线程同步
同步主线程与子线程
test.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void* ret_result_thread1;
sem_t *sem;
void* thread1Func(void* arg)
{
printf("childThread id:%u is running\n", syscall(SYS_gettid));
sleep(2);
sem_post(sem);
pthread_exit((void*)0);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("main thread start\n");
const char* semName="sem_name";
sem = sem_open(semName,O_CREAT,0644,0);
pthread_t thread1;
int ret1;
if( (ret1 = pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread1Func,NULL)) != 0)
{
perror("thread1 create failed");
}
sem_wait(sem);
printf("main thread end\n");
pthread_join(thread1,ret_result_thread1);
sem_close(sem);
sem_unlink(semName);
return 0;
}子线程之间的同步
使用单个信号量
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void* ret_result_thread1;
void* ret_result_thread2;
sem_t *sem;
void* thread1Func(void* arg)
{
printf("childThread1 is running\n");
sleep(2);
sem_post(sem);
pthread_exit((void*)0);
}
void* thread2Func(void* arg)
{
sem_wait(sem);
printf("childThread2 is running\n");
sleep(2);
pthread_exit((void*)0);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("main thread start\n");
const char* semName="sem_name";
sem = sem_open(semName,O_CREAT,0644,0);
pthread_t thread1,thread2;
int ret1;
int ret2;
if( (ret1 = pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread1Func,NULL)) != 0)
{
perror("thread1 create failed");
}
if( (ret2 = pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,thread2Func,NULL)) != 0)
{
perror("thread2 create failed");
}
printf("main thread end\n");
pthread_join(thread1,ret_result_thread1);
pthread_join(thread2,ret_result_thread2);
sem_close(sem);
sem_unlink(semName);
return 0;
}
使用两个信号量
test.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void* ret_result_thread1;
void* ret_result_thread2;
sem_t *sem1;
sem_t *sem2;
void* thread1Func(void* arg)
{
sem_wait(sem1);
printf("childThread1 is running\n");
sleep(2);
sem_post(sem2);
pthread_exit((void*)0);
}
void* thread2Func(void* arg)
{
sem_wait(sem2);
printf("childThread2 is running\n");
sleep(2);
sem_post(sem1);
pthread_exit((void*)0);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("main thread start\n");
const char* semName1="sem_name1";
sem1 = sem_open(semName1,O_CREAT,0644,1);
const char* semName2="sem_name2";
sem2 = sem_open(semName2,O_CREAT,0644,0);
pthread_t thread1,thread2;
int ret1;
int ret2;
if( (ret1 = pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,thread1Func,NULL)) != 0)
{
perror("thread1 create failed");
}
if( (ret2 = pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,thread2Func,NULL)) != 0)
{
perror("thread2 create failed");
}
printf("main thread end\n");
pthread_join(thread1,ret_result_thread1);
pthread_join(thread2,ret_result_thread2);
sem_close(sem1);
sem_close(sem2);
sem_unlink(semName1);
sem_unlink(semName2);
return 0;
}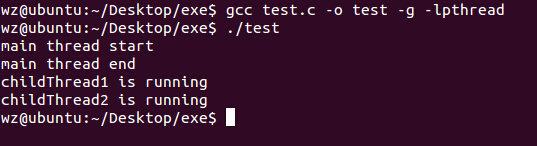
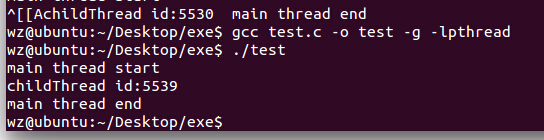
主线程运行结束后,线程1开始运行,休眠2秒后开始运行线程2






















 4437
4437

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








