的事件,如果是常用的读写事件的话,可以直接调用接口函数enableReading或enableWriting来注册对应fd上的事件,disable*是销毁指定的事件;然后通过 set*Callback 来设置事件发生时的回调。
注册事件时函数调用关系,如下:Channel::update()->EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel*)->Poller::updateChannel(Channel*),最终向 poll 系统调用的监听事件表注册或修改事件。
Channel.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H
#define MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H
#include <boost/function.hpp>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/weak_ptr.hpp>
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
class EventLoop;
///
/// A selectable I/O channel.
///
/// This class doesn't own the file descriptor.
/// The file descriptor could be a socket,
/// an eventfd, a timerfd, or a signalfd
/* 事件分发类,主要包括 fd fd监听的事件、事件回调函数 */
class Channel : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
/* 事件回调函数模板 */
typedef boost::function<void()> EventCallback;
/* 读操作回调函数,需要传入时间 */
typedef boost::function<void(Timestamp)> ReadEventCallback;
/*
* 一个Channel只负责一个fd,但Channel不拥有fd
* EventLoop调用Poller监听事件集合,就绪的事件元素就是Channel
* Channel不仅是返回就绪事件,还可以处理事件
*/
Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd);
~Channel();
/*
* Channel的核心
* 处理事件,一般由Poller通过EventLoop来调用
* 当fd对应的事件就绪后Channel::handleEvent()执行相应的事件回调
* 如可读事件执行 readCallback_()
*/
void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);
/* 设置四种回调函数 */
void setReadCallback(const ReadEventCallback& cb)
{ readCallback_ = cb; }
void setWriteCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ writeCallback_ = cb; }
void setCloseCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ closeCallback_ = cb; }
void setErrorCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ errorCallback_ = cb; }
#ifdef __GXX_EXPERIMENTAL_CXX0X__
/* C++11版本 右值语义 */
void setReadCallback(ReadEventCallback&& cb)
{ readCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
void setWriteCallback(EventCallback&& cb)
{ writeCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
void setCloseCallback(EventCallback&& cb)
{ closeCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
void setErrorCallback(EventCallback&& cb)
{ errorCallback_ = std::move(cb); }
#endif
/// Tie this channel to the owner object managed by shared_ptr,
/// prevent the owner object being destroyed in handleEvent.
void tie(const boost::shared_ptr<void>&);
/* 返回该Channel负责的fd*/
int fd() const { return fd_; }
/* 返回 fd 注册的事件 */
int events() const { return events_; }
/*
* 进行poll或者epoll_wait后,根据fd的返回事件调用此函数,设定fd的就绪事件类型
* handleEvent 根据就绪事件类型(revents_)来决定执行哪个事件回调函数
*/
void set_revents(int revt) { revents_ = revt; } // used by pollers
// int revents() const { return revents_; }
/* 判断fd是不是 没有 事件监听 */
bool isNoneEvent() const { return events_ == kNoneEvent; }
/* update 通过eventloop 去更新epoll中fd的监听事件 */
/* fd 注册可读事件 */
void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }
/* 销毁读事件 */
void disableReading() { events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update(); }
/* fd 注册可写事件 */
void enableWriting() { events_ |= kWriteEvent; update(); }
/* 销毁写事件 */
void disableWriting() { events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update(); }
/* 停止监听所有事件 */
void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); }
/* 是否注册了读写事件 */
bool isWriting() const { return events_ & kWriteEvent; }
bool isReading() const { return events_ & kReadEvent; }
// for Poller
// 还不懂
int index() { return index_; }
void set_index(int idx) { index_ = idx; }
// for debug
string reventsToString() const;
string eventsToString() const;
void doNotLogHup() { logHup_ = false; }
/* 返回持有本Channel的EventLoop 指针 */
EventLoop* ownerLoop() { return loop_; }
/* 将Channel 从EventLoop中移除 */
void remove();
private:
static string eventsToString(int fd, int ev);
/* 通过调用loop_->updateChannel()来注册或改变本fd在epoll中监听的事件 */
void update();
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
static const int kNoneEvent; //无事件
static const int kReadEvent; //可读事件
static const int kWriteEvent; //可写事件
EventLoop* loop_; //本Channel所属的EventLoop
const int fd_; //本Channel负责的文件描述符,Channel不拥有fd
int events_; //fd 注册的事件
int revents_; //通过poll返回的就绪事件类型
int index_; //被Poller使用的下标 used by Poller.
bool logHup_; //是否生成某些日志
boost::weak_ptr<void> tie_;
bool tied_;
bool eventHandling_; //是否正在处理事件
bool addedToLoop_;
/* 四种回调函数,使用boost提供的function模板*/
ReadEventCallback readCallback_; //读事件回调函数
EventCallback writeCallback_; //写事件回调函数
EventCallback closeCallback_; //关闭事件回调函数
EventCallback errorCallback_; //错误事件回调函数
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_HChannel.cc
/* 事件 */
const int Channel::kNoneEvent = 0;
const int Channel::kReadEvent = POLLIN | POLLPRI;
const int Channel::kWriteEvent = POLLOUT;
Channel::Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd__)
: loop_(loop),
fd_(fd__),
events_(0),
revents_(0),
index_(-1),
logHup_(true),
tied_(false),
eventHandling_(false),
addedToLoop_(false)
{
}
Channel::~Channel()
{
assert(!eventHandling_);
assert(!addedToLoop_);
if (loop_->isInLoopThread())
{
assert(!loop_->hasChannel(this));
}
}
/* 通过调用loop中的函数来改变对应fd在epoll中监听的事件 */
void Channel::update()
{
addedToLoop_ = true;
/* loop中又会去调用Poller中的函数来实现 */
loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
/* 和上面类似,通过EventLoop 从epoll/poll 中删除fd*/
void Channel::remove()
{
assert(isNoneEvent());
addedToLoop_ = false;
/* EventLoop 会调用Poller中的函数 */
loop_->removeChannel(this);
}
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
boost::shared_ptr<void> guard;
if (tied_)
{
guard = tie_.lock();
if (guard)
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
else
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
/* 处理各种事件 */
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
eventHandling_ = true;
LOG_TRACE << reventsToString();
if ((revents_ & POLLHUP) && !(revents_ & POLLIN))
{
if (logHup_)
{
LOG_WARN << "fd = " << fd_ << " Channel::handle_event() POLLHUP";
}
if (closeCallback_) closeCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & POLLNVAL)
{
LOG_WARN << "fd = " << fd_ << " Channel::handle_event() POLLNVAL";
}
if (revents_ & (POLLERR | POLLNVAL)) //错误事件处理
{
if (errorCallback_) errorCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & (POLLIN | POLLPRI | POLLRDHUP)) //可读
{
if (readCallback_) readCallback_(receiveTime);
}
if (revents_ & POLLOUT) //可写
{
if (writeCallback_) writeCallback_();
}
eventHandling_ = false;
}IO multiplexing 类 Poller
Poller 类是IO复用类的基类,muduo 同时支持poll 和 epoll 两种IO multiplexing 机制,它有两个PollPoller 和 EpollPoller 两个子类,内部分别采用 poll 和 epoll 实现。它的职责仅仅是IO复用,事件分发交给 Channel 完成,生命期和 EventLoop 一样长。
拿 epoll 对 Poller 的实现来说,基本是 epoll 功能的封装,poll 函数调用 epoll_wait 来监听注册了的文件描述符,将返回的就绪事件装入 activeChannels 数组,还可以控制 channel 中事件的增删改。
Poller.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_POLLER_H
#define MUDUO_NET_POLLER_H
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
class Channel;
///
/// Base class for IO Multiplexing
///
/// This class doesn't own the Channel objects.
class Poller : boost::noncopyable //不拥有Channel
{
public:
typedef std::vector<Channel*> ChannelList;
/* 用于返回就绪事件集合 */
Poller(EventLoop* loop);
virtual ~Poller();
/// Polls the I/O events.
/// Must be called in the loop thread.
/* Poller的核心功能,将就绪事件加入到 activeChannels 中 */
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels) = 0;
/// Changes the interested I/O events.
/// Must be called in the loop thread.
/* 更新 fd 的监听事件
* Channel::update()->EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel* channel)->Poller::updateChannel(Channel* channel)
*/
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
/// Remove the channel, when it destructs.
/// Must be called in the loop thread.
/* 从poll/epoll 中移除fd 停止监听此fd
* EventLoop::removeChannel(Channel*)->Poller::removeChannel(Channel*)
*/
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
/* 判断该poll//epoll 模型是否监听了Channel对应的fd */
virtual bool hasChannel(Channel* channel) const;
/* */
static Poller* newDefaultPoller(EventLoop* loop);
/* 断言 确保没有跨线程 */
void assertInLoopThread() const
{
ownerLoop_->assertInLoopThread();
}
protected:
/*
* 记录fd到Channel的对应关系
* 底层的epoll每次监听完fd,要根据这个映射关系去寻找对应的Channel
*/
typedef std::map<int, Channel*> ChannelMap;
ChannelMap channels_;//保存epoll监听的fd,及其对应的Channel指针
private:
/* 这个Poller对象所属的 EventLoop */
EventLoop* ownerLoop_;
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_POLLER_Hepoll对Poller的实现 :poller/EPollPoller.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_POLLER_EPOLLPOLLER_H
#define MUDUO_NET_POLLER_EPOLLPOLLER_H
#include <muduo/net/Poller.h>
#include <vector>
struct epoll_event;
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
///
/// IO Multiplexing with epoll(4).
///
class EPollPoller : public Poller
{
public:
EPollPoller(EventLoop* loop);
virtual ~EPollPoller();
/* 内部调用 epoll_wait,初始化对应的channel,加入到activeChannels */
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels);
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel);
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel);
private:
static const int kInitEventListSize = 16;
static const char* operationToString(int op);
/* 将epoll_wait 返回的活跃事件填充到activeChannels */
void fillActiveChannels(int numEvents,
ChannelList* activeChannels) const;
/* 更改 channel ,调用epoll_ctl */
void update(int operation, Channel* channel);
typedef std::vector<struct epoll_event> EventList;
int epollfd_; //epollfd
EventList events_; //epoll事件数组
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_POLLER_EPOLLPOLLER_HEventLoop 类
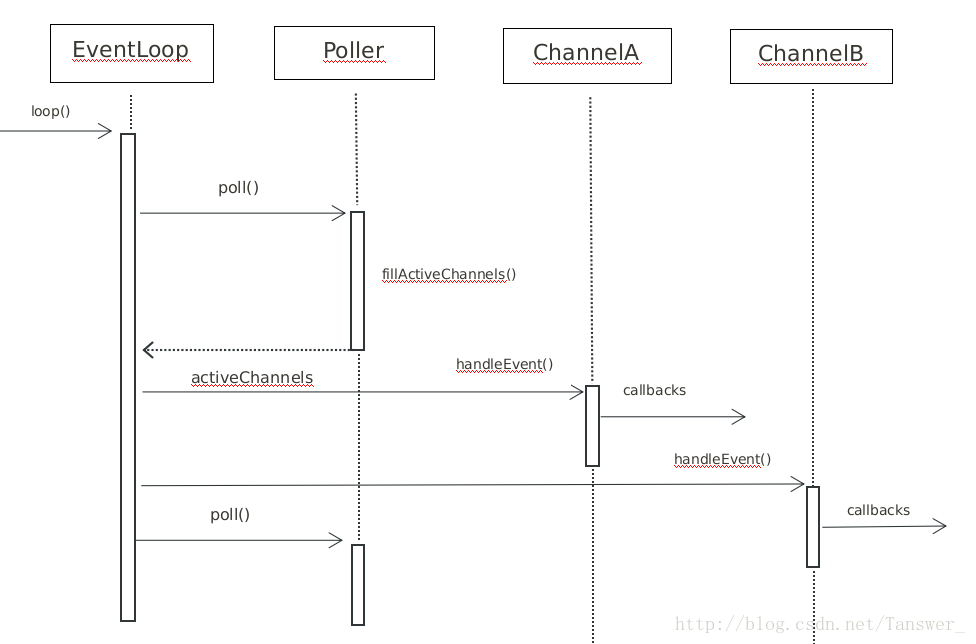
EventLoop类是Reactor模式的核心,一个线程一个事件循环,即one loop per thread,EventLoop 对象的生命周期通常与其所属的线程一样长。其主要功能是运行事件循环,等待事件发生,然后调用回调处理发生的事件。EventLoop::loop() -> Poller::poll() 填充就绪事件集合 activeChannels,然后遍历该容器,执行每个 channel 的 Channel::handleEvent() 完成对应就绪事件回调。
EventLoop.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#define MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#include <vector>
#include <boost/any.hpp>
#include <boost/function.hpp>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <boost/scoped_ptr.hpp>
#include <muduo/base/Mutex.h>
#include <muduo/base/CurrentThread.h>
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h>
#include <muduo/net/Callbacks.h>
#include <muduo/net/TimerId.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
class Channel; //前向声明,事件分发器主要用于事件注册与回调
class Poller; //IO复用类,监听事件集合,即 epoll /poll 的功能
class TimerQueue;
///
/// Reactor, at most one per thread.
///
/// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details.
/* EventLoop 是不可拷贝的 muduo中的大多数class都是不可拷贝的 */
class EventLoop : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef boost::function<void()> Functor; //回调函数
EventLoop();
~EventLoop(); // force out-line dtor, for scoped_ptr members.
///
/// Loops forever.
///
/// Must be called in the same thread as creation of the object.
///
/*
* IO线程创建了EventLoop对象,是这个类的核心接口
* 用来启动事件循环
* EventLoop::loop()->Poller::Poll()获得就绪的事件集合
* 再通过Channel::handleEvent()执行就绪事件回调
*/
void loop();
/// Quits loop.
///
/// This is not 100% thread safe, if you call through a raw pointer,
/// better to call through shared_ptr<EventLoop> for 100% safety.
//终止事件循环
void quit();
///
/// Time when poll returns, usually means data arrival.
///
Timestamp pollReturnTime() const { return pollReturnTime_; }
int64_t iteration() const { return iteration_; }
void runInLoop(const Functor& cb);
void queueInLoop(const Functor& cb);
size_t queueSize() const;
#ifdef __GXX_EXPERIMENTAL_CXX0X__
void runInLoop(Functor&& cb);
void queueInLoop(Functor&& cb);
#endif
// timers
//在某个绝对时间点执行定时回调
TimerId runAt(const Timestamp& time, const TimerCallback& cb);
///
///
//相对时间 执行定时回调
TimerId runAfter(double delay, const TimerCallback& cb);
///
//每隔interval执行定时回调
TimerId runEvery(double interval, const TimerCallback& cb);
///
///
//删除某个定时器
void cancel(TimerId timerId);
#ifdef __GXX_EXPERIMENTAL_CXX0X__
TimerId runAt(const Timestamp& time, TimerCallback&& cb);
TimerId runAfter(double delay, TimerCallback&& cb);
TimerId runEvery(double interval, TimerCallback&& cb);
#endif
// internal usage
// 唤醒IO线程
void wakeup();
// 更新某个事件分发器
// 调用poller->updateChannel(channel)完成 fd 向事件集合注册事件及事件回调函数
void updateChannel(Channel* channel);
// 删除某个事件分发器
void removeChannel(Channel* channel);
bool hasChannel(Channel* channel);
// pid_t threadId() const { return threadId_; }
void assertInLoopThread()
{
if (!isInLoopThread()) //若运行线程不拥有EventLoop则退出,保证one loop per thread
{
abortNotInLoopThread();
}
}
/* 判断当前线程是否为拥有此 EventLoop 的线程 */
bool isInLoopThread() const { return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); }
// bool callingPendingFunctors() const { return callingPendingFunctors_; }
bool eventHandling() const { return eventHandling_; }
void setContext(const boost::any& context)
{ context_ = context; }
const boost::any& getContext() const
{ return context_; }
boost::any* getMutableContext()
{ return &context_; }
/* 返回此线程的EventLoop对象 */
static EventLoop* getEventLoopOfCurrentThread();
private:
/* 在不拥有EventLoop 线程中终止 */
void abortNotInLoopThread();
/* wakeupFd_ 上可读事件回调 */
void handleRead(); // waked up
/* 执行队列pendingFunctors 中的用户任务回调 */
void doPendingFunctors();
void printActiveChannels() const; // DEBUG
typedef std::vector<Channel*> ChannelList;
bool looping_; /* atomic */ //运行标志
bool quit_; /* atomic and shared between threads, okay on x86, I guess. */ //退出循环标志
bool eventHandling_; /* atomic */
bool callingPendingFunctors_; /* atomic *///是否正在执行用户任务回调
int64_t iteration_;
const pid_t threadId_; //EventLoop 的附属线程ID
Timestamp pollReturnTime_;
boost::scoped_ptr<Poller> poller_; //多路复用类Poller
boost::scoped_ptr<TimerQueue> timerQueue_;//定时器队列用于存放定时器
int wakeupFd_; //eventfd返回的eventfd,用于唤醒EventLoop所在的线程
// unlike in TimerQueue, which is an internal class,
// we don't expose Channel to client.
// 通过wakeupChannel_观察wakeupFd_上的可读事件
// 当可读表明需要唤醒EventLoop所在线程执行用户回调
boost::scoped_ptr<Channel> wakeupChannel_;
boost::any context_;
// scratch variables
ChannelList activeChannels_; //活跃的事件集合,类似epoll的就绪事件集合
Channel* currentActiveChannel_; //当前活跃的事件
mutable MutexLock mutex_;
std::vector<Functor> pendingFunctors_; // @GuardedBy mutex_ //存放用户任务回调
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H下面主要看一下 loop() 和 quit() 的实现:
/* 主循环,监听事件集合,执行就绪事件的处理函数 */
void EventLoop::loop()
{
assert(!looping_);
assertInLoopThread();
looping_ = true;
quit_ = false; // FIXME: what if someone calls quit() before loop() ?
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " start looping";
while (!quit_)
{
activeChannels_.clear();
/* activeChannels_ 为就绪事件集合 */
pollReturnTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_);
++iteration_;
if (Logger::logLevel() <= Logger::TRACE)
{
printActiveChannels();
}
// TODO sort channel by priority
eventHandling_ = true;
for (ChannelList::iterator it = activeChannels_.begin();
it != activeChannels_.end(); ++it)
{
currentActiveChannel_ = *it; //取一个就绪事件
currentActiveChannel_->handleEvent(pollReturnTime_); //执行相应事件回调
}
currentActiveChannel_ = NULL;
eventHandling_ = false;
doPendingFunctors();
}
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " stop looping";
looping_ = false;
}
void EventLoop::quit()
{
quit_ = true; //设置标志位,有延迟不会马上停止循环,当下次检查while(!quit_)时起效
// There is a chance that loop() just executes while(!quit_) and exits,
// then EventLoop destructs, then we are accessing an invalid object.
// Can be fixed using mutex_ in both places.
if (!isInLoopThread())
{
wakeup(); //其他线程唤醒 EventLoop线程并终止
}
}主要是先了解 Reactor 模式的关键结构,所以上面注释的内容是 muduo 的 Reactor 模式的核心内容,一些细节没有详细说明。流程图如下:
























 939
939











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








