PyTorch提供了大量的对Tensor进行操作的函数或方法
这些函数内部使用指针实现对矩阵的形状变化、拼接和拆分等操作
1、Tensor.nelement
Tensor.nelement用来查看矩阵元素的个数
例:

输出为:

2、Tensor.ndimension
Tensor.ndimension用来查看矩阵元素的轴的个数
例:

输出为:

3、ndimension.size
ndimension.size用来查看矩阵元素的维度
属性Tensor.shape也可以用来查看Tensor的维度
例:

输出为:

4、Tensor.view和Tensor.reshape
PyTorch中,Tensor.view和Tensor.reshape都能被用来更改Tensor的维度。
区别:
1、Tensor.view
Tensor.view要求Tensor的物理存储必须是连续的,否则将会报错。Tensor.view返回的一定是一个索引,更改返回值,则原始值同样被更改。
例:

输出为:

2、Tensor.reshape
Tensor.reshape则没有这种要求。Tensor.reshape返回的是引用还是复制是不确定的。
例:
(1)

输出为:

(2)

输出为:

相同点:
1、都是接收要输出的维度作为参数
2、输出的矩阵元素个数不能改变
3、可以在维度中输入-1
4、PyTorch会自动推断它的数值
5、torch.squeeze和torch.unsqueeze
torch.squeeze和torch.unsqueeze用于去掉和添加轴
1、torch.squeeze
torch.squeeze用于去掉维度为1的轴。
例:

输出为:

2、torch.unsqueeze
torch.unsqueeze用于给Tensor的指定位置添加一个维度为1的轴。
例:

输出为:

6、torch.t和torch.transpose
这两个函数只接收二维Tensor
tensor.t是torch.transpose的简化版
例:
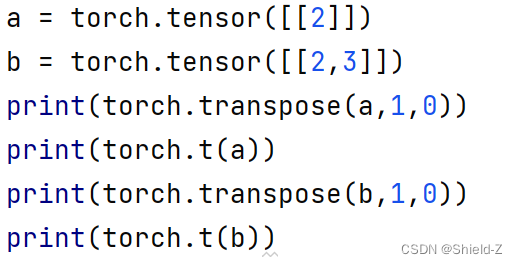
输出为:

7、permute
对于高维度Tensor,可以使用permute方法来变化维度。
例:

输出为:

8、torch.cat和torch.stack
PyTorch提供了torch.cat和torch.stack用于拼接矩阵。
不同:
1、torch.cat在已有的轴dim上拼接矩阵
2、给定轴的维度可以不同,而其他轴的维度必须相同。
3、torch.stack在新的轴上拼接,它要求被拼接的矩阵的所有维度都相同。
例:
下例可以清楚地表明它们的使用方法和区别:
(1)torch.cat:
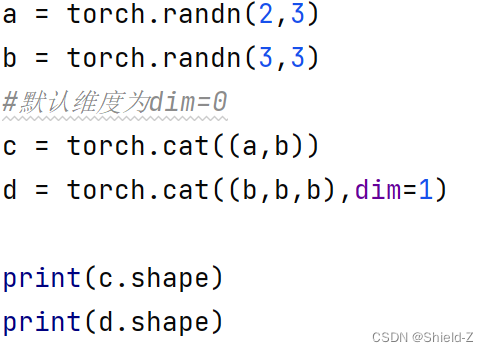
输出为:

(2)torch.stack:

输出为:

9、torch.split和torch.chunk
除了拼接矩阵,PyTorch还提供torch.split和torch.chunk用于拆分矩阵。
不同:
1、torch.split传入的是拆分后每个矩阵的大小
2、可以传入list,也可以传入整数
3、torch.chunk传入的是拆分的矩阵个数
例:
(1)

输出为:

(2)

输出为:

(3)

输出为:

10、代码:
import torch
a = torch.rand(1,2,3,4,5)
print("元素个数:",a.nelement())
print("轴的个数:",a.ndimension())
print("矩阵维度:",a.size(),a.shape)
b = a.view(2*3,4*5)
print(b.shape)
c = a.reshape(-1)
print(c.shape)
d = a.reshape(2*3,-1)
print(d.shape)
a = torch.rand(1,2,3,4,5)
b = torch.squeeze(a)
print(torch.unsqueeze(b,0).shape)
a = torch.tensor([[2]])
b = torch.tensor([[2,3]])
print(torch.transpose(a,1,0))
print(torch.t(a))
print(torch.transpose(b,1,0))
print(torch.t(b))
a = torch.rand((1,224,224,3))
print(a.shape)
b = a.permute(0,3,1,2)
print(b.shape)
a = torch.randn(2,3)
b = torch.randn(3,3)
#默认维度为dim=0
c = torch.cat((a,b))
d = torch.cat((b,b,b),dim=1)
print(c.shape)
print(d.shape)
b = torch.randn(3,3)
c = torch.stack((b,b),dim=1)
d = torch.stack((b,b),dim=0)
print(c.shape)
print(d.shape)
a = torch.randn(10,3)
for x in torch.split(a,[1,2,3,4],dim=0):
print(x.shape)
for x in torch.split(a,4,dim=0):
print(x.shape)
for x in torch.chunk(a,4,dim=0):
print(x.shape)




















 1921
1921











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








