一、节点流与处理流
1、节点流:封装数据源的流
2、处理流:封装其它流对象的流
二、字节缓冲流
1、两个类
BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputStream
2、作用
提高字节传输效率
3、使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream("E:/abc.png");
BufferedInputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream(in);
int size=0;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("E:/abc2.png");
BufferedOutputStream bout=new BufferedOutputStream(out);
while((size=bin.read(bytes))!=-1){
bout.write(bytes,0,size);
}
bin.close();
bout.flush();// 刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区中所有的字节全部写入到对应文件中
bout.close();
}4、核心
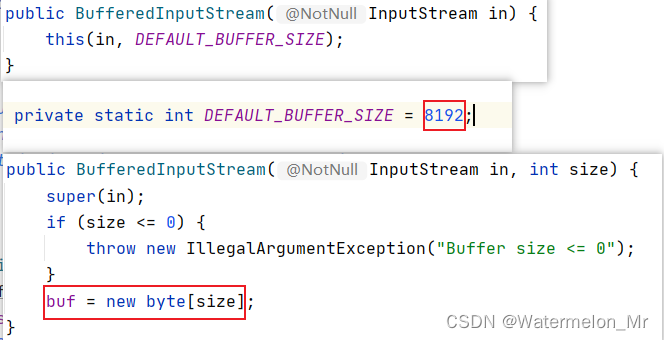
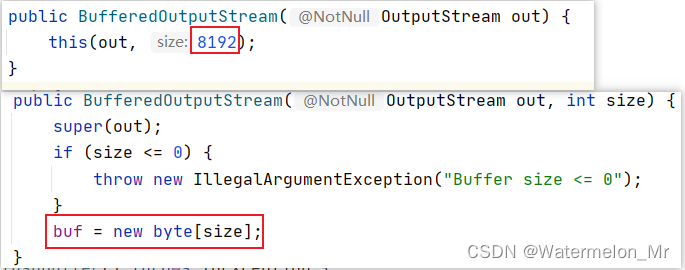
两个类中都有默认长度为8192的缓冲数组,通过缓冲数组可提高传输字节的效率
BufferedInputStream中有一个默认长度为8192的数组,可自定义数组大小
![]()
BufferedOutputStream中有一个默认长度为8192的数组,可自定义数组大小
![]()
BufferedOutputStream中write方法源码:
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (len >= buf.length) {
/* If the request length exceeds the size of the output buffer,
flush the output buffer and then write the data directly.
In this way buffered streams will cascade harmlessly. */
flushBuffer();
out.write(b, off, len);
return;
}
if (len > buf.length - count) {
flushBuffer();
}
System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);
count += len;
}三、数据输入输出流
1、两个类
DataOutputStream
DataInputStream
2、作用
在输出流中将字节数组转为字符串
在输入流中奖字符串转为字节数组
3、使用
使用字节流FileOutputStream和FileInputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s="你好";
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("E:/c.txt");
byte[]bytes=s.getBytes();
out.write(bytes);// 实际向外发送时,需要转为byte数组
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream("E:/c.txt");
byte[]bytes1=new byte[100];
int size=in.read(bytes1);// 对方接收之后,拿到的也是byte数组
s=new String(bytes1,0,size);
System.out.println(s);
}使用处理流DataOutputStream、DataInputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("E:/c.txt");
DataOutputStream dou=new DataOutputStream(out);
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream("E:/c.txt");
DataInputStream din=new DataInputStream(in);
String s="你好";
dou.writeUTF(s);// 传到文件外的是字节数组,在底层完成了字节数组向字符串的转换
s=din.readUTF();// 传到程序外的是字符串,在底层完成了字符串向字节数组的转换
System.out.println(s);
}注意:在使用readUTF进行读取读取的必须是writeUTF写入的字符串
五、字符流
1、文件输入字符流 FileReader
2、文件输出字符流 FileWriter
3、使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader=new FileReader("E:/a.txt");
FileWriter writer=new FileWriter("E:/d.txt");
char[]chars=new char[100];
int size=0;
while((size=reader.read(chars))!=-1){
writer.write(chars,0,size);
}
reader.close();
writer.close();
}四、字符缓冲流
1、两个流
字符缓冲输入流:BufferedReader
字符缓冲输出流:BufferedWriter
2、作用
提高传输效率;实现数据持久性保存
3、核心
底层有一个大小为8192的缓冲数组
4、使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader=new FileReader("E:/a.txt");
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(reader);
FileWriter writer=new FileWriter("E:/e.txt",true);// true: 输出时,保持原有内容不变,将新内容追加到原有内容后面
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter=new BufferedWriter(writer);
// 一次读取一行数据,并返回对应字符串,读完返回null
String s=null;
while((s=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
bufferedWriter.write(s);// 一次向外输出一个字符串
bufferedWriter.newLine();// 插入一个换行符
}
bufferedReader.close();
bufferedWriter.flush();
bufferedWriter.close();
}六、Printer打印流
1、特点
只有输出没有输入
2、分类
1、字节打印流
2、字符打印流
(1)1个类
PrintWriter
(2)作用
用于服务器端向客户端响应数据
(3)举例
服务器端的java程序向浏览器客户端输出一段前端代码,通过浏览器解析之后可在浏览器界面中显示出对应的效果
(4)使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintWriter printWriter=new PrintWriter("E:/index.html");
printWriter.write("<h1>你好,中国</h1>");
printWriter.close();
}七、对象输入流和对象输出流
1、两个类
ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream
2、作用
实现运行中对象信息的持久保存
3、用途
有时候,需要将运行中的对象信息持久保存起来,但对象在内存中,程序如果终止,对象信息就不存在了,如游戏中服务器更新
4、两个关键词
(1)对象的序列化:将对象信息输出文件的过程
(2)对象的反序列化:将对象信息从文件输入到java程序的过程,会在内存中重新创建新的对象保存数据,因此,对象的反序列化也是java中创建对象的一种方式
5、使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("E:/f.txt");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream=new ObjectOutputStream(out);
Date date=new Date();// 记录当前对象创建的时间
String s=new String("abc");
// 将对象信息保存到文件中 (序列化)
objectOutputStream.writeObject(date);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(s);
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream("E:/f.txt");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream(in);
// 将对象信息从文件中取出来 (反序列化)
Date date1=(Date) objectInputStream.readObject();
String s1=(String)objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(date1);
System.out.println(s1);
objectOutputStream.flush();
objectOutputStream.close();
objectInputStream.close();
}八、序列化接口
1、自定义类要想实现对象的序列化,必须实现Serializable接口,否则会报java.io.NotSerializableException这个异常,
2、一旦一个类实现了Serializable接口,java的序列化机制会自动为该类生成一个唯一的序列化ID,这个ID被称为seriallVerUID
3、自定义类仅仅实现Serializable接口,如果该类的信息发生改变,那么在该类对象反序列化时会出现问题(该类会有多个UID),因此我们要使用idea工具为我们的类手动生成一个序列化ID
对idea工具做一个配置:Settings-->Editor-->INspections-->Java-->Seralization issues-->Serialzable class without 'serialVersionUID' 打钩

4、添加了transient关键字修饰的属性,在序列化对象时不会被保存到文件中






















 4533
4533

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








