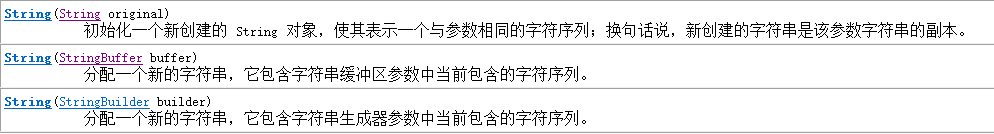
String类
一、构造函数:
1.使用byte字节数组作为参数构造String
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte b[] = {97,98,99};
String s = new String(b);
System.out.println("s="+s);结果:s=//abc
}
}
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] b = { -60, -29 };
String s4 = null;
try {
s4 = new String(b, "gb2312");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("s4=" + s4);//结果:s4=你
}
}
2.使用Char字符数组作为参数构造String
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char []c = {'a','b','c','d'};
String s = new String(c);
System.out.println("s = "+s);//结果:s = abcd
String s2 = new String(c, 1, 2 );
System.out.println("s2 = "+s2);//结果:s2 = bc
}
}
3.使用String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer等作为参数构造String
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Abcde");
String s = new String(sb);
System.out.println("s = "+s+",sb = "+sb);
//结果:s = Abcde,sb = Abcde
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder("ees23d");
String s2 = new String(sb2);
System.out.println("s2 = "+s2+",sb2 = "+sb2);
//结果:s2 = ees23d,sb2 = ees23d
}
}
二、常用的方法:
1.获取:
int length():获取字符串长度(返回int)。
char charAt(int index):返回指定索引处的 char 值。
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s.length()); //长度:6
System.out.println(s.charAt(3));//索引3:d
}
}
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = new String("abcdefdfabcd");
int index = s.indexOf('d');
System.out.println(index); //d的索引:3
int index2 = s.indexOf('d', 4);
System.out.println(index2);//从索引4开始索引d:6
int index3 = s.indexOf("abcd");
System.out.println(index3);//"abcd"字串出现在索引:0
int index4 = s.indexOf("abcd", 3);
System.out.println(index4);//从索引3开始,字符串"abcd"出现的索引是:8
}
}
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdefdfabcd";
int index1 = s.lastIndexOf('d');
//从后往前,第一个出现的字符d的索引是:11
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = s.lastIndexOf('d', 10);
//从索引10往前找,第一个出现的字符d的索引是:6
System.out.println(index2);
int index3 = s.lastIndexOf("abcd");
//从后往前,第一次出现字符串"abcd"的索引是:8
System.out.println(index3);
int index4 = s.lastIndexOf("abcd", 7);
//从索引7往前找,第一次出现字符串"abcd"的索引是:0
System.out.println(index4);
}
}
注意:
参数:
beginIndex - 起始索引(包括)。
endIndex - 结束索引(不包括)。
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdefghi";
System.out.println(s.substring(5)); // 结果:fghi
System.out.println(s.substring(3, 5));// 结果:de
}
}
2.转换:
byte[] getBytes():使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
char[] toCharArray():将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组。
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdefghi";
System.out.println(s.substring(5)); // 结果:fghi
System.out.println(s.substring(3, 5));// 结果:de
byte[] b = s.getBytes();
// 返回:97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
System.out.print(b[i] + ",");
}
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
// 返回字符数组:a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
System.out.print(c[i] + ",");
}
}
}
String[] split(String regex):根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
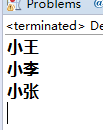
String s = "小王,小李,小张";
String []s2 = s.split(",");
for (int i = 0; i < s2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s2[i]);
}
}
}
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "小王.小李.小张";
String []s2 = s.split("\\.");
for (int i = 0; i < s2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s2[i]);
}
}
}
注意:如果使用小数点”.”做分割,那么必须转译,而且必须是两次,因为”.”和”.”都是正则表达式中的符号。
String toUpperCase():使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。
String toLowerCase():使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写。
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdeFGHI";
//只改变了小写部分:ABCDEFGHI
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
//只改变了大写部分:abcdefghi
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
}
}
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar):返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。
String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。
public class Demo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "apple";
System.out.println(s.replace('p', 'o'));//结果:aoole
System.out.println(s.replaceAll("pp", "ee"));//结果:aeele
}
}
String trim():返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白。
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = " a b c ";
//只能去掉开头和结尾的空白,实用:用户输入登录名误输入空格
System.out.println(s.trim());//结果:a b c
}
}
String concat(String str):将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。
和”+”功能差不多,感觉更牛!。。。
3.判断:
boolean isEmpty():当且仅当 length() 为 0 时返回 true。
boolean equals(Object anObject):将此字符串与指定的对象比较。
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString):将此 String 与另一个 String 比较,不考虑大小写。
boolean startsWith(String prefix):测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始。
boolean endsWith(String suffix):测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。
boolean contains(CharSequence s):当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true。
注:
使用:
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "javademo";
s.isEmpty();//false
s.equals("javademo");//true
s.equalsIgnoreCase("JaVaDeMo");//true
s.startsWith("j");//true
s.endsWith("x");//false
s.contains("java");//true
}
}
4.比较:
int compareTo(String anotherString)按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
public class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcdefg";
String s2 = "bcdefgh";
String s3 = "abcdefg";
String s4 = "azdas";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//负数:小于
System.out.println(s2.compareTo(s1));//正数:大于
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3));//0:等于
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4));//-24:比较了字符'z'和'b',返回差值24
/**总结:说明compareTo比较的是按字符逐个比较,例如:
"azdas"和"abcdefg",字符'a'比较相等,则比较字符'z'和'b',并返回差值,
之后就不比较了。
*/
}
}
String intern():当调用 intern 方法时,如果池已经包含一个等于此 String 对象的字符串(用 equals(Object) 方法确定),则返回池中的字符串。否则,将此 String 对象添加到池中,并返回此 String 对象的引用。
它遵循以下规则:对于任意两个字符串 s 和 t,当且仅当 s.equals(t) 为 true 时,s.intern() == t.intern() 才为 true。
我的理解:例如,String s1 =”abc”;String s2 = “abc”.intern();则s1=s2,指向同一个对象。可以理解为,如果常量池存在调用intern()的对象,则返回该对象的引用。
public class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
String s2 = new String("abcd");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
String s3 = s1.intern();
String s4 = s2.intern();
System.out.println(s3==s4);//true
System.out.println(s1==s3);//true
System.out.println(s2==s3);//false
}
}
**练习:**1.给定一个字符串数组,按照字典顺序进行从小到大的排序
{“nba”,”abc”,”cba”,”zz”,”qq”,”haha”}
public class Test1{
public static void main(String []args){
String []arr = {"www","nba","abc","cba","zz","qq","haha","aaa"};
printArray(arr);
String []s1 = sortArray(arr);
printArray(s1);
}
public static String[] sortArray(String []arr){
boolean flag = true;
for(int i = 1;i<arr.length&&flag;i++){
flag = false;
for(int j=0;j<arr.length-i;j++){
if((arr[j].compareTo(arr[j+1]))>0){
swap(arr,j,j+1);
flag = true;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
public static void swap(String []s,int j,int i){
String temp = s[j];
s[j] = s[i];
s[i] = temp;
}
public static void printArray(String []arr){
System.out.print("{");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(i!=arr.length-1){
System.out.print(arr[i]+",");
}else{
System.out.print(arr[i]+"}");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
2.一个字串在整串中出现的次数
例如:”nbaernbatynbauinbaopnba”中”nba”有5次!
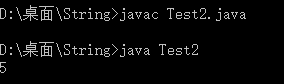
public class Test2{
public static void main(String []args){
String s = "nbaernbatynbauinbaopnba";
String key = "nba";
int count = getCounts(s,key);
System.out.println(count);
}
public static int getCounts(String s,String key){
int index = 0,count = 0;
while((index = s.indexOf(key,index))!=-1){
count++;
index = index + key.length();
}
return count;
}
}
3.两个字符串中最大相同的字串
“qwerabcdtyuioq”
“xcabcdvbn”
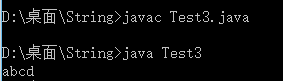
public class Test3{
public static void main(String []args){
String s1 = "qwerabcdtyuioq";
String s2 = "xcabcdvbn";
String s = getMaxSubstring(s1,s2);
System.out.print(s);
}
public static String getMaxSubstring(String s1,String s2){
String max = (s1.length()>s2.length()?s1:s2);
String min = (max.equals(s1)?s2:s1);
String temp = null;
for(int i=0;i<max.length();i++){
for(int first=0,last=max.length()-i;last<max.length()+1;first++,last++){
temp = max.substring(first,last);
if(min.contains(temp)){
return temp;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
4.模拟一个trim功能方法,去除字符串两端空白
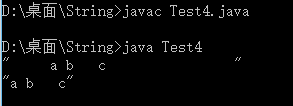
public class Test4{
public static void main(String []args){
String s = " a b c ";
stringPrint(s);
String s2 = myTrim(s);
stringPrint(s2);
}
public static void stringPrint(String s){
System.out.print("\"");
System.out.print(s);
System.out.print("\"");
System.out.println();
}
public static String myTrim(String s){
int start = 0;
int end = s.length()-1;
while(start<=end&&s.charAt(start)==' '){
start++;
}
while(start<=end&&s.charAt(end)==' '){
end--;
}
return s.substring(start,end+1);
}
}
StringBuffer类
StringBuffer:就是字符缓冲区,用于存储数据的容器。它是线程安全的。与之对应的有StringBuilder。
特点:
1.长度可变
2.可以存储不同类型数据
3.最终要转变成字符串进行使用
一、构造函数:
可以看到,StringBuffer没有String那么多构造方法,只有通过new来构建。并且它默认构建初始容量为16个字节的字符缓冲区。
StringBuffer sb =new StringBuffer("abc");
二、常用的方法:
1.添加
StringBuffer append(data):将数据添加到序列,并返回当前引用。
StringBuffer insert(index,data)在指定位置插入数据。
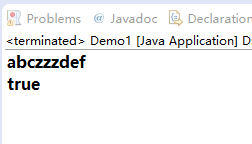
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb1 =new StringBuffer("abc");
StringBuffer sb2 = sb1.append("def");
StringBuffer sb3 = sb1.insert(3, "zzz");
System.out.println(sb1);
System.out.println(sb3==sb1&&sb3==sb2&&sb1==sb2);
}
}
p.s:append()方法被调用后,返回了当前引用,所以,sb1,sb2,sb3指向同一个引用。
2.查找
1.char charAt(index)
2.intindexOf(String str, int fromIndex):从指定的索引处开始,返回第一次出现的指定子字符串在该字符串中的索引。
int indexOf(String str)
3.int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):返回最后一次出现的指定子字符串在此字符串中的索引。
int lastIndexOf(String str)
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("apple");
char c = sb1.charAt(4);
System.out.println(c);//结果:e
int index = sb1.indexOf("p", 1);
System.out.println(index);//结果:1
int index2 = sb1.lastIndexOf("p",4);
System.out.println(index2);//结果:2
}
}
3.删除
StringBuffer delete(int start, int end): 移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。(包含头,不包含尾)
StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index):移除此序列指定位置的 char。
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("abcde");
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("abc");
sb1.deleteCharAt(3);
System.out.println(sb1);//结果:abce
sb2.delete(1, 2);
System.out.println(sb2);//结果:ac
}
}
4.修改
StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str):使用给定 String 中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。(包含头,不包含尾!)
void setCharAt(int index, char ch):将给定索引处的字符设置为 ch。
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("java");
sb1.setCharAt(2, 'b');
System.out.println(sb1);//结果:jaba
sb1.replace(0, 3, "dot");
System.out.println(sb1);//返回:dota
}
}
5.其他方法:
StringBuffer reverse():将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。
CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end):返回一个新的字符序列,该字符序列是此序列的子序列。(包含头,不包含尾!)
String substring(int start, int end):返回一个新的 String,它包含此序列当前所包含的字符子序列。(包含头,不包含尾!)
String substring(int start):返回一个新的 String,它包含此序列当前所包含的字符子序列。
String substring(int start)
void setLength(int newLength):设置字符序列的长度。
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("abcdefg");
String s1 = (String) sb1.subSequence(2, 4);
System.out.println(s1);//结果:cd
String s2 = sb1.substring(1, 5);
System.out.println(s2);//结果:bcde
sb1.reverse();
System.out.println(sb1);//反转结果:gfedcba
}
}
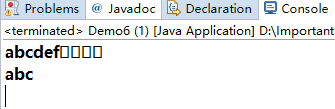
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("abcdef");
//设置长度小于原长度
sb1.setLength(10);
System.out.println(sb1);
//设置长度大于原长度
sb1.setLength(3);
System.out.println(sb1);
}
}
p.s.
setLength()方法改变了字符缓冲区长度:
1.若小于已有字符序列长度,相当于清除一部分内容。
2.若大于已有字符串长度,相当于扩充缓冲区,扩充部分内容用空格字符填充。
StringBuilder类
一个可变的字符序列。此类提供一个与 StringBuffer 兼容的 API,但不保证同步。该类被设计用作 StringBuffer 的一个简易替换,用在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候(这种情况很普遍)。如果可能,建议优先采用该类,因为在大多数实现中,它比 StringBuffer 要快。
注意:将 StringBuilder 的实例用于多个线程是不安全的。如果需要这样的同步,则建议使用 StringBuffer。
JDK一把升级的目的:
1.简化书写
2.tigaoxiaolv
3.增加安全性
/**
*将一个字符数组变成字符串:
*arr[] = {3,1,5,4,8}
*最好带一个格式[3,1,5,4,8]
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer []arr = {3,1,5,4,8};
String s = arrayToString(arr);
System.out.println(s);
}
public static String arrayToString(Integer []arr) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i!=arr.length-1){
sb.append(arr[i]).append(",");
}else{
sb.append(arr[i]).append("]");
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
基本数据类型的对象包装类
为了方便基本数据类型的操做,将其封装成对象,在对象里定义了属性并丰富了该数据的操作。
用于描述该对象的类称为基本数据类型对象包装类。
| 基本类型 | 类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
包装对象主要用于字符串和基本数据类型之间的转换:
基本类型—->字符串:
String类中的方法:valueOf();
字符串—->基本类型
1.使用包装类中的静态方法:
static int parseInt(String s):将字符串参数作为有符号的十进制整数进行解析。
static long parseLong(String s):将 string 参数解析为有符号十进制 long。
static short parseShort(String s):将字符串参数解析为有符号的十进制 short。
static boolean parseBoolean(String s):将字符串参数解析为 boolean 值。
2.使用静态方法valueOf(String s);将字符串转换成基本类型。
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//基本类型---->字符串:
int j = 123;
String s = String.valueOf(j);
System.out.println(s+1);//结果:1231,说明是字符串
//字符串---->基本类型
String s1 = "1234";
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(s1);
System.out.println(i+1);//结果:1235,说明是数字
int k = Integer.parseInt(s1);
System.out.println(k+2);//结果:1236,说明是数字
if(Boolean.parseBoolean("true")&&Boolean.valueOf("true")){ //true
System.out.println("true");
}
}
}
十进制—->其他进制
static String toBinaryString(int i):以二进制(基数 2)无符号整数形式返回一个整数参数的字符串表示形式。
static String toHexString(int i):以十六进制(基数 16)无符号整数形式返回一个整数参数的字符串表示形式。
static String toOctalString(int i):以八进制(基数 8)无符号整数形式返回一个整数参数的字符串表示形式。
static String toString(int i, int radix):返回用第二个参数指定基数表示的第一个参数的字符串表示形式。
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//二进制
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(9));//结果:1001
//十六进制
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(17));//结果:11
//八进制
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(10));//结果:12
//自定义进制
//1.自定义四进制
System.out.println(Integer.toString(8, 4));//结果:20
//2.自定义五进制
System.out.println(Integer.toString(9, 5));//结果:14
}
}
其他进制—->十进制
static int parseInt(String s, int radix):使用第二个参数指定的基数,将字符串参数解析为有符号的整数。
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//二进制转十进制
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("110", 2));//结果:6
//二进制转八进制
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("11", 8));//结果:9
//二进制转十六进制
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("3c", 16));//结果:60
}
}
练习:
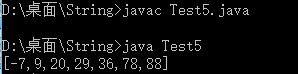
public class Test5{
public static void main(String []args){
String s = "20 78 9 -7 88 36 29";
// 1.将字符串转换为字符数组
String []sar = toStringArray(s);
// 2.将字符数组转换成int数组
int []arr = tointArray(sar);
// 3.排序
sortArray(arr);
printArray(arr);
}
// int数组打印
public static void printArray(int []arr){
System.out.print("[");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(i!=arr.length-1){
System.out.print(arr[i]+",");
}else{
System.out.print(arr[i]+"]");
}
}
}
// 字符串切割,转字符数组
public static String[] toStringArray(String s){
String []arr = s.split(" ");
return arr;
}
// String数组转int数组
public static int[] tointArray(String []s){
int []arr = new int[s.length];
for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[i]);
}
return arr;
}
// 排序
public static void sortArray(int []arr){
boolean flag = true;
for(int i=1;i<arr.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arr.length-i;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}






























 371
371

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








