本文概述
本文讲述了LR(1)文法的原理及如何用C语言实现。详细描述了代码的运行流程和结构,并在给出的代码中实现了拓广文法,项目集族的构造与输出,分析表的构造与输出,和对任意输入字符串的分析。
实验要求
根据文法规则构建项目集族,建立LR(1)分析表,并对任意的输入串进行语法分析。要求输出项目集族,LR(1)分析表,和分析过程。
实验内容
(一)实验原理
LR分析法是一种自底向上的语法分析方法,广泛应用于编译器设计中。它通过构造有限状态自动机(FSA)来识别输入字符串是否符合给定的文法,LR分析法包含LR(0),SLR(1),LR(1)等。
其中LR(1) 中的 “L” 表示从左到右扫描输入,“R” 表示生成最右边的派生,而 “1” 表示使用一个符号的 lookahead(向前查看一个符号)来进行决策。
LR分析方法的逻辑结构
一个LR分析器由3个部分组成:
- LR分析程序,又称总控程序。所有的LR分析器的总控程序都是相同的。
- 分析栈,包括文法符号栈和相应的状态栈,它们均是先进后出栈(这两栈的长度总是相等的,即符号栈移进一个符号时,状态栈也会移进一个状态;归约时符号栈移出多少个符号,状态栈就移出多少个状态)。
- 分析表(分析函数),不同的文法分析表不同,同一个文法采用的LR分析器不同时,分析表也不同,分析表又可分为动作表(ACTION)和状态转换(GOTO)表两个部分,它们都可用二维数组表示。

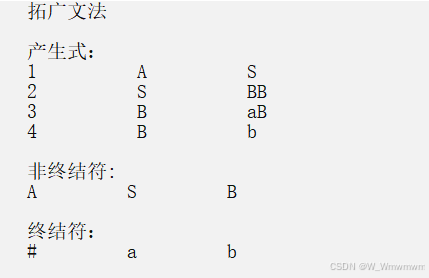
对于文法:
(1) S→BB
(2) B→aB
(3) B→b
的LR(1)分析表(动作表(ACTION)和状态转换(GOTO)表)如下所示:

其中动作表(Action):用于处理终结符,包含以下操作:
- Si:将输入符号压入栈中,并转移到状态 Si。
- ri: 根据产生式(i) 进行归约。
- acc:表示分析成功。
- 空白:表示语法错误。
状态转换(GOTO)表:用于处理非终结符,指示从当前状态转移到下一个状态。会在归约后根据归约后的当前状态和归约后入栈的非终结符查询。
总控程序分析过程:
在LR分析器的总控程序控制下对输入串进行分析,即根据输入串的当前符号和分析栈的栈顶状态查找分析表应采取的动作,对状态栈和符号栈进行相应的操作,即移进、归约、接受或报错。具体说明如下:
- 若ACTION[S,a]=Sj,a 为终结符,则把a移入符号栈,j移入状态栈。
- 若ACTION[S,a]=rj,a为终结符或#号,则用第j个产生式归约,并将两个栈的指针减去k,其中k为第j个产生式部的符号串长度,这时当前面临符号为第j个产生式左部的非终结符,不妨设为A,归约后栈顶状态假设为n,则再进行GOTO[n,A]。
- 若ACTION[S,a]=acc,a应为#号,则为接受,表示分析成功。
- 若GOTO[S,A]=j,A为非终结符,表明前一动作是用关于A的产生式归约的,当前面临的非终结符A应移入符号栈,j移入状态栈。
- 若ACTION[S,a]为空白,则转向出错处理。
用上述的 LR(1)分析表给出对输入串abab#的 分析,其状态栈、符号栈及输入串的变化过程如下图所示:

LR(1)分析表的构造:
其实LR分析器就是基于有限状态自动机(FSA)识别字符串的代码实现,且通过分析表来存储状态图。项目集是构造有限状态自动机(FSA)的基础。每个项目集对应一个状态,状态之间的转换由输入符号和转移动作(GOTO)决定。通过构造项目集族,可以生成一个完整的状态图,同时构建分析表。如下用LR(1)识别上述文法的FSA:

-
项目集
在 LR分析中,项目(Item)是带有 · 的产生式,· 表示当前解析到的位置。例如,对于产生式 A → α · β,其中 · 表示当前解析到 α 的末尾,接下来需要解析 β。为了区分不同的上下文,LR(1) 项目还包括一个或多个展望符,表示当前项目后面可能跟随的输入符号。因此,一个完整的 LR(1) 项目可以表示为 A → α · β, a,其中 a 是展望符。 -
构造 LR(1) 项目集
LR分析的核心是构造项目集,并根据这些项目集构建有限状态自动机(FSA)。以下是构造 LR(1) 项目集的步骤:-
拓广文法并初始化:
从文法的起始符号 S 开始,构造初始项目集 I0,包含项目 S’ → · S, #,其中 S’ 是一个新的起始符号,# 是输入结束符。 -
闭包(Closure):
对于每个项目集 I,计算其闭包 CLOSURE(I)。闭包操作会添加所有可以从当前项目推导出的项目,并带上适当的 展望符:1. I的任何项目都属于CLOSURE(I)。 2. 若项目[A→a•Bp, a]属于CLOSURE(I),B→♾ 是一个产生式,那么,对于FIRST(♾a) 中的每个终结符b,如果[B→•♾, b]原来不在CLOSURE(I)中,则把它加进去。 3. 重复执行步骤2,直至CLOSURE(I)不再增大为止。 -
转移动作(GOTO):
对于每个项目集 I 和每个非终结符 X,计算 GOTO(I, X),即从 I 中所有形如 A → α · X β, a 的项目出发,将指针移动到 X 之后,形成新的项目集。
例如,对于项目 A → α · X β, a,GOTO(I, X) 会生成项目 A → α X · β, a。 -
构造状态图(手算时):
使用 CLOSURE 和 GOTO 操作,逐步构造状态图,每个状态对应一个项目集。状态图中的边表示从一个项目集到另一个项目集的转换,边上的标签是输入符号。
-
-
分析表构造
基于上面构造的状态图构造分析表(代码实现中项目集和分析表的构造是同时进行的),构造规则如下图所示:

-
文法要求
如果一个文法的LR(1)分析表不含多重入口(表中每个位置只能被赋值一次),即任何一个LR(1)项目集中无移进 - 归约冲突,归约 - 归约冲突,则称该文法为LR(1)文法。
(二)程序结构及功能介绍
程序总流程为:从文件读取文法 -> 输出拓广后的文法信息 -> 计算First集并输出 -> 构造项目集族并输出 -> 构造LR(1)分析表并输出 -> 判断是否是LR(1)文法 -> 手动输入要分析的字符串 -> 输出分析过程和结果
读取文件
本程序的文法是从文件中读取的,事先要准备一个规则.txt文件,如下:

非终结符要求必须是大写字母,一行只能有一条规则,可用‘|’表示或,空用$表示
程序读取后输出拓广后的文法:
//产生式的读取,非终结符必须为大写字母,$表示空
void read_rule(char* rulefile, noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote);
void print_rule(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter); //产生式输出
First集的计算输出
程序会先计算出各非终结符的First集,为后面构造项目集族做准备:

void find_first(noterminal* h_noter); //生成FIRST集
构造项目集族和分析表
在代码实现中,此两者是同时进行的,即构造一个项目集就填一行表,其中项目集是边构造边输出,分析表是后面另外用一个函数输出:
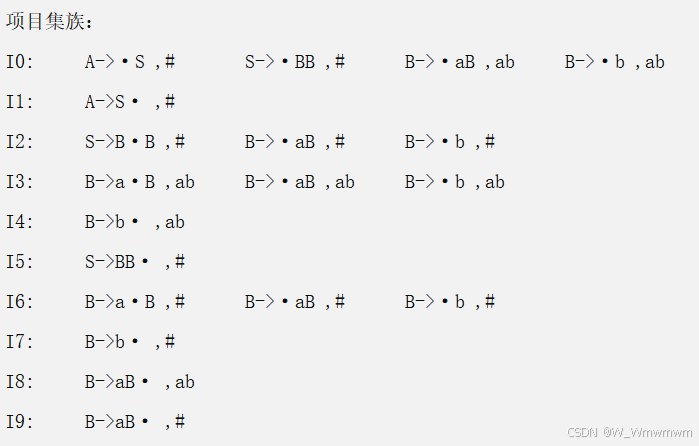

void find_state(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote); //计算状态集
void analyse_table(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote); //输出分析表
判断是否是LR(1)文法
判断是边填分析表边判断的,如果填表时不为空,则表示出现了冲突,然后就调用错误输出函数判断并输出冲突类型,然后停止分析并退出程序。

void error_treat(int number,int now,int before); //报错输出
输入与分析
最后,手动输入要分析的字符串,程序会进行分析并输出:

int lr1_analyse(statenote* h_stnote, noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, char* st); //LR(1)分析
(三)完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//非终结符
typedef struct noterminal
{
int number; //编号
char ch;
char* First; //对应first集
char* guize[10]; //对应产生式
int size = 0; //产生式个数
struct noterminal* next;
}noterminal;
//终结符
typedef struct terminal
{
int number; //编号
char ch;
struct terminal* next;
}terminal;
//项目集
typedef struct stateset
{
int size; //项目数目
char* guize[20]; //项目
char* look[20]; //展望集
}stateset;
//状态结点
typedef struct statenote
{
int number; //编号
int* action; //action表
int* gt; //Goto表
stateset* hert; //识别项目集
stateset* allset; //完整项目集
struct statenote* next;
}statenote;
/*在分析表中,表的值为状态编号加1,
0表示出错,-1表示接受态,
小于-1的值取绝对值即为归约产生式对应序号*/
//头指针
noterminal* h_noter;
terminal* h_ter;
statenote* h_stnote;
int noterminalsize;
int terminalsize;
void error_treat(int number,int now,int before); //报错输出
void free_list(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote); //释放链表空间
bool in_char(char* string, char ch); //检查字符串string中是否有字符ch
int combin(char* ch, char* bech); //set字符串ch和bech于ch
void read_rule(char* rulefile, noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote); //产生式的读取,非终结符必须为大写字母,$表示空
noterminal* check_noterminal(char ch, noterminal* h_noter); //检查非终结符是否已拥有
terminal* check_terminal(char ch, terminal* h_ter); //检查终结符是否已拥有
statenote* check_statenote(int i, statenote* h_stnoter); //查找状态结点
void print_rule(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter); //产生式输出
int first_add(noterminal* noter, int site, int r_site, int len); //FIRST集加入元素
void find_first(noterminal* h_noter); //生成FIRST集
int in_stateset(stateset* set, char* gz, char* lk); //判断项目集对一项目的包含度
void free_first(noterminal* h_noter,char* first, char* str, char* look); //计算任意串的first集
int in_note(statenote* h_stnote, stateset* set); //判断项目集是否存在状态链表结点中
int seek_guize(noterminal* h_noter, char* gui); //找到产生式对应的序号
int* seek_guize(noterminal* h_noter, int i); //找到对应序号的产生式
void find_state(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote); //计算状态集
void analyse_table(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote); //输出分析表
int lr1_analyse(statenote* h_stnote, noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, char* st); //LR(1)分析
int main() {
char rulefile[100] = "D:\\新建文件夹\\Desktop\\编译原理\\实验五\\规则.txt";
//初始化
h_noter = (noterminal*)malloc(1+sizeof(noterminal));
h_noter->next = NULL;
h_noter->First = NULL;
h_noter->size = 0;
h_ter = (terminal*)malloc(1+sizeof(terminal));
h_ter->next = NULL;
h_stnote = (statenote*)malloc(1+sizeof(statenote));
h_stnote->next = NULL;
//读取文法
read_rule(rulefile, h_noter, h_ter,h_stnote);
//输出文法
print_rule(h_noter, h_ter);
//计算first集
find_first(h_noter);
//计算状态集
find_state(h_noter, h_ter, h_stnote);
//输出分析表
analyse_table(h_noter, h_ter, h_stnote);
//对输入符号串进行分析
char st[100];
int h = 1;
while (h) {
printf("\n\n\t请输入要分析的字符串:");
scanf_s("%s", st, 99);
int sign = lr1_analyse(h_stnote, h_noter, h_ter, st);
if (sign == 0) printf("\t非法输入!\n\n");
else printf("\t合法输入!\n\n");
printf("\t是否继续输入(0退出,1继续):");
scanf_s("%d", &h);
}
free_list(h_noter, h_ter, h_stnote);
return 0;
}
noterminal* check_noterminal(char ch, noterminal* h_noter) {
int sign = 0;
noterminal* h_n = h_noter;
while (h_n->next != NULL)
{
h_n = h_n->next;
if (h_n->ch == ch) {
sign = 1;
break;
}
};
if (sign == 0) return NULL;
else return h_n;
}
terminal* check_terminal(char ch, terminal* h_ter) {
int sign = 0;
terminal* h_n = h_ter;
while (h_n->next != NULL)
{
h_n = h_n->next;
if (h_n->ch == ch) {
sign = 1;
break;
}
};
if (sign == 0) return NULL;
else return h_n;
}
statenote* check_statenote(int i, statenote* h_stnoter) {
statenote* stnote = h_stnoter;
while (stnote->next != NULL) {
stnote = stnote->next;
if (stnote->number == i) return stnote;
}
return NULL;
}
bool in_char(char* string, char ch) {
int coutn = strlen(string);
int i = 0;
for (; i < coutn; i++) {
if (string[i] == ch) break;
}
return coutn == i ? false : true;
}
int combin(char* ch, char* bech) {
int cont = strlen(ch);
int sign = 0;
for (int i = 0; bech[i] != 0; i++) {
if (bech[i] != '$' && !in_char(ch, bech[i])) {
ch[cont++] = bech[i];
sign = 1;
}
}
return sign;
}
void read_rule(char* rulefile, noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote) {
FILE* yuan = NULL;
noterminal* noter, * r_noter = h_noter;
terminal* ter, * r_ter = h_ter;
//非终结符加入'#'
ter = (terminal*)malloc(1+sizeof(terminal));
ter->ch = '#';
ter->number = 0;
ter->next = NULL;
r_ter->next = ter;
r_ter = ter;
char ch;
int size = 1; //终结符个数
int size2 = 1; //终结符个数
if (fopen_s(&yuan, rulefile, "r") != 0) {
printf("规则 文件打开失败!");
exit(1);
}
while ((ch = fgetc(yuan)) != -1) {
if (64 < ch && ch < 91) {
noterminal* h_n = check_noterminal(ch, h_noter);
//增加非终结符结点
if (h_n == NULL) {
noter = (noterminal*)malloc(1+sizeof(noterminal));
noter->number = size2;
noter->ch = ch;
noter->next = NULL;
noter->First = NULL;
noter->size = 0;
r_noter->next = noter;
r_noter = noter;
size2++;
}
else {
noter = h_n;
}
//读取产生式
char chsh[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) ch = fgetc(yuan);
int quit = 0;
while ((ch = fgetc(yuan))) {
if (ch == '|' || ch == '\n' || ch == -1) {
//存储产生式
chsh[quit] = '\0';
quit = 0;
noter->guize[noter->size++] = (char*)malloc(1+sizeof(char[10]));
int s = 0;
do {
noter->guize[noter->size - 1][s] = chsh[s];
} while (chsh[s++] != '\0');
if (ch == '\n' || ch == -1) {
break;
}
}
else {
chsh[quit++] = ch;
//增加终结符
if (ch < 65 || ch>90) {
terminal* h_t = check_terminal(ch, h_ter);
if (h_t == NULL) {
ter = (terminal*)malloc(1+sizeof(terminal));
ter->ch = ch;
ter->next = NULL;
ter->number = size;
r_ter->next = ter;
r_ter = ter;
size++;
}
}
}
}
}
else {
printf("产生式错误");
}
}
//初始化表
noterminalsize = size2;
terminalsize = size;
h_stnote->action = (int*)malloc(1+(size+1)*sizeof(int));
h_stnote->gt = (int*)malloc(1+(size2+1)*sizeof(int));
//拓广文法
char ch2 = 'A';
noterminal* newnoter;
for (int i = 1; i < 24; i++) {
if ((newnoter = check_noterminal(ch2, h_noter)) != NULL) ch2++;
else break;
}
newnoter = (noterminal*)malloc(1+sizeof(noterminal));
newnoter->ch = ch2;
newnoter->First = NULL;
newnoter->number = 0;
newnoter->size = 1;
newnoter->guize[0] = (char*)malloc(1+sizeof(char[10]));
newnoter->guize[0][0] = h_noter->next->ch;
newnoter->guize[0][1] = 0;
newnoter->next = h_noter->next;
h_noter->next = newnoter;
fclose(yuan);
}
void print_rule(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter) {
printf("\t拓广文法\n\n");
printf("\t产生式:\n");
noterminal* noter = h_noter;
int i = 0;
while (noter->next != NULL) {
noter = noter->next;
for (int j = 0; j < noter->size; j++) {
printf("\t%-10d %-10c %-10s\n", ++i, noter->ch, noter->guize[j]);
}
}
printf("\n\t非终结符:\n\t");
noter = h_noter;
while (noter->next != NULL) {
noter = noter->next;
printf("%-10c", noter->ch);
}
printf("\n\n\t终结符:\n\t");
terminal* ter = h_ter;
while (ter->next != NULL) {
ter = ter->next;
printf("%-10c", ter->ch);
}
printf("\n\n\n");
}
int first_add(noterminal* noter, int site, int r_site, int len) {
char ch = noter->guize[r_site][site];
int sign = 0;
if (64 < ch && ch < 91) {
noterminal* h_n = check_noterminal(ch, h_noter);
if (h_n->First != NULL) {
if (noter->First == NULL) {
noter->First = (char*)malloc(1+sizeof(char[20]));
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) noter->First[j] = 0;
}
sign = combin(noter->First, h_n->First);
if (in_char(h_n->First, '$')) {
if (site == len - 1) {
//防治反复判空
if (!in_char(noter->First, '$')) {
noter->First[strlen(noter->First)] = '$';
sign = 1;
}
}
else {
sign += first_add(noter, site + 1, r_site, len);
}
}
}
}
//首字符为终结符
else {
//first集为空
if (noter->First == NULL) {
noter->First = (char*)malloc(1+sizeof(char[20]));
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) noter->First[j] = 0;
noter->First[0] = ch;
sign = 1;
}
else {
if (!in_char(noter->First, ch)) {
noter->First[strlen(noter->First)] = ch;
sign = 1;
}
}
}
return sign;
}
void find_first(noterminal* h_noter) {
int sign;
do
{
sign = 0;
noterminal* noter = h_noter;
//对每个非终结符进行一轮分析
while (noter->next != NULL)
{
noter = noter->next;
//对一个非终结符进行一轮分析
for (int i = 0; i < noter->size; i++) {
//防治sign值被覆盖
sign += first_add(noter, 0, i, strlen(noter->guize[i]));
}
}
} while (sign);
//输出first集
noterminal* noter = h_noter;
printf("\tFIRST集:\n\n");
while (noter->next != NULL) {
noter = noter->next;
printf("\t%-10c", noter->ch);
printf("first=%-10s\n", noter->First);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
//项目与展望集都不相同-1,都相同-2,只有项目相同返回项目位置
int in_stateset(stateset* set, char* gz, char* lk) {
int sign = -1;
//判断项目
int i = 0;
for (; i < set->size; i++) {
int j = 0;
for (; j <= strlen(set->guize[i]); j++) {
if (set->guize[i][j] != gz[j]) break;
}
if (j > strlen(set->guize[i])) break;
}
if (i < set->size) {
sign = i;
//判断展望集
char ch1[20];
char ch2[20];
for (int q = 0; q < 20; q++) ch1[q] = set->look[i][q];
for (int q = 0; q < 20; q++) ch2[q] = lk[q];
int in = 0;
in += combin(ch1, ch2);
in += combin(ch2, ch1);
if (!in) {
sign = -2;
}
}
return sign;
}
void free_first(noterminal* h_noter, char* first, char* str,char* look) {
int size = strlen(str); //长度
if (size == 0) {
combin(first, look);
return;
}
int z = 0;
//为终结符
if (str[z] < 65 || str[z]>90) {
first[0] = str[0];
}
//为非终结符
else {
noterminal* h_n = check_noterminal(str[z], h_noter);
combin(first, h_n->First);
while (in_char(h_n->First, '$'))
{
//后都有空
if (z == size - 1) {
combin(first, look);
break;
}
char a = str[++z];
//为非终结符
if (a > 64 && a < 91) {
h_n = check_noterminal(a, h_noter);
combin(first, h_n->First);
}
//为终结符
else {
if (!in_char(first, a)) {
first[strlen(first)] = a;
}
break;
}
}
}
}
//存在返回状态编号,不存在返回-1
int in_note(statenote* h_stnote, stateset* set) {
statenote* stnote = h_stnote;
while (stnote->next != NULL) {
stnote = stnote->next;
stateset* stset = stnote->hert;
if (stset->size != set->size) continue;
int i = 0;
for (; i < stset->size; i++) {
int z = in_stateset(stset,set->guize[i],set->look[i]);
if (z != -2) break;
}
if (i == set->size) return stnote->number;
}
return -1;
}
int seek_guize(noterminal* h_noter, char* gui) {
noterminal* n_noter = check_noterminal(gui[0], h_noter);
noterminal* noter = h_noter;
int size = 0;
while (noter->next != n_noter) {
noter = noter->next;
size += noter->size;
}
char guize[10] = { 0 };
for (int i = 3; i < strlen(gui); i++) {
guize[i - 3] = gui[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n_noter->size; i++) {
int j = 0;
for (; j <= strlen(n_noter->guize[i]); j++) {
if (guize[j] != n_noter->guize[i][j]) break;
}
if (j > strlen(n_noter->guize[i])) {
return size + 1;
}
size++;
}
printf("出错");
return 0;
}
void find_state(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote)
{
printf("\t项目集族:\n\n");
int size = terminalsize;
int size2 = noterminalsize;
int size3 = 1; //项目集个数
//I0状态集初始化
statenote* newnote = NULL;
newnote = (statenote*)malloc(1+sizeof(statenote));
newnote->number = 0;
newnote->action = (int*)malloc(1+ (size + 1) * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) newnote->action[i] = 0;
newnote->gt = (int*)malloc(1+ (size2 + 1) * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < size2; i++) newnote->gt[i] = 0;
newnote->next = NULL;
newnote->hert = NULL;
newnote->hert = (stateset*)malloc(1+sizeof(stateset));
newnote->hert->size = 1;
newnote->hert->guize[0] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
char ch[20] = { 0 };
ch[0] = h_noter->next->ch;
ch[1] = '-';
ch[2] = '>';
ch[3] = -95;
ch[4] = -92;
ch[5] = h_noter->next->next->ch;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) newnote->hert->guize[0][i] = ch[i];
newnote->hert->look[0] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) newnote->hert->look[0][i] = 0;
newnote->hert->look[0][0] = '#';
h_stnote->next = newnote;
statenote* r_stnote = newnote; //尾指针
statenote* nownote = h_stnote;
while (nownote->next != NULL) {
nownote = nownote->next;
stateset* copy = (stateset*)malloc(1+sizeof(stateset));
nownote->allset = (stateset*)malloc(1+sizeof(stateset));
nownote->allset->size = nownote->hert->size;
//复制心
for (int j = 0; j < nownote->allset->size; j++) {
nownote->allset->guize[j] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
nownote->allset->look[j] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
nownote->allset->guize[j][i] = nownote->hert->guize[j][i];
nownote->allset->look[j][i] = nownote->hert->look[j][i];
}
}
//扩展
for (int j = 0; j < nownote->allset->size; j++) {
char* gui = nownote->allset->guize[j];
//找到·
int w = 0;
for (; w < strlen(gui); w++) {
if (gui[w] == -95 && gui[w + 1] == -92) {
w++;
break;
}
}
//如果后为非终结符
if (64 < gui[w + 1] && gui[w + 1] < 91) {
//展望集
char lk[20] = { 0 };
char str[20] = { 0 };
for (int e = w + 2; e < 10; e++) str[e - w - 2] = gui[e];
free_first(h_noter, lk, str, nownote->allset->look[j]);
noterminal* noter = check_noterminal(gui[w + 1], h_noter);
for (int r = 0; r < noter->size; r++) {
//列出一项
char newch[20] = { 0 };
newch[0] = noter->ch;
newch[1] = '-';
newch[2] = '>';
newch[3] = -95;
newch[4] = -92;
for (int t = 0; t < strlen(noter->guize[r]); t++) {
newch[t + 5] = noter->guize[r][t];
}
//无则加入
int z = in_stateset(nownote->allset, newch, lk);
if (z == -1) {//都
int sz = nownote->allset->size;
nownote->allset->guize[sz] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
for (int y = 0; y < 20; y++) nownote->allset->guize[sz][y] = newch[y];
nownote->allset->look[sz] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
for (int y = 0; y < 20; y++) nownote->allset->look[sz][y] = lk[y];
nownote->allset->size++;
}
if (z > 0) {//展望集
combin(nownote->allset->look[z], lk);
}
}
}
}
//copy
copy->size = nownote->allset->size;
for (int j = 0; j < copy->size; j++) {
copy->guize[j] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
copy->look[j] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
copy->guize[j][i] = nownote->allset->guize[j][i];
copy->look[j][i] = nownote->allset->look[j][i];
}
}
//输出状态
printf("\tI%d:", nownote->number);
for (int j = 0; j < copy->size; j++) {
printf("\t%s ,%s", copy->guize[j], copy->look[j]);
}
printf("\n\n");
//分析
char inch;
while (true) {
//找同状态项目并判断是否为归约
stateset* same = NULL;
same = (stateset*)malloc(1+sizeof(stateset));
same->size = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < copy->size; j++) {
if (copy->guize[j] == NULL) continue;
k++;
char* gui = copy->guize[j];
int w = 0;
for (; w < strlen(gui); w++) {
if (gui[w] == -95 && gui[w + 1] == -92) {
w++;
break;
}
}
//归约产生式
if (gui[w + 1] == 0 && k ==1) {
gui[w] = 0;
gui[w - 1] = 0;
//找到序号
int num = seek_guize(h_noter, gui);
if (num == 1) {
//acc,3
nownote->action[0] = -1;
}
else {
//更新表项,2
for (int u = 0; u < strlen(copy->look[j]); u++) {
terminal* ter2 = check_terminal(copy->look[j][u], h_ter);
if (nownote->action[ter2->number] != 0)
error_treat(nownote->number,-num, nownote->action[ter2->number]);
nownote->action[ter2->number] = -num;
}
}
copy->guize[j] = NULL;
copy->look[j] = NULL;
k = 0;
continue;
}
if (k == 1) {
inch = gui[w + 1];
}
//加入same,移出copy
if (inch == gui[w + 1]) {
gui[w + 1] = gui[w];
gui[w] = gui[w - 1];
gui[w - 1] = inch;
same->guize[same->size] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
same->look[same->size] = (char*)malloc(1+20);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
same->guize[same->size][i] = gui[i];
same->look[same->size][i] = copy->look[j][i];
}
same->size++;
copy->guize[j] = NULL;
copy->look[j] = NULL;
}
}
//分析完成
if (k == 0) {
break;
}
//判断same是否已经存在并判断状态转变
int zht = in_note(h_stnote, same);
//不存在
if (zht == -1) {
//新建状态
newnote = (statenote*)malloc(1+sizeof(statenote));
newnote->number = size3;
newnote->action = (int*)malloc(1+ (size + 1) * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) newnote->action[i] = 0;
newnote->gt = (int*)malloc(1+ (size2 + 1) * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < size2; i++) newnote->gt[i] = 0;
newnote->next = NULL;
newnote->hert = same;
//插入链表
r_stnote->next = newnote;
r_stnote = newnote;
size3++;
//更新表项,1,4
if (64 < inch && inch < 91) {
noterminal* noter2 = check_noterminal(inch, h_noter);
nownote->gt[noter2->number] = size3;
}
else {
terminal* ter2 = check_terminal(inch, h_ter);
if (nownote->action[ter2->number] != 0)
error_treat(nownote->number, size3, nownote->action[ter2->number]);
nownote->action[ter2->number] = size3;
}
}
//存在
else {
//更新表项,4,1
if (64 < inch && inch < 91) {
noterminal* noter2 = check_noterminal(inch, h_noter);
nownote->gt[noter2->number] = zht + 1;
}
else {
terminal* ter2 = check_terminal(inch, h_ter);
if (nownote->action[ter2->number] != 0)
error_treat(nownote->number, zht+1, nownote->action[ter2->number]);
nownote->action[ter2->number] = zht + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
void analyse_table(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote) {
printf("\n\tLR(1)分析表:\n\n");
printf("\t状态");
terminal* ter = h_ter;
noterminal* noter = h_noter->next;
statenote* stnote = h_stnote;
while (ter->next != NULL) {
ter = ter->next;
printf(" %c", ter->ch);
}
while (noter->next != NULL) {
noter = noter->next;
printf(" %c", noter->ch);
}
printf("\n\n");
int size = terminalsize;
int size2 = noterminalsize;
while (stnote->next != NULL) {
stnote = stnote->next;
printf("\t %-9d",stnote->number);
int zhi;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
zhi = stnote->action[i];
if (zhi > 0) {
int s = zhi - 1;
printf("S%-6d",s);
}
else if (zhi < 0) {
if (zhi == -1) {
printf("acc ");
}
else {
int r = -zhi;
printf("r%-6d", r);
}
}
else {
printf(" ");
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < size2; i++) {
int zhi = stnote->gt[i];
if (zhi == 0) {
printf(" ");
}
else {
printf("%-7d", zhi-1);
}
}
printf("\n\n");
}
}
void error_treat(int number,int now,int before) {
printf("\t-----------------------------------------------------\n");
if (now < 0 && before < 0) {
printf("\n\t 项目集I%d中出现归约——归约冲突\n\n",number);
}
else if (now * before < 0) {
printf("\n\t 项目集I%d中出现移进——归约冲突\n\n",number);
}
else;
printf("\t-----------------此文法不是LR(1)文法-----------------\n\n\n");
free_list(h_noter, h_ter,h_stnote);
exit(-1);
}
void free_list(noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, statenote* h_stnote) {
noterminal* noter = h_noter;
terminal* ter = h_ter;
statenote* stnote = h_stnote;
while (h_noter != NULL) {
h_noter = h_noter->next;
free(noter);
noter = h_noter;
}
while (h_ter != NULL) {
h_ter = h_ter->next;
free(ter);
ter = h_ter;
}
while (h_stnote != NULL) {
h_stnote = h_stnote->next;
free(stnote);
stnote = h_stnote;
}
}
int* seek_guize(noterminal* h_noter, int i) {
noterminal* noter = h_noter;
int* masseg = (int*)malloc(1+3 * sizeof(int));
while (noter->next != NULL) {
noter = noter->next;
if (noter->size < i) {
i -= noter->size;
}
else {
masseg[0] = (int)noter->ch;
masseg[1] = (int)strlen(noter->guize[i - 1]);
masseg[2] = noter->number;
return masseg;
}
}
return NULL;
}
int lr1_analyse(statenote* h_stnote, noterminal* h_noter, terminal* h_ter, char* st)
{
printf("\t状态栈 符号栈 输入串 ACTION GOTO\n");
int state[20] = { -1 }; //状态栈
int topt = 0;
state[topt++] = 0;
char fuhao[20] = { 0 }; //符号栈
int topf = 0;
fuhao[topf++] = '#';
st[strlen(st) + 1] = 0; //输入符
st[strlen(st)] = '#';
int tops = 0;
while (true) {
//输出三栈
int sum = 0;
printf("\t");
for (int i = 0; i < topt; i++) {
if (state[i] != -1) {
if (state[i] < 10) {
sum++;
printf("%d", state[i]);
}
else {
printf("(%d)", state[i]);
sum += 4;
}
}
}
char black[100] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 20 - sum; i++) black[i] = ' ';
printf("%s", black);
printf("%-15s", fuhao);
printf("%-15s", st);
//取出tops与tops进行分析
int zt = state[topt - 1];
char ch = st[tops];
statenote* noter = check_statenote(zt, h_stnote);
terminal* ter = check_terminal(ch, h_ter);
if (ter == NULL) {
printf("出错!\n");
return 0;
}
int zhi = noter->action[ter->number];
if (zhi > 0) {
fuhao[topf++] = ch;
st[tops++] = ' ';
state[topt++] = zhi - 1;
printf(" S%-8d\n", zhi - 1);
}
else if (zhi < 0) {
if (zhi == -1) {
printf(" acc\n");
return 1;
}
else {
int* masseg = seek_guize(h_noter, -zhi);
topt -= masseg[1];
topf -= masseg[1];
fuhao[topf++] = (char)masseg[0];
fuhao[topf] = 0;
printf(" r%-8d", -zhi);
zt = state[topt - 1];
noter = check_statenote(zt, h_stnote);
int kk1 = masseg[0];
int kk2 = masseg[1];
int kk = masseg[2];
zhi = noter->gt[masseg[2]];
if (zhi > 0) {
state[topt++] = zhi - 1;
printf("%d\n", zhi - 1);
}
else {
printf("出错!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
else {
printf("出错!\n");
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
/*每个malloc里都加1的原因:防治出现异常:Unhandled exception at 0x777F5624 (ntdll.dll) in php.exe: 0xC0000374: 堆已损坏。
堆被破坏的问题通常是因为内存写越界造成的。
因为你分配的两段内存可能恰好连续,前一段内存在写的时候越界,写到第二段的开头,将一些堆数据破坏了。
所以多分配一个空间,以防写越界时会破坏堆数据*/
(四)代码不足
- 输入的字符串最好不要超过15个字符,不然输出的分析过程的排版不会对齐,而且可能会导致栈溢出。

- 如果代码还有其他不足之处,欢迎在评论区指出。























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








