🍇线程的创建
🍐1.继承 Thread 类
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new MyThread();
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("hello main");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
🍐2.实现Runnable接口
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("hello thread2");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("hello main2");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
🍐3.匿名内部类
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("hello thread3");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
};
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println(" hello main");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
🍐4.匿名内部类创建 Runnable ⼦类对象
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread((Runnable) () ->{
while (true){
System.out.println("hello thread4");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println(" hello main4");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
🍐5.lambda 表达式创建 Runnable ⼦类对象
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
while (true){
System.out.println("hello thred5");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println(" hello main5");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
🍎线程中断
终止线程,在Java中所有的终止程序都只是“提醒,建议”。真正的是否结束都是由线程本体 自己决定的。
在系统原生的线程中,是有办法让别的线程强制终止的,但这种设定不太好,所以Java没有采纳
主要原因还是线程之间的调度是随机的。
🥝1.自己设定条件
之所以可以结束,是因为thread线程外面写了isRunning这样的条件,所以才能控制
如果thread代码不这样写,那么thread都会继续执行,不会在意外面的条件
最终决定权还是在thread手中。
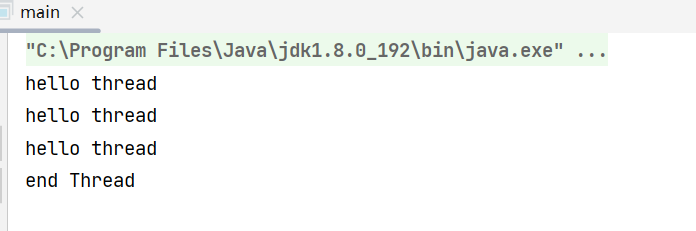
private static boolean isRunning = true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
while (isRunning){//自己书写条件控制线程的结束
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
//三秒之后
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
isRunning = false;
//三秒之后设置 条件 终止线程
System.out.println("end Thread");
}
运行结果如下
缺点

🥝2.使用interrupt和isInterrupted方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
// t.isInterrupted();
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("hello thead");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
t.interrupt();
}
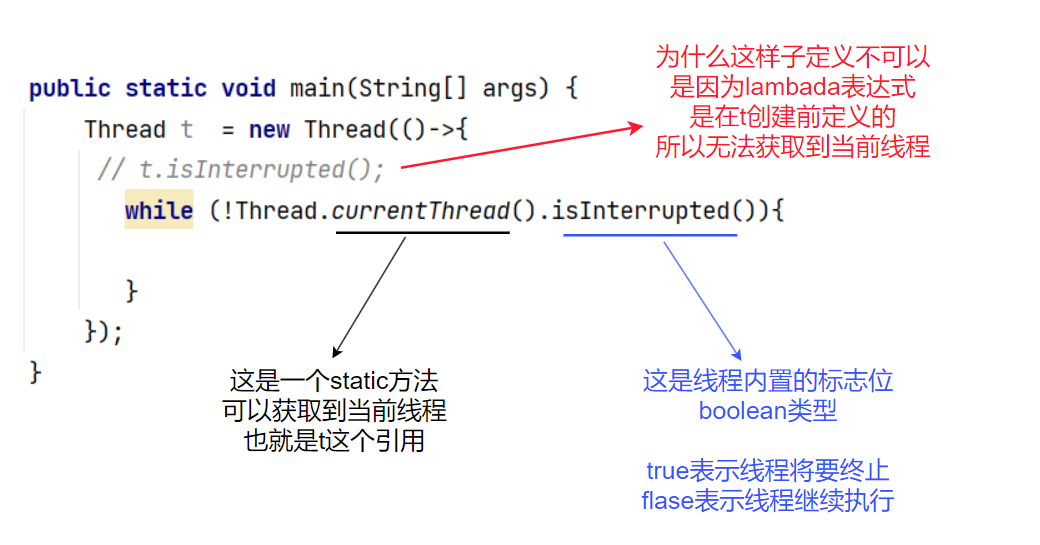

运行程序
发现3s之后,线程确实是结束了。但是是以抛出异常中断的情况结束,
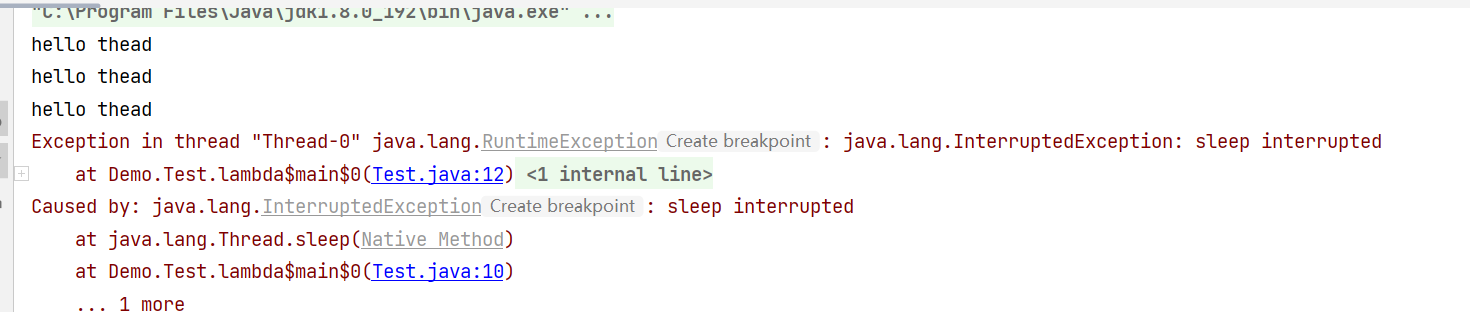
这样会使结果不那么美观。那么接下来就要解决这样的问题。
解决方法
我们不抛出异常,而是打印出异常。
继续运行,看看结果是怎样的。

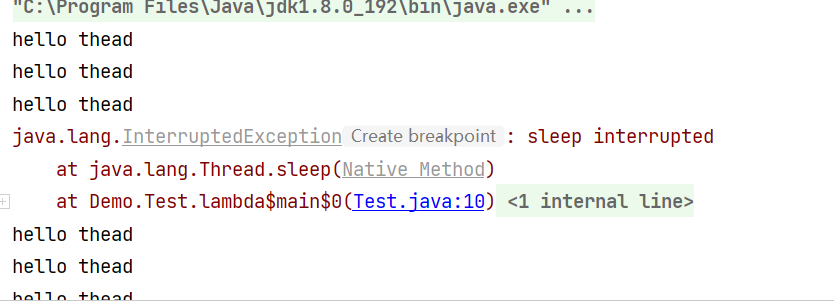
我们可以看到结果中,打印出了异常,而线程并没有结束
我们确确实实使用了interrupt方法,使标志位修改成了true了,那为什么线程还会继续执行呢?
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数Python工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Python开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。




既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上前端开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以扫码获取!!!(备注Python)
nvert/6c361282296f86381401c05e862fe4e9.png)

既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上前端开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以扫码获取!!!(备注Python)























 547
547











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








