I will analyze the process of the local video playback in Android 4.1 on Pandaboard. Hardware acceleration for HD video playback also will be discussed. You can read the official article about Media to get a big picture http://source.android.com/devices/media.html.
1. Video File
A video file usually contains two part: File Header and Coded Video Frames. So there are two steps for video playback: Parse file header and Decode video frames. The media player must implement the two functionalities. A media player consist of a media player engine and media codec plugin. The former is used to parse the file header, and the latter is used to decode video frames.
a general video file
2. Architecture Overview
The diagram shows the layers from media player application to DSP driver/firmware. Please keep the picture in your mind.
3. Multimedia Framework Evolution
The media player engine in Android is evolving. There are many articles on android media framework which are based on the different Android version. If you don't know about the media framework evolution, you may be confused by the articles. Both of the engine and the directory structure are changed.
- Engine
OpenCore was the player engine in Android 1.6. StareFright and Nuplayer replaced OpenCore gradually. StageFight is used to play the local media file. Nuplayer can play the stream online.

- Directory
In 4.1 JB: The native codes of Media Framework,
include libeffects, libmedia, libmediaplayerservice,
libstagefright, mediaserver,
are moved from
AOSP/frameworks/base/media
to
AOSP/frameworks/av/media
4. Jellybean MM Architecture
I got the diagram from internet. It shows the structure of the main classes/files in JellyBean's media framework.
5. Local Video Playback Process
The diagram shows a simple and clear local video playback process in JAVA API layer. In next sections, I will introduce the details under the APIs.
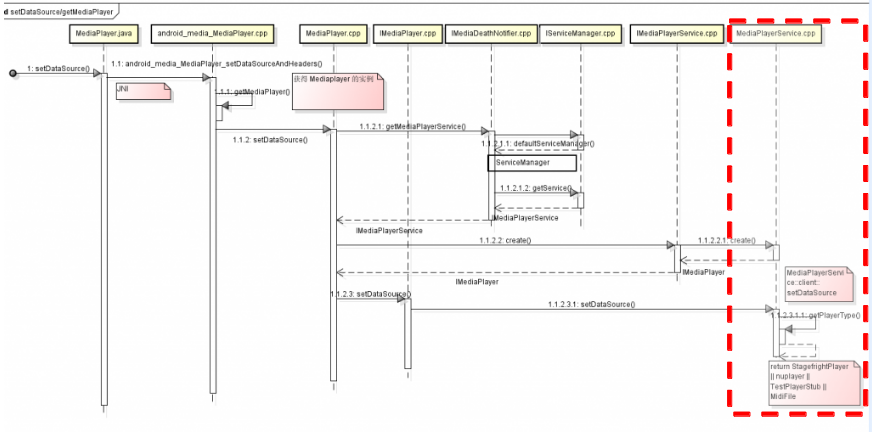
6. Select Media Player Engine
MediaPlayer::setDataSource() is a key function which is used to
- Get the proper media player engine for the specified media file type
- Create mediaExtractor to parse the metadata of the media file
We can follow the diagram to trace the code. Let's see how the correct player is selected. We call getPlayerType() to get the player type for the URL.
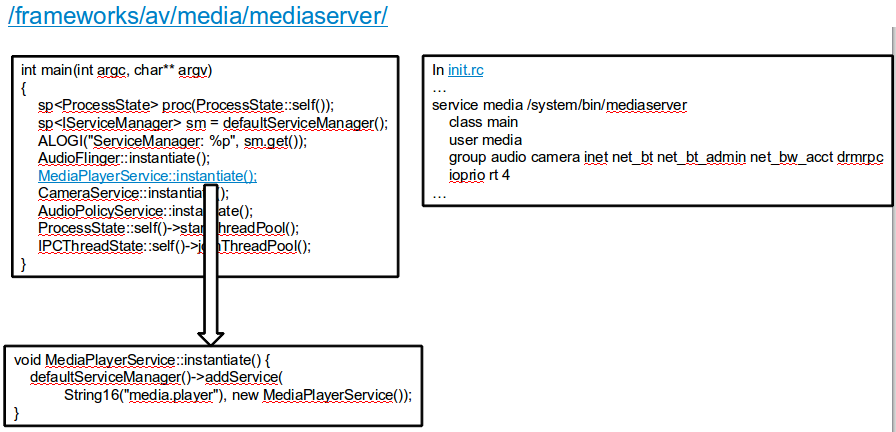
The rightest slot in the sequence diagram is MediaPlayerService, which is an important service in android. MediaPlayerService is added into Service Manger by Media Server which is started in Android boot process.
7. Load Media Codec Plugin
The correct media player engine is created. The engine can parse the file, but it can not decode the video frames. We need to load the Media Codec Plugin which will be connected with Media Player Engine to decode the video frames.
There are two plugins: hardware and software. AOSP implements a soft OMX plugin, while the chipset vendor usually implements a hardware OMX plugin. Let's see how the Hardware OMX plugin is created and added. The code for the two steps depends on the hardware platform. I will analyze the code on PandaBoard.
1. Create OMX Plugin.
The vendor's hardware OMX plugin is loaded dynamically from .so file.
TIOMXPlugin() initialize the function pointers, e.g. mInit, mGetHandle which will be used later.
In OMX plugin initialization function, a table of Media Format--Decoder mapping is created. We use the table to find matching decoder for the specific media format.
2. Add OMX Plugin
Now we can add the initialized plugin into the plugins list of media player engine. OMXMaster keeps the plugins list. The media player engine can get the pointer to OMXMaster. So Media Player Engine is connected with Media Codec.
8. Match and Init a Decoder
There are many MediaFormat--Decoder mappings in the ComponentTable of the plugin. We should find the matching decoder and initialize it. The process is complex, and there are 3 steps. The entrance is in MediaPlayer::prepareAsync().

1. Match a Codec.
There is a component table which keeps the Media Format--Decoder mapping for a plugin. We should find the matching codec in the table.
2. Create Video Decoder Component Thread.
The matching codec is found. Let's initialize it and create a thread for the decoder.
Do you remember where mGetHandle is initialized? This function loads the matching decoder dynamically, and then initializes the decoder component.
3. Start OMX Codec.
The decoder thread is running. We can send the command to initialize codec in DSP via DSP Bridge.
I think you should be confused by the OMX handle, component, decoder, LCML, Node, Bridge and so on. Let's see next section.
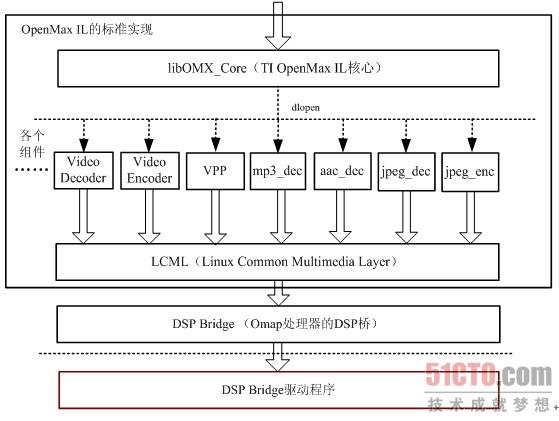
9. TI OpenMAX IL Architecture
It's helpful to read the OpenMax spec for understanding the code above. Don't just look at the diagram below, Read the OpenMax documents first!
10. Load DSP Bridge Driver and DSP firmware
The DSP Bridge driver is loaded into kernel in Android boot process. The driver loads the DSP firmware. Both of them are not open source.
useful links:
http://www.omappedia.org/wiki/DSPBridge_Project
http://elinux.org/BeagleBoard/DSP_Howto
If load successfully, you can see the message in log:
11. Boot kernel with DSP
The kernel boot parameters must be set for the memory section which is used by DSP.
useful link
http://code.google.com/p/rowboat/wiki/DSP#Boot








































 252
252

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








