decorator design pattern
装饰模式的概念、装饰模式的结构、装饰模式的优缺点、装饰模式的使用场景、装饰模式与代理模式的区别、装饰模式的实现示例、装饰模式的源码分析
1、装饰模式的概念
装饰模式,即在不改变现有对象结构的前提下,动态的给对象增加一些职责(即增加其额外功能)的模式。
2、装饰模式的结构
- 抽象组件角色:即被装饰对象的抽象角色,定义被装饰对象的行为属性。
- 具体组件角色:即被装饰的具体对象,继承抽象组件角色,实现其具体的对象行为。
- 装饰器角色:继承抽象组件角色,引用抽象组件角色。
- 具体装饰器角色:继承装饰器角色,实现其具体的装饰行为。

3、装饰模式的优缺点
- 优点:
- 装饰类和被装饰类可以独立发展,互不耦合。
- 代替继承模式,动态扩展一个类的功能。
- 缺点:
- 多层装饰比较复杂。
4、装饰模式的使用场景
-
当不能采用继承的方式扩展系统或采用继承的方式扩展系统不利于系统维护时。
不能采用继承的情况主要有两类:
- 系统中存在大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的子类,使系统类爆炸。
- 类定义不能被继承。
-
在不影响其它对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
-
当对象的功能要求可以动态增加、撤销时。
5、装饰模式与代理模式的区别
装饰模式与静态代理模式的区别:
- 相同点:
- 都要实现与目标类相同的业务接口。如装饰模式中的抽象组件角色,静态代理模式中的抽象目标。
- 在两个类中都要生命目标对象,即对目标对象的引用。
- 都可以在不修改目标类的前提下增强目标类。
- 不同点:
- 目的不同,装饰模式的目的是增强目标对象,代理模式的目的是保护目标对象。
- 获取目标对象的方式不同,装饰是由外界传递进来或通过构造方法获取的;代理模式是直接在代理类内部创建的,以此来隐藏目标对象。
6、装饰模式的实现示例
抽象组件角色:
public abstract class FastFood {
private String name;
private Float price;
public FastFood() {}
public FastFood(String name, Float price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Float price) {
this.price = price;
}
public abstract Float cost();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "FastFood{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
具体组件角色一:
public class NoodlesFastFood extends FastFood {
public NoodlesFastFood() {
super("面条", 12f);
}
@Override
public Float cost() {
return getPrice();
}
}
具体组件角色二:
public class RiceFastFood extends FastFood {
public RiceFastFood() {
super("米饭", 10f);
}
@Override
public Float cost() {
return getPrice();
}
}
装饰器:
public abstract class Decorator extends FastFood {
private FastFood fastFood;
public Decorator(FastFood fastFood, String name, Float price) {
super(name, price);
this.fastFood = fastFood;
}
public FastFood getFastFood() {
return fastFood;
}
public void setFastFood(FastFood fastFood) {
this.fastFood = fastFood;
}
}
具体装饰器一:
public class MeatDecorator extends Decorator {
public MeatDecorator(FastFood fastFood) {
super(fastFood, "肉", 8f);
}
@Override
public Float cost() {
setPrice(this.getFastFood().getPrice() + this.getPrice());
setName(this.getFastFood().getName() + this.getName());
return this.getPrice();
}
}
具体装饰器二:
public class VegetableDecorator extends Decorator {
public VegetableDecorator(FastFood fastFood) {
super(fastFood, "蔬菜", 2f);
}
@Override
public Float cost() {
setPrice(this.getFastFood().getPrice() + this.getPrice());
setName(this.getFastFood().getName() + this.getName());
return this.getPrice();
}
}
测试:
public class DecoratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FastFood fastFood = new NoodlesFastFood();
fastFood.cost();
System.out.println(fastFood);
fastFood = new MeatDecorator(fastFood);
fastFood.cost();
System.out.println(fastFood);
fastFood = new VegetableDecorator(fastFood);
fastFood.cost();
System.out.println(fastFood);
}
}
测试结果:
FastFood{name='面条', price=12.0}
FastFood{name='面条肉', price=20.0}
FastFood{name='面条肉蔬菜', price=22.0}
7、装饰模式的源码分析
jdk 的 io 设计中就用到了装饰模式。
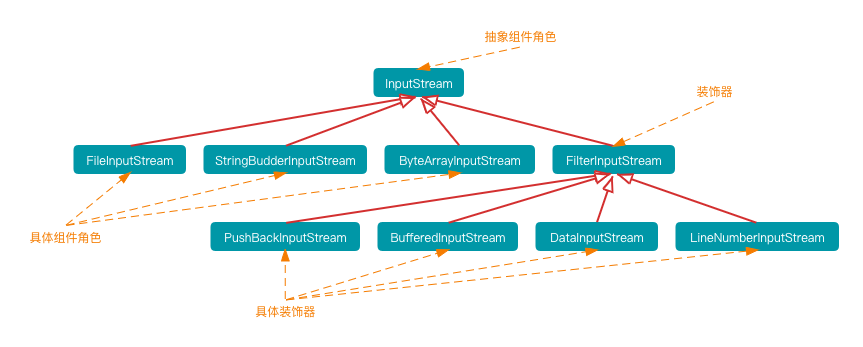
inputStream 作为抽象组件角色,其有多种扩展的具体组件角色,负责从不同的数据源输入,如从字节数组输入、从文件输入、从 String 对象产生输入等;同时其子类 FilterInputStream 为装饰器,且也有多个具体的装饰器实现,在这些装饰中都加入了缓冲的功能,避免每次读取时都进行实际的写操作。所以在此应用中给被装饰对象增加的职能就是缓冲的作用。
io 中的其它设计如 OutputStream、Writer、Reader 等都是用了装饰模式。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// fw 即被装饰的对象
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("/Users/xgllhz/Documents/project/local/test/test.txt");
// bw 即装饰器对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.write("hello world");
bw.close();
}
























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








