针对C++primer中关联容器11.9的问题
先来一道程序看看吧。程序如下如题目要求是定义一个map,将单词与一个行号的list关联,list中保存单词出现的行号、现在继续
//定义一个map,将单词与一个行号的list关联,list中保存单词出现的行号
//map<string,list<int>>word_lineno
#include <iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include <map>
#include<list>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string &tran(string &s)
{
for (int p = 0; p < s.size(); ++p)
{
if (s[p] >= 'A'&&s[p] <= 'Z')
{
s[p] -= ('A' - 'a');
}
else if (s[p] == ',' || s[p] == '.')
{
s.erase(p, 1);
}
}
return s;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
map<string, list<int>>word_lineno;
string line;
string word;
int leneno = 0;
while (getline(cin, line))
{
leneno++;
while (cin>>word)
{
tran(word);
word_lineno[word].push_back(leneno);
}
cin.clear();
}
for (const auto &w:word_lineno)
{
cout << w.first <<"所在行:";
for (auto v:w.second)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 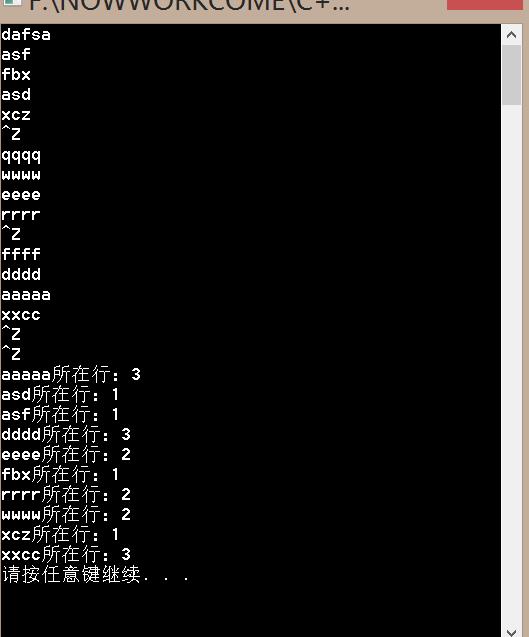
其中本来答案中需要in文件流绑定,我却用了两个cin来控制文件输入单词以及行号控制。在这里需要注意的是cin的状态,在我们按下一次CTRL+Z后cin状态已经为false了也就是说,在后面再有cin>>word这个语句是无效的,在这样的情况下,需要对cin的状态进行恢复,也就是代码中的cin.clear();
- 对于map
针对在map中遇到什么问题使用count,在什么情况下使用find?
- find是查找关键字在容器中出现的位置,而count还会统计关键字出现的次数,因此:
- 当我们需要知道(允许重复关键字出现的情况)容器中有多少元素的关键字相同时,我们使用count;
- 但是当我们只关心这个关键字是否存在于这个容器内,那么,只需要find就足够了。
- 总之,对于不允许重复关键字的容器,count和find能达到同样的效果;
- 最后,说一下find和下标操作的区别,就是当给定关键字不在容器内时,下标操作会插入一个关键字并将他的值定为0,所以在这种情况下,我们应该使用find进行查找。
2.如果给定的关键字不在容器内,upper_bound、lower_bound、equal_range分别会返回什么.
- lower_bound返回第一个具有给定关键字的元素,upper_bound则返回第一个具有给定关键字的元素之后的位置,就是这两个迭代器构成包含所有给定关键字元素的范围。若是给定关键字不在容器内,两个操作显然应该构成一个空范围,他们返回相当的迭代器,指出关键字的正确插入位置,–还不影响关键字的排序。如果给定关键字比所有关键字都大,那么他插在原先end尾后区域。
- equal_range返回的是一个pair,他的first成员相当于lower_bound返回的迭代器,second成员相当于upper_bound返回的迭代器。因此若是给定关键字不在容器内,first和second都指向关键字的正确插入位置,两个迭代器构成一个空范围。
编程练习,编写程序,定义一个作者及其相关作品的multimap,使用find在容器内查找一个元素并用erase删除他,确保就算容器内没有这个元素也能运行成功。
#include <iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void remove_author(multimap<string, string>&book, const string &author)//删除某个作者及其所映射的书,可以理解成某个作者犯事了,然后被要求,这个作者的书必须的下架。就是这么个意思
{
auto pos = book.equal_range(author);
if (pos.first == pos.second)
{
cout << "并没有" << "这个作者" << endl;
}
else
book.erase(pos.first, pos.second);
}
void print_books(multimap<string, string>&book)
{
cout << "当前数目有:" << endl;
for (auto v:book)
{
cout << v.first << ",《" << v.second << "》" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/*vector<pair<string, int>>data;//pair的vector
string words;
int v;
while (cin>>words&&cin>>v)//在这里明显cin不可以用。需要读取文件,或许本来就应该按照文件流的方式读取,
{
data.push_back(pair<string, int>(words, v));
}
for (auto v:data)
{
cout << v.first <<" "<< v.second << endl;
}
*/
multimap<string, string>books;
books.insert({ "Barth,Jhon", "Sot-Weed Factor" });
books.insert({ "金庸", "笑傲江湖" });
books.insert({ "忘语", "凡人修仙传" });
print_books(books);
remove_author(books,"忘语");
print_books(books);
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果如下:

1. 这里做的操作就是插入三本书,输出,删除一本书,在输出的效果。
2. 在这里还可以使用find和lower_bound、upper_bound也可以实现目标,但是相对而言没有上文简单
单词计数程序
#include <map>
using std::map;
#include <string>
using std::string;
#include <utility>
using std::pair;
#include <cstddef>
using std::size_t;
#include <iostream>
using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
// count the number of times each word occurs in the input
map<string, size_t> word_count; // empty map from string to size_t
string word;
while (cin >> word)
++word_count[word];
for (const auto &w : word_count)
cout << w.first << " occurs " << w.second << " times" << endl;
// get an iterator positioned on the first element
auto map_it = word_count.cbegin();
// compare the current iterator to the off-the-end iterator
while (map_it != word_count.cend()) {
// dereference the iterator to print the element key--value pairs
cout << map_it->first << " occurs "
<< map_it->second << " times" << endl;
++map_it; // increment the iterator to denote the next element
}
return 0;
}
上述代码是C++primer最后一题的标准答案,由此可以看出人家总体的风格较好,比我这个菜鸟水平好多了,考虑的也很周全。
单词转换函数
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <sstream>
using std::map; using std::string; using std::vector;
using std::ifstream; using std::cout; using std::endl;
using std::getline;
using std::runtime_error; using std::istringstream;
map<string, string> buildMap(ifstream &map_file)
{
map<string, string> trans_map; // holds the transformations
string key; // a word to transform
string value; // phrase to use instead
// read the first word into key and the rest of the line into value
while (map_file >> key && getline(map_file, value))
if (value.size() > 1) // check that there is a transformation
trans_map[key] = value.substr(1); // skip leading space
else
throw runtime_error("no rule for " + key);
return trans_map;
}
const string &
transform(const string &s, const map<string, string> &m)
{
// the actual map work; this part is the heart of the program
auto map_it = m.find(s);
// if this word is in the transformation map
if (map_it != m.cend())
return map_it->second; // use the replacement word
else
return s; // otherwise return the original unchanged
}
// first argument is the transformations file;
// second is file to transform
void word_transform(ifstream &map_file, ifstream &input)
{
auto trans_map = buildMap(map_file); // store the transformations
// for debugging purposes print the map after its built
cout << "Here is our transformation map: \n\n";
for (auto entry : trans_map)
cout << "key: " << entry.first
<< "\tvalue: " << entry.second << endl;
cout << "\n\n";
// do the transformation of the given text
string text; // hold each line from the input
while (getline(input, text)) { // read a line of input
istringstream stream(text); // read each word
string word;
bool firstword = true; // controls whether a space is printed
while (stream >> word) {
if (firstword)
firstword = false;
else
cout << " "; // print a space between words
// transform returns its first argument or its transformation
cout << transform(word, trans_map); // print the output
}
cout << endl; // done with this line of input
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// open and check both files
if (argc != 3)
throw runtime_error("wrong number of arguments");
ifstream map_file(argv[1]); // open transformation file
if (!map_file) // check that open succeeded
throw runtime_error("no transformation file");
ifstream input(argv[2]); // open file of text to transform
if (!input) // check that open succeeded
throw runtime_error("no input file");
word_transform(map_file, input);
return 0; // exiting main will automatically close the files
}//其实代码风格也没有多好,如果仔细看的话。就先这样吧。
























 609
609











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








