★
一,HashTable
哈希表,它相比于hashMap结构简单点,它没有涉及红黑树,直接使用链表的方式解决哈希冲突。
我们看它的字段,和hashMap差不多,使用table存放元素
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
private transient int count; //entry 节点数量
private int threshold; //rehash 刷新的 阈值
private float loadFactor; //负载因子
private transient int modCount = 0; 节点Entry:
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
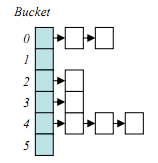
Entry<K,V> next;注意这个结构,数组+链表
它没有常量字段,默认值是在构造方法里面直接体现的,我们看一下无参构造:
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor; //负载因子
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity]; //初始化大小
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}1.get()方法
根据key,计算hash值,获得Index,通过数组的随机访问,直接获得entry节点,再变量entry链表,比较hash和key都相同的entry,获取内部的value值。
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
//计算下标
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
//遍历查找,e=e.next
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}2.put()方法
与get()方法类似,也是遍历table,然后调用addEntry()实现添加。
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
//如果已经存在,则覆盖,返回老的值
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
//不存在,直接添加
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}addEntry()
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) { //大小超过阈值,要扩容
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
//添加
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); //放到链表头部
count++;
}扩容: 直接 OldCapacity*2+1,然后将存在的entry重新计算hash值,导入新容器中。
注意这里的手法,直接将新来的节点,放到头部,这样就可以不管后面是否存在节点,都不会出现问题
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
二,TreeMap
TreeMap和之前的两个map就不同了,它没有使用哈希表,而是直接使用红黑树解决,它的字段只保存了根节点。
注意:之所以说treeMap是有序的,是因为treemap在插入的时候,比较的是key的值,而hashTable和HashMap比较的只是key的hash值,所以产生了不同。因为hash值要用来构建数组,进行映射,无法达到有序的状态,而TreeMap不需要数组,根节点直接就是树状,所以能够达到有序!
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; //排序比较器
private transient Entry<K,V> root; //根节点
private transient int size = 0;
private transient int modCount = 0;entry节点:
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;1.get()
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}getEntry()
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
//左右分流
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}2.put() 涉及红黑树的操作,所以代码比较长
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}3.remove()
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p); //实际方法
return oldValue;
}






















 370
370











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








