陈硕大神的muduo库设计巧,但是难读懂,这里简单做个总结,注意回调函数太多,需仔细研究回调的传递和调用。两个核心梳理主线:EventLoopThreadPool::start、EventLoop::runInLoop,其次陈硕认为网络编程的本质是处理三个半事件,重点关注之:
-
连接的建立
-
连接的断开:包括主动断开和被动断开
-
消息到达,文件描述符可读
-
消息发送完毕。这个算半个事件
使用
3步:
- 调用构造函数创建
Server对象 Server对象调用start函数- 传给
Server的EventLoop对象调用loop函数
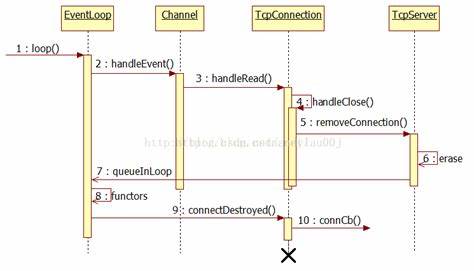
整体逻辑时序图如下:
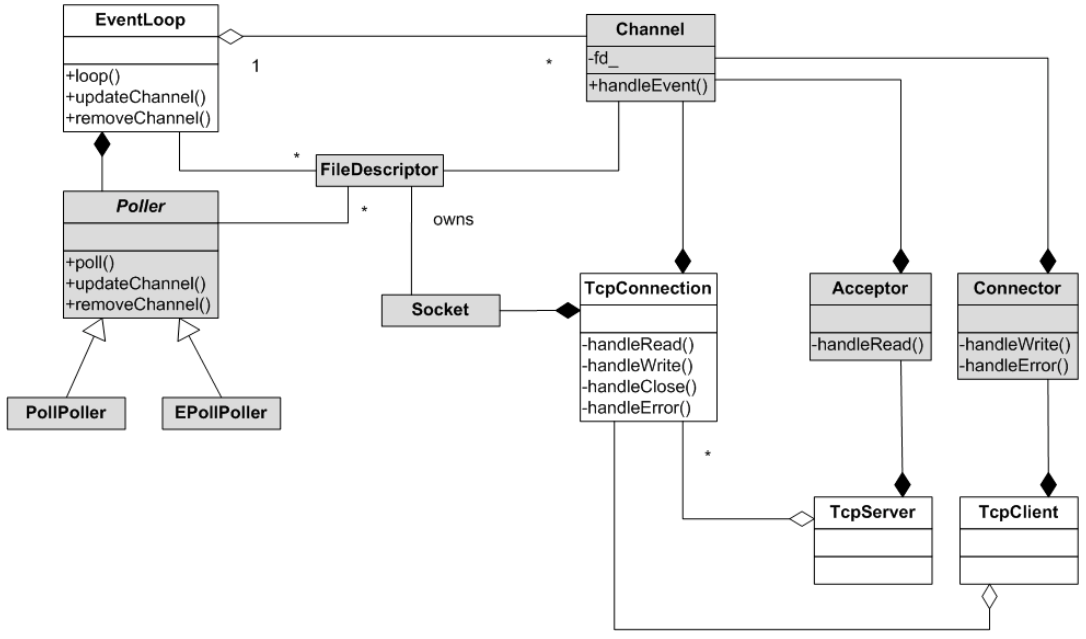
类图如下:
三剑客
channel
封装sockfd和event,还绑定Poller返回的具体事件,因此类中包含sockfd、events、revents成员,Channel通过EventLoop来和Poller交互,因此也包括EventLoop成员。定义如下(省略部分不重要代码):
class Channel : noncopyable
{
public:
using EventCallback = std::function<void()>; // muduo仍使用typedef 两种回调函数
using ReadEventCallback = std::function<void(Timestamp)>;
Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd);
~Channel();
// fd得到Poller通知以后 处理事件 handleEvent在EventLoop::loop()中调用
void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);
......
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
......
EventLoop *loop_; // 事件循环
const int fd_; // fd,Poller监听的对象
int events_; // 注册fd感兴趣的事件
int revents_; // Poller返回的具体发生的事件,传出参数
......
// 4个回调 因为channel通道里可获知fd最终发生的具体的事件events,所以它负责调用具体事件的回调操作
ReadEventCallback readCallback_;
EventCallback writeCallback_;
EventCallback closeCallback_;
EventCallback errorCallback_;
};
如上所述故引申出事件回调和设置事件状态函数,4种事件对应4回调函数,经handleEvent调handleEventWithGuard被调用,判断4种不同事件类型调用不同事件回调函数,设置事件状态函数通过loop调用EPollPoller的Channel操作函数,本质是调用epoll_ctl
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
if (tied_)
{
std::shared_ptr<void> guard = tie_.lock();
if (guard)
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
else
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
//4种事件对应的回调函数
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
LOG_INFO("channel handleEvent revents:%d\n", revents_);
// 关闭
if ((revents_ & EPOLLHUP) && !(revents_ & EPOLLIN))
{
if (closeCallback_)
{
closeCallback_();
}
}
// 错误
if (revents_ & EPOLLERR)
{
if (errorCallback_)
{
errorCallback_();
}
}
// 读
if (revents_ & (EPOLLIN | EPOLLPRI))
{
if (readCallback_)
{
readCallback_(receiveTime);
}
}
// 写
if (revents_ & EPOLLOUT)
{
if (writeCallback_)
{
writeCallback_();
}
}
}
Poller和EPollPoller
Poller类是虚基类,提供IO复用统一接口:poll、updateChannel、removeChannel。定义ChannelMap和EventLoop类对象
// muduo库中多路事件分发器的核心IO复用模块
class Poller
{
public:
using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel *>;
Poller(EventLoop *loop);
virtual ~Poller() = default;
// 给所有IO复用保留统一的接口
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) = 0;
virtual void updateChannel(Channel *channel) = 0;
virtual void removeChannel(Channel *channel) = 0;
......
protected:
// map的key:sockfd value:sockfd所属的channel通道类型
using ChannelMap = std::unordered_map<int, Channel *>;
ChannelMap channels_;
private:
EventLoop *ownerLoop_; // 定义Poller所属的事件循环EventLoop
};
EPollPoller先重写Poller的接口,定义epollfd和EventList成员,表示监听fd和存放epoll_wait返回的事件的fd集合。
class EPollPoller : public Poller
{
public:
EPollPoller(EventLoop *loop);
~EPollPoller() override;
// 重写基类Poller的抽象方法
Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) override;
void updateChannel(Channel *channel) override;
void removeChannel(Channel *channel) override;
private:
static const int kInitEventListSize = 16;
......
using EventList = std::vector<epoll_event>; // C++中可以省略struct 直接写epoll_event即可
int epollfd_; // 监听fd,epoll_create创建返回的fd保存在epollfd_中
EventList events_; // 用于存放epoll_wait返回的所有发生的事件的文件描述符事件集
};
poll调epoll_wait,将发生事件文件描述符集合写入EventList,并将发生事件的Channel压入ChannelList对象
Timestamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels)
{
int numEvents = ::epoll_wait(epollfd_, &*events_.begin(), static_cast<int>(events_.size()), timeoutMs);
int saveErrno = errno;
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
if (numEvents > 0)
{
fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels);
if (numEvents == events_.size()) // 扩容操作
{
events_.resize(events_.size() * 2);
}
}
else if (numEvents == 0)//timeout
{
}
else
{
if (saveErrno != EINTR)
{
errno = saveErrno;
}
}
return now;
}
// 填写活跃的连接
void EPollPoller::fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < numEvents; ++i)
{
Channel *channel = static_cast<Channel *>(events_[i].data.ptr);
channel->set_revents(events_[i].events);
activeChannels->push_back(channel); // EventLoop就拿到了它的Poller给它返回的所有发生事件的channel列表了
}
}
updateChannel经Channel对象调EventLoop对象成员函数被调用,最终调epoll_ctl
removeChannel类似updateChannel,但会将传入参数channel从ChannelMap成员对象中删除
EventLoop
事件循环可理解为Reactor,一Reactor可处理多sockfd,故一EventLoop对应多Channel,但多Channel不能对应同EventLoop。EventLoop是Channel和Poller的桥梁,因此成员变量包括Channel和Poller对象,及存储上层回调的队列,从而引申出wakeup和handleRead,doPendingFunctors、runInLoop和queueInLoop函数
相关函数时序:
runInLoop->queueInLoop->wakeup->poll->handleRead->doPendingFunctors
主loop收到事件,若不在主线程,则调runInLoop,调用queueInLoop,若再主线程直接调cb,否则将回调给子loop(该回调需子loop执行 但它阻塞在poll处) queueInLoop调wakeup写数据,系统检测到写事件,下次解除epoll_wait的阻塞,完成主从通信。
// 在当前loop中执行cb
void EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor cb)
{
if (isInLoopThread()) // 单Reactor模型 当前EventLoop中执行回调
{
cb();
}
else //多Reactor模型 在非当前EventLoop线程中执行cb,就需要唤醒EventLoop所在线程执行cb
{
queueInLoop(cb);
}
}
queueInLoop将回调添加到队列,同时通过wakeup唤醒poll调用队列内的回调
// 把cb放入队列中 唤醒loop所在的线程执行cb
void EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor cb)
{
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
pendingFunctors_.emplace_back(cb);
}
if (!isInLoopThread() || callingPendingFunctors_)
{
wakeup(); // 唤醒loop所在线程
}
}
wakeup巧妙,构造函数调eventfd创建可用于等待唤醒的eventfd对象wakeupFd_,每当多Reactor模型时(单Reactor模型直接调cb),将上层回调放入队列时,判断是否非当前EventLoop或当前loop正在执行回调,调wakup唤醒loop所在子线程
// 用来唤醒loop所在线程 向wakeupFd_写一个数据 wakeupChannel就发生读事件 当前loop线程就会被唤醒
void EventLoop::wakeup()
{
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = write(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
if (n != sizeof(one))
{
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::wakeup() writes %lu bytes instead of 8\n", n);
}
}
handleRead,当wakeup被调用,则wakeupFd_有写数据,此时该回调被调用,下次epoll_wait则检测到事件解除阻塞
void EventLoop::handleRead()
{
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = read(wakeupFd_, &one, sizeof(one));
if (n != sizeof(one))
{
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::handleRead() reads %lu bytes instead of 8\n", n);
}
}
doPendingFunctors也巧妙,处理挂起事件,先交换后遍历执行 functor,既减少锁的临界区范围又避免死锁(执行functor再临界区时若functor中调用queueInLoop会死锁)
void EventLoop::doPendingFunctors()
{
std::vector<Functor> functors;
callingPendingFunctors_ = true;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
functors.swap(pendingFunctors_); // 交换的方式减少了锁的临界区范围 提升效率 同时避免了死锁 如果执行functor()在临界区内 且functor()中调用queueInLoop()就会产生死锁
}
for (const Functor &functor : functors)
{
functor(); // 执行当前loop需要执行的回调操作
}
callingPendingFunctors_ = false;
}
注意quit中设quit_为true要wakeup,因退出循环时,可能阻塞再epoll_wait处,需被唤醒,并执行完剩余回调,下次再退出循环
/**
* 1. 如果loop在自己的线程中调用quit成功了 说明当前线程已经执行完毕了loop()函数的poller_->poll并退出
* 2. 如果不是当前EventLoop所属线程中调用quit退出EventLoop 需要唤醒EventLoop所属线程的epoll_wait
*
* 比如在一个subloop(worker)中调用mainloop(IO)的quit时 需要唤醒mainloop(IO)的poller_->poll 让其执行完loop()函数
*
* !!! 注意: 正常情况下 mainloop负责请求连接 将回调写入subloop中 通过生产者消费者模型即可实现线程安全的队列
* !!! 但是muduo通过wakeup()机制 使用eventfd创建的wakeupFd_ notify 使得mainloop和subloop之间能够进行通信
**/
void EventLoop::quit()
{
quit_ = true;
if (!isInLoopThread())
{
wakeup();
}
}
线程类
Thread
线程类,核心函数start,信号量同步并调设置的EventLoopThread::threadFunc回调(见下)
void Thread::start()
{
started_ = true;
sem_t sem;
sem_init(&sem, false, 0); // false指的是 不设置进程间共享
// 开启线程
thread_ = std::shared_ptr<std::thread>(new std::thread([&]() {
tid_ = CurrentThread::tid(); // 获取线程的tid值
sem_post(&sem);
func_(); // 开启一个新线程 专门执行该线程函数
}));
// 这里必须等待获取上面新创建的线程的tid值
sem_wait(&sem);
}
EventLoopThread
EventLoop和Thread的结合,因而有EventLoop、Thread的成员变量,也包括线程同步的互斥锁和条件变量
class EventLoopThread : noncopyable
{
public:
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop *)>;
EventLoopThread(const ThreadInitCallback &cb = ThreadInitCallback(),
const std::string &name = std::string());
~EventLoopThread();
EventLoop *startLoop();
private:
void threadFunc();
EventLoop *loop_;
bool exiting_;
Thread thread_;
std::mutex mutex_; // 互斥锁
std::condition_variable cond_; // 条件变量
};
核心是startLoop和threadFunc,前者再EventLoopThreadPool::start中被创建EventLoopThread对象,并调用startLoop,启动线程并生成EventLoop对象
EventLoop *EventLoopThread::startLoop()
{
thread_.start(); // 启用底层线程Thread类对象thread_中通过start()创建的线程
EventLoop *loop = nullptr;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
while(loop_ == nullptr)
{
cond_.wait(lock);
}
loop = loop_;
}
return loop;
}
后者会创建EventLoop,one loop per thread将给loop地址赋值给成员变量,并唤醒阻塞再startLoop中的循环,执行loop
// 下面这个方法 是在单独的新线程里运行的
void EventLoopThread::threadFunc()
{
EventLoop loop; // 创建一个独立的EventLoop对象 和上面的线程是一一对应的 级one loop per thread
if (callback_)
{
callback_(&loop);//若设置初始化线程的回调则执行
}
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
loop_ = &loop;
cond_.notify_one();
}
loop.loop(); // 执行EventLoop的loop() 开启了底层的Poller的poll()
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
loop_ = nullptr;
}
EventLoopThreadPool
包含EventLoop和EventLoopThread的成员,核心是start,创建线程池,startLoop中调thread的start,并调用构造时传入的threadFunc,阻塞直到创建一个新EventLoop并解除阻塞
void EventLoopThreadPool::start(const ThreadInitCallback &cb)
{
started_ = true;
for(int i = 0; i < numThreads_; ++i)
{
char buf[name_.size() + 32];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "%s%d", name_.c_str(), i);
EventLoopThread *t = new EventLoopThread(cb, buf);
threads_.push_back(std::unique_ptr<EventLoopThread>(t));//创建指定数量线程池,
loops_.push_back(t->startLoop()); // 底层创建线程 绑定一个新的EventLoop 并返回该loop的地址
}
if(numThreads_ == 0 && cb) // 整个服务端只有一个线程运行baseLoop直接调用回调
{
cb(baseLoop_);
}
}
Acceptor
包含EventLoop、Socket和Channel成员对象,handleRead监听套接字的可读事件,有新连接时回调设置的newConnection
// listenfd有事件发生了,就是有新用户连接了
void Acceptor::handleRead()
{
InetAddress peerAddr;
int connfd = acceptSocket_.accept(&peerAddr);
if (connfd >= 0)
{
if (NewConnectionCallback_)//实际调用设置的newConnection回调
{ //会被设置为newConnection
NewConnectionCallback_(connfd, peerAddr); // 轮询找到subLoop 唤醒并分发当前的新客户端的Channel
}
else
{
::close(connfd);
}
}
else
{
if (errno == EMFILE)//sockfd reached limit
{
}
}
}
TCP
TcpConnection
主要有Socket和Channel、EventLoop成员对象,因此也就有4种注册到Channel及5种上层回调函数,以及EventLoop相关函数
class TcpConnection : noncopyable, public std::enable_shared_from_this<TcpConnection>
{
public:
TcpConnection(EventLoop *loop,
const std::string &nameArg,
int sockfd,//accept返回的已连接的文件描述符
const InetAddress &localAddr,
const InetAddress &peerAddr);
~TcpConnection();
void handleRead(Timestamp receiveTime);
void handleWrite();
void handleClose();
void handleError();
void sendInLoop(const void *data, size_t len);
EventLoop *loop_; // TcpServer中创建的线程数决定,若为多Reactor 指向subloop 若为单Reactor指向baseloop
// Socket Channel 这里和Acceptor类似 Acceptor => mainloop TcpConnection => subloop
std::unique_ptr<Socket> socket_;
std::unique_ptr<Channel> channel_;
// 这些回调TcpServer也有 用户通过写入TcpServer注册 TcpServer再将注册的回调传递给TcpConnection TcpConnection再将回调注册到Channel中
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; // 有新连接时的回调
MessageCallback messageCallback_; // 有读写消息时的回调
WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 消息发送完成以后的回调
HighWaterMarkCallback highWaterMarkCallback_;
CloseCallback closeCallback_;
};
5种设置上层回调的回调函数,实际就是注册给eventLoop中的doPendingFunctors处理的上层回调函数。4种回调是注册给到Channel中的handleEvent处理channel对应的sockfd的读、写、关闭、错误4种回调
// 读是相对服务器而言的 当对端客户端有数据到达 服务器端检测到EPOLLIN 就会触发该fd上的回调 handleRead取读走对端发来的数据
void TcpConnection::handleRead(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
int savedErrno = 0;
ssize_t n = inputBuffer_.readFd(channel_->fd(), &savedErrno);
if (n > 0) // 有数据到达
{
// 已建立连接的用户有可读事件发生了 调用用户传入的回调操作onMessage
messageCallback_(shared_from_this(), &inputBuffer_, receiveTime);
}
else if (n == 0) // 客户端断开
{
handleClose();
}
else // 出错了
{
errno = savedErrno;
handleError();
}
}
void TcpConnection::handleWrite()
{
if (channel_->isWriting())
{
int savedErrno = 0;
ssize_t n = outputBuffer_.writeFd(channel_->fd(), &savedErrno);//即使一次没写完,也会下次触发写
if (n > 0)
{
outputBuffer_.retrieve(n);
if (outputBuffer_.readableBytes() == 0)
{
channel_->disableWriting();
if (writeCompleteCallback_)
{
// TcpConnection对象在其所在的subloop中 向pendingFunctors_中加入回调
loop_->queueInLoop(
std::bind(writeCompleteCallback_, shared_from_this()));
}
if (state_ == kDisconnecting)
{
shutdownInLoop(); // 在当前所属的loop中把TcpConnection删除掉
}
}
}
else
{
}
}
else
{
LOG_ERROR("TcpConnection fd=%d is down, no more writing", channel_->fd());
}
}
void TcpConnection::handleClose()
{
setState(kDisconnected);
channel_->disableAll();
TcpConnectionPtr connPtr(shared_from_this());
connectionCallback_(connPtr); // 执行连接关闭的回调
closeCallback_(connPtr); // 执行关闭连接的回调 执行的是TcpServer::removeConnection回调方法
}
void TcpConnection::handleError()
{
int optval;
socklen_t optlen = sizeof optval;
int err = 0;
if (::getsockopt(channel_->fd(), SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &optval, &optlen) < 0)
{
err = errno;
}
else
{
err = optval;
}
LOG_ERROR("TcpConnection::handleError name:%s - SO_ERROR:%d\n", name_.c_str(), err);
}
sendInLoop是核心,若Channel第一次开始写数据或者缓冲区没有待发送数据,就写数据,若未出错且还剩余,就调用queueInLoop唤醒loop所在的线程执行handleWrite回调
void TcpConnection::sendInLoop(const void *data, size_t len)
{
ssize_t nwrote = 0;
size_t remaining = len;
bool faultError = false;
if (state_ == kDisconnected) // 之前调用过该connection的shutdown 不能再进行发送了
{
LOG_ERROR("disconnected, give up writing");
}
// 表示channel_第一次开始写数据或者缓冲区没有待发送数据
if (!channel_->isWriting() && outputBuffer_.readableBytes() == 0)
{
nwrote = ::write(channel_->fd(), data, len);
if (nwrote >= 0)
{
remaining = len - nwrote;
if (remaining == 0 && writeCompleteCallback_)
{
// 既然在这里数据全部发送完成,就不用再给channel设置epollout事件了
loop_->queueInLoop(
std::bind(writeCompleteCallback_, shared_from_this()));
}
}
else // nwrote < 0
{
nwrote = 0;
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK) // EWOULDBLOCK表示非阻塞情况下没有数据后的正常返回 等同于EAGAIN
{
LOG_ERROR("TcpConnection::sendInLoop");
if (errno == EPIPE || errno == ECONNRESET) // SIGPIPE RESET
{
faultError = true;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 说明当前这一次write并没有把数据全部发送出去 剩余的数据需要保存到缓冲区当中,触发写事件
**/
if (!faultError && remaining > 0)
{
// 目前发送缓冲区剩余的待发送的数据的长度
size_t oldLen = outputBuffer_.readableBytes();
if (oldLen + remaining >= highWaterMark_ && oldLen < highWaterMark_ && highWaterMarkCallback_)
{
loop_->queueInLoop(
std::bind(highWaterMarkCallback_, shared_from_this(), oldLen + remaining));
}
outputBuffer_.append((char *)data + nwrote, remaining);
if (!channel_->isWriting())
{
channel_->enableWriting(); // 这里一定要注册channel的写事件 否则poller不会给channel通知epollout
}
}
}
TcpServer
构造函数初始化主loop、ip端口、线程名、接收器、线程池、上层回调函数
// 对外的服务器编程使用的类
class TcpServer
{
public:
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop *)>;
TcpServer(EventLoop *loop,
const InetAddress &listenAddr,
const std::string &nameArg,
Option option = kNoReusePort);
~TcpServer();
// 开启服务器监听
void start();
private:
using ConnectionMap = std::unordered_map<std::string, TcpConnectionPtr>;
EventLoop *loop_; // baseloop 用户自定义的loop
const std::string ipPort_;
const std::string name_;
std::unique_ptr<Acceptor> acceptor_; // 运行在mainloop 任务就是监听新连接事件
std::shared_ptr<EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool_; // one loop per thread
//上层回调
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; //有新连接时的回调
MessageCallback messageCallback_; // 有读写事件发生时的回调
WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 消息发送完成后的回调
ThreadInitCallback threadInitCallback_; // loop线程初始化的回调
ConnectionMap connections_; // 保存所有的连接
};
当有新用户连接时,Acceptor类中绑定的acceptChannel有读事件发生,执行handleRead调用TcpServer.newConnection回调,负责将mainLoop接收到的请求连接通过回调轮询分发给subLoop去处理,上层回调会被传给TcpConnection对象
// 有新连接,acceptor会执行,负责将mainLoop接收到的请求连接通过回调轮询分发给subLoop去处理
void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress &peerAddr)
{
// 轮询算法 选择一个subLoop 来管理connfd对应的channel
EventLoop *ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
char buf[64] = {0};
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_; // 这里没有设置为原子类是因为其只在mainloop中执行 不涉及线程安全问题
std::string connName = name_ + buf;
// 通过sockfd获取其绑定的本机的ip地址和端口信息
sockaddr_in local;
::memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(local);
if(::getsockname(sockfd, (sockaddr *)&local, &addrlen) < 0)
{
LOG_ERROR("sockets::getLocalAddr");
}
InetAddress localAddr(local);
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop,connName,sockfd,localAddr,peerAddr));
connections_[connName] = conn;
// 下面的回调都是用户设置给TcpServer => TcpConnection的,至于Channel绑定的则是TcpConnection设置的四个,handleRead,handleWrite... 这下面的回调用于handlexxx函数中
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);
// 设置了如何关闭连接的回调
conn->setCloseCallback(
std::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
ioLoop->runInLoop(
std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}
核心是start,实际调用EventLoopThreadPool的start,函数中构造EventLoopThread对象,并在其构造函数绑定threadFunc,接着执行主loop的runInLoop函数
// 开启服务器监听
void TcpServer::start()
{
if (started_++ == 0) // 防止一个TcpServer对象被start多次
{
threadPool_->start(threadInitCallback_); // 启动底层的loop线程池
loop_->runInLoop(std::bind(&Acceptor::listen, acceptor_.get()));//主loop的runInLoop
}
}
补充
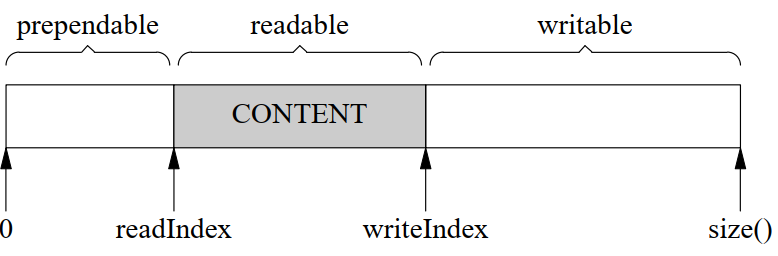
buffer类,使用readindex和writeindex记录读和写的位置,将缓存分成三部分,读开辟两块缓冲区,放不下则放入栈空间(尽快将内核数据挪到inputbuffer);enable_shared_from_this帮助在类内拿到this的shared_ptr指针
























 2835
2835











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








