CompletableFuture在JDK1.8提供了一种更加强大的异步编程的api。它实现了Future接口,也就是Future的功能特性CompletableFuture也有;除此之外,它也实现了CompletionStage接口,CompletionStage接口定义了任务编排的方法,执行某一阶段,可以向下执行后续阶段。
CompletableFuture相比于Future最大的改进就是提供了类似观察者模式的回调监听的功能,也就是当上一阶段任务执行结束之后,可以回调你指定的下一阶段任务,而不需要阻塞获取结果之后来处理结果。
CompletableFuture常见api详解:
1、实例化CompletableFuture
// 构造方法创建
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
completableFuture.complete("hello");
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
// 静态方法创建
/**
supply 和 run 的主要区别就是 supply 可以有返回值,run 没有返回值。
Executor 就是用来执行异步任务的线程池,
如果不传Executor 的话,默认是ForkJoinPool这个线程池的实现。
一旦通过静态方法来构造,会立马开启异步线程执行Supplier或者Runnable提交的任务。
**/
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);
// 一旦任务执行完成,就可以打印返回值,这里的使用方法跟Future是一样的。
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello");
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
使用构造方法需要其它线程主动调用complete来表示任务执行完成,因为很简单,因为在构造的时候没有执行异步的任务,所以需要其它线程主动调用complete来表示任务执行完成。
2、获取任务执行结果
public T get();
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent);
public T join();
- get()和get(long timeout, TimeUnit
unit)是实现了Future接口的功能,两者主要区别就是get()会一直阻塞直到获取到结果,get(long timeout,
TimeUnit unit)值可以指定超时时间,当到了指定的时间还未获取到任务,就会抛出TimeoutException异常。 - getNow(T valueIfAbsent):就是获取任务的执行结果,但不会产生阻塞。如果任务还没执行完成,那么就会返回你传入的
valueIfAbsent 参数值,如果执行完成了,就会返回任务执行的结果。 - join():跟get()的主要区别就是,get()会抛出检查时异常,join()不会。
3、主动触发任务完成
public boolean complete(T value);
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex);
- complete:主动触发当前异步任务的完成。调用此方法时如果你的任务已经完成,那么方法就会返回false;如果任务没完成,就会返回true,并且其它线程获取到的任务的结果就是complete的参数值。
- completeExceptionally:跟complete的作用差不多,complete是正常结束任务,返回结果,而completeExceptionally就是触发任务执行的异常。
4、对任务执行结果进行下一步处理
// 只能接收任务正常执行后的回调
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
这类回调的特点就是,当任务正常执行完成,没有异常的时候就会回调。
- thenApply:可以拿到上一步任务执行的结果进行处理,并且返回处理的结果
- thenRun:拿不到上一步任务执行的结果,但会执行Runnable接口的实现
- thenAccept:可以拿到上一步任务执行的结果进行处理,但不需要返回处理的结果
// 只能接收任务处理异常后的回调
public CompletionStage<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn);
当上面的任务执行过程中出现异常的时候,会回调exceptionally方法指定的回调,但是如果没有出现异常,是不会回调的。
exceptionally能够将异常给吞了,并且fn的返回值会返回回去。
其实这个exceptionally方法有点像降级的味道。当出现异常的时候,走到这个回调,可以返回一个默认值回去。
// 能同时接收任务执行正常和异常的回调
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public CompletionStage<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> actin);
不论前面的任务执行成功还是失败都会回调的这类方法指定的回调方法。
- handle :
跟exceptionally有点像,但是exceptionally是出现异常才会回调,两者都有返回值,都能吞了异常,但是handle正常情况下也能回调。 - whenComplete:能接受正常或者异常的回调,并且不影响上个阶段的返回值,也就是主线程能获取到上个阶段的返回值;当出现异常时,whenComplete并不能吞了这个异常,也就是说主线程在获取执行异常任务的结果时,会抛出异常。
示例:
@Test
public void then(){
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 10)
.thenApply(v -> ("上一步的执行的结果为:" + v));
System.out.println(completableFuture1.join());
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 10)
.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("上一步执行完成"));
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 10)
.thenAccept(v -> System.out.println("上一步执行完成,结果为:" + v));
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture5 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 100;
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println("出现异常了,返回默认值");
return 110;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture5.join());
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture6 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int i = 1 / 0;
return 100;
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println("出现异常了,返回默认值");
return 110;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture6.join());
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture4 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//模拟异常
int i = 1 / 0;
return 10;
}).thenApply(v -> ("上一步的执行的结果为:" + v));
System.out.println(completableFuture4.join());
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture7 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int i = 1 / 0;
return 10;
}).whenComplete((r, e) -> {
System.out.println("whenComplete被调用了");
});
System.out.println(completableFuture7.join());
}
上一步的执行的结果为:10
上一步执行完成
上一步执行完成,结果为:10
100
出现异常了,返回默认值
110
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
whenComplete被调用了
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
5、对任务结果进行合并
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine
(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
这个方法的意思是,当前任务和other任务都执行结束后,拿到这两个任务的执行结果,回调 BiFunction ,然后返回新的结果。
6、以Async结尾的方法
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
thenAcceptAsync跟thenAccept的主要区别就是thenAcceptAsync会重新开一个线程来执行下一阶段的任务,而thenAccept还是用上一阶段任务执行的线程执行。
两个thenAcceptAsync主要区别就是一个使用默认的线程池来执行任务,也就是ForkJoinPool,一个是使用方法参数传入的线程池来执行任务。
当然除了thenAccept方法之外,上述提到的方法还有很多带有Async结尾的对应的方法,他们的主要区别就是执行任务是否开启异步线程来执行的区别。
CompletableFuture实战测试:
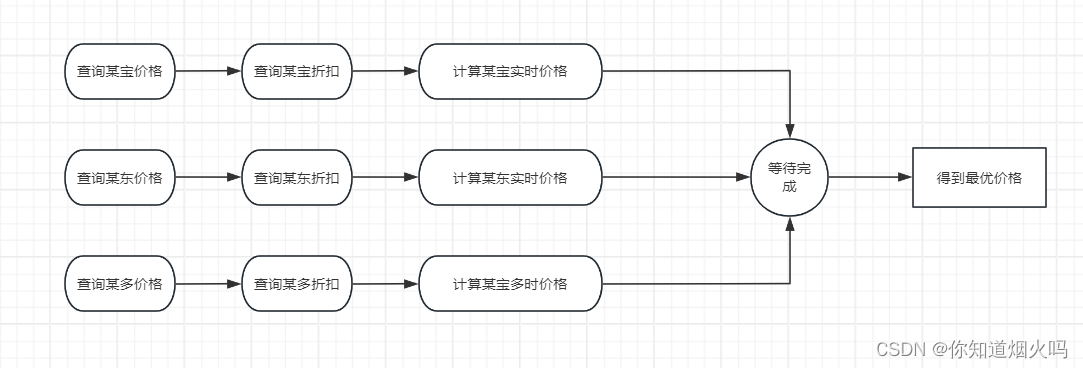
场景:
- 从某宝、某东、某多多去获取某个商品的价格、折扣
- 并计算出实际付款金额
- 最终返回最优的平台与价格信息
多线程形式:
@Slf4j
public class CompleteFutureTest1 {
static ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
50,
100,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(200),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) {
userFutureTask();
}
private static void userFutureTask(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<BigDecimal> moubaoFuture = threadPool.submit(() -> {
// 1、查询某宝价格
log.info("查询 某宝价格");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("100");
// 2、查询某宝折扣
log.info("查询 某宝折扣");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
BigDecimal discount = new BigDecimal("0.6");
// 3、计算某宝实时价格
log.info("计算 某宝实时价格");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
return bigDecimal.multiply(discount);
});
Future<BigDecimal> moudongFuture = threadPool.submit(() -> {
// 1、查询某宝价格
log.info("查询 某东价格");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("100");
// 2、查询某宝折扣
log.info("查询 某东折扣");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
BigDecimal discount = new BigDecimal("0.6");
// 3、计算某宝实时价格
log.info("计算 某东实时价格");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
return bigDecimal.multiply(discount);
});
Future<BigDecimal> mouduoFuture = threadPool.submit(() -> {
// 1、查询某宝价格
log.info("查询 某多价格");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("100");
// 2、查询某宝折扣
log.info("查询 某多折扣");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
BigDecimal discount = new BigDecimal("0.6");
// 3、计算某宝实时价格
log.info("计算 某多实时价格");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
return bigDecimal.multiply(discount);
});
BigDecimal minPrice = Stream.of(moubaoFuture, moudongFuture, mouduoFuture)
.map(priceResultFuture -> {
try {
return priceResultFuture.get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception:{}", e.getMessage());
return null;
}
})
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.sorted(BigDecimal::compareTo)
.findFirst()
.get();
log.info("minPrice: {}", minPrice);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("耗时: {}" + (end - start));
}
}
17:54:09.417 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 查询 某宝价格
17:54:09.417 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 查询 某东价格
17:54:09.417 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 查询 某多价格
17:54:11.421 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 查询 某多折扣
17:54:11.421 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 查询 某东折扣
17:54:11.421 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 查询 某宝折扣
17:54:13.421 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 计算 某宝实时价格
17:54:13.421 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 计算 某东实时价格
17:54:13.421 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 计算 某多实时价格
17:54:15.422 [main] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - minPrice: 60.0
17:54:15.423 [main] INFO com.ooamo.example.E13.CompleteFutureTest1 - 耗时: {}6050
使用多线程的方法去实现,耗时为6s
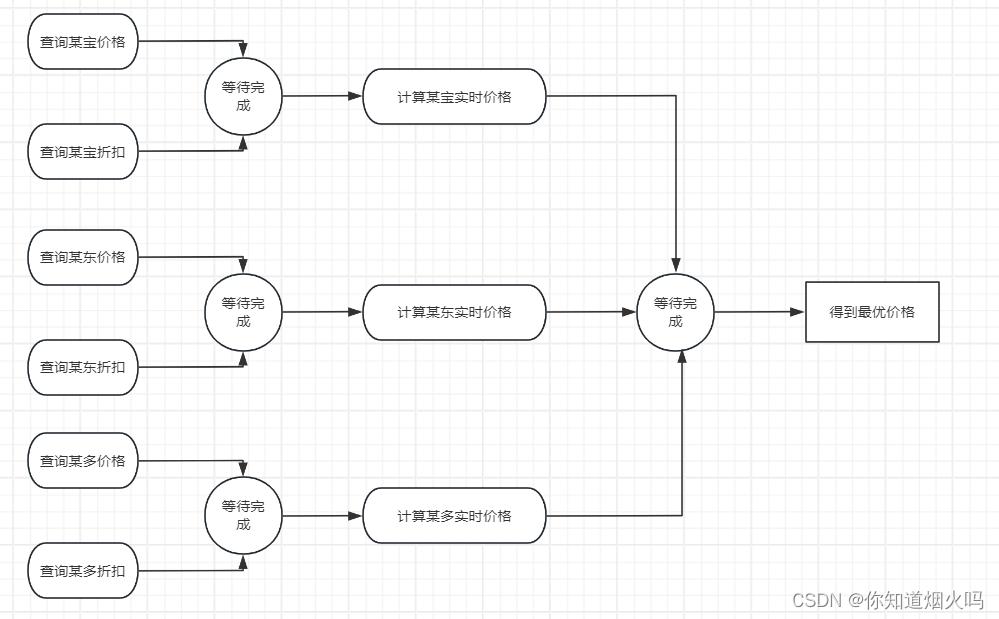
CompletableFuture形式:
@Slf4j
public class CompleteFutureTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
userFutureTask();
}
private static void userFutureTask(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<BigDecimal> moubao = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 1、查询某宝价格
log.info("查询 某宝价格");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new BigDecimal("100");
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 2、查询某宝折扣
log.info("查询 某宝折扣");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new BigDecimal("0.6");
}), CompleteFutureTest2::computeRealPrice);
CompletableFuture<BigDecimal> moudong = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 1、查询某宝价格
log.info("查询 某东价格");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new BigDecimal("100");
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 2、查询某宝折扣
log.info("查询 某东折扣");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new BigDecimal("0.6");
}), CompleteFutureTest2::computeRealPrice);
CompletableFuture<BigDecimal> mouduo = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 1、查询某宝价格
log.info("查询 某多价格");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new BigDecimal("100");
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 2、查询某宝折扣
log.info("查询 某多折扣");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new BigDecimal("0.6");
}), CompleteFutureTest2::computeRealPrice);
BigDecimal minPrice = Stream.of(moubao, mouduo, moudong).map(future -> {
try {
return future.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).filter(Objects::nonNull).sorted(BigDecimal::compareTo).findFirst().get();
log.info("minPrice: {}", minPrice);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("耗时: {}" + (end - start));
}
private static BigDecimal computeRealPrice(BigDecimal price, BigDecimal discount){
log.info("计算价格");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return price.multiply(discount);
}
}
18:10:35.199 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-6] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 查询 某多折扣
18:10:35.199 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 查询 某宝折扣
18:10:35.199 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 查询 某宝价格
18:10:35.199 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-4] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 查询 某东折扣
18:10:35.199 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-13] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 查询 某多价格
18:10:35.199 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-11] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 查询 某东价格
18:10:37.203 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 计算价格
18:10:37.203 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-4] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 计算价格
18:10:37.203 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-13] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 计算价格
18:10:39.203 [main] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - minPrice: 60.0
18:10:39.205 [main] INFO com.ooamo.example.E14.CompleteFutureTest2 - 耗时: {}4038
使用CompletableFuture的方法耗时为4s








 本文详细介绍了CompletableFuture在Java1.8中的功能,包括其与Future的区别、实例化方法、获取任务结果、主动触发任务、回调处理、结果合并以及在多线程场景下的实战应用。
本文详细介绍了CompletableFuture在Java1.8中的功能,包括其与Future的区别、实例化方法、获取任务结果、主动触发任务、回调处理、结果合并以及在多线程场景下的实战应用。














 8680
8680











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








