最新发现资源文件中sm2.c 654行(KDF函数中)的i++需要删除,现在CSDN付费资源不能修改,请下载的同学自行删除这行,十分抱歉!
在网上搜过关于SM2/SM3的资源,很少有在单片机上实现的代码。主要是因为大数运算基本都用 Miracl/Openssl库,移植到嵌入式平台上很麻烦。所以索性自己动手写了一下Fp域(质数域)下的SM2算法实现(动态申请内存)。包括SM2算法三步曲——数字签名,秘钥交换和公钥加密,以及SM3哈希杂凑算法的实现。由于SM3算法比较简单,所以本文主要介绍SM2算法。本文所有代码参考国家密码管理局官方文档https://sca.gov.cn/sca/xwdt/2010-12/17/1002386/files/b791a9f908bb4803875ab6aeeb7b4e03.pdf 完整代码点这里。有任何问题可以私信联系。
1. 国密SM2介绍
SM2是国家密码管理局于2010年12月17日发布的椭圆曲线公钥密码算法。SM2算法和RSA算法都是公钥密码算法,SM2算法是一种更先进安全的算法,在我们国家商用密码体系中被用来替换RSA算法。SM2是ECC(Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem)算法的一种,基于椭圆曲线离散对数问题,计算复杂度是指数级,求解难度较大,同等安全程度要求下,椭圆曲线密码较其他公钥秒速昂发所需密钥长度小很多。
随着密码技术和计算机技术的发展,目前常用的1024位RSA算法面临严重的安全威胁,我们国家密码管理部门经过研究,决定采用SM2椭圆曲线算法替换RSA算法。
2. SM2数字签名算法
数字签名算法由一个签名者对数据产生数字签名,并由一个验证者验证签名的可靠性。每个签名者有一个公钥和一个私钥,其中私钥用于产生签名,验证者用签名者的公钥验证签名。在签名的生成过程之前,要用密码杂凑函数对 M ‾ \overline{M} M (包含Z A _A A和待签消息M)进行压缩;在验证过程之前,要用密码杂凑函数对 M ‾ \overline{M} M’(包含Z A _A A和验证消息M′)进行压缩。
2.1 数字签名生成算法流程: 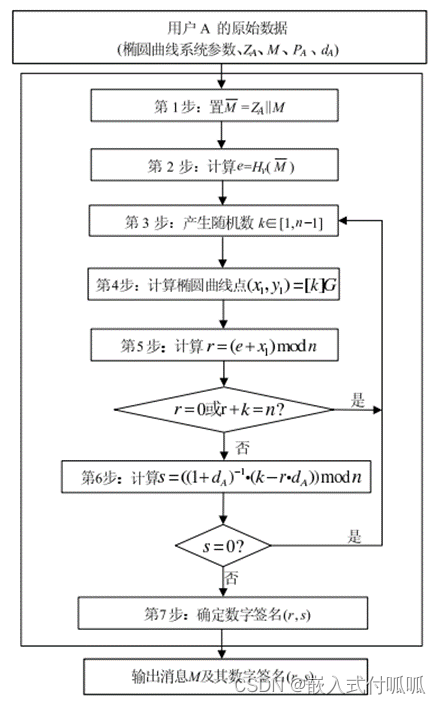

1. SM2Signature* SM2Sign(char* message, int messageSizeInBit, char* IDA, uint16_t ENTLAInBit, EccPoint* G, EccPoint* pubKey, uint64_t* privKey)
2. {
3. //ZA = SM3(ENT LA ∥ IDA ∥ a ∥ b ∥ xG ∥ yG ∥ xA ∥ yA)。
4. uint8_t* Z = malloc(2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32), * ZA = malloc(32);
5. uint256_t tmpN = { 0 };
6. SM2Signature* result = malloc(sizeof(SM2Signature));
7.
8. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
9. {
10. tmpN[i] = ellipticCurve_n[3 - i];
11. }
12. Z[0] = ENTLAInBit >> 8;
13. Z[1] = ENTLAInBit & 0xff;
14. memcpy(Z + 2, IDA, ENTLAInBit / 8);
15. Uint256ToString(ZA, Ec->a);
16. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8, ZA, 32);
17. Uint256ToString(ZA, Ec->b);
18. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32, ZA, 32);
19. Uint256ToString(ZA, G->x);
20. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 2, ZA, 32);
21. Uint256ToString(ZA, G->y);
22. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 3, ZA, 32);
23. Uint256ToString(ZA, pubKey->x);
24. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 4, ZA, 32);
25. Uint256ToString(ZA, pubKey->y);
26. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 5, ZA, 32);
27. SM3(Z, 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32, ZA);//ZA = SM3(ENT LA ∥ IDA ∥ a ∥ b ∥ xG ∥ yG ∥ xA ∥ yA)。
28. free(Z);
29.
30. uint8_t* M_ = malloc(messageSizeInBit / 8 + 32), * e = malloc(32);
31. memcpy(M_, ZA, 32);
32. memcpy(M_ + 32, message, messageSizeInBit / 8);
33. SM3(M_, messageSizeInBit / 8 + 32, e); //e = H256(M_):
34. free(M_);
35.
36. uint8_t* x1 = malloc(32), * y1 = malloc(32), * r = malloc(32), * s = malloc(32);
37. uint256_t randomK = { 0 }, tmpE = { 0 }, tmpX = { 0 }, tmpR = { 0 }, num1 = { 1 };
38. EccPoint* point1 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint));
39. GetRandomNumber(randomK, tmpN);
40. #ifdef DEBUG_MODE
41. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //测试时随机数先固定
42. {
43. randomK[i] = exRandomK[3 - i];
44. }
45. #endif
46.
47. CurvePointMul(point1, G, randomK);
48. Uint256ToString(x1, point1->x);
49. Uint256ToString(y1, point1->y);
50. free(point1);
51. StringToUint256(tmpE, e);
52. StringToUint256(tmpX, x1);
53. vli_modAdd(tmpR, tmpE, tmpX, tmpN);
54. Uint256ToString(r, tmpR); //r=(e+x1) modn
55.
56. vli_modAdd(tmpE, num1, privKey, tmpN);
57. vli_modInv(tmpX, tmpE, tmpN); //(1+dA)^-1
58. vli_modMult(tmpE, tmpR, privKey, tmpN);
59. vli_modSub(tmpE, randomK, tmpE, tmpN);
60. vli_modMult(tmpX, tmpX, tmpE, tmpN);
61. Uint256ToString(s, tmpX); //s = ((1+dA)^-1 * (k - r*dA))modn
62. memcpy(result->r, r, 32);
63. memcpy(result->s, s, 32);
64. free(ZA);
65. free(e);
66. free(x1);
67. free(y1);
68. free(r);
69. free(s);
70.
71. return result;
72. }
2.2 数字签名的验证算法及流程



注:如果Z
A
_A
A不是用户A所对应的杂凑值,验证自然通不过。
1. BOOL SM2SignatureVerify(char* message, int messageSizeInBit, SM2Signature* sign, char* IDA, uint16_t ENTLAInBit, EccPoint* G, EccPoint* pubKey)
2. {
3. uint256_t tmp = { 0 }, tmpN = { 0 }, num1 = { 1 };
4.
5. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
6. {
7. tmpN[i] = ellipticCurve_n[3 - i];
8. }
9. vli_modSub(tmpN, tmpN, num1, Ec->p); //因为n是大质数必定为奇数,所以这里可以直接n[0] = n[0] - 1,不必像我这样写
10. StringToUint256(tmp, sign->r);
11. if (IsZeroUint256(tmp) || vli_cmp(tmp, tmpN) >= 0) //make sure r∈[1,n-1]
12. {
13. return FALSE;
14. }
15. StringToUint256(tmp, sign->s);
16. if (IsZeroUint256(tmp) || vli_cmp(tmp, tmpN) >= 0) //make sure s∈[1,n-1]
17. {
18. return FALSE;
19. }
20. vli_modAdd(tmpN, tmpN, num1, Ec->p);
21.
22. //ZA = SM3(ENT LA ∥ IDA ∥ a ∥ b ∥ xG ∥ yG ∥ xA ∥ yA)。
23. uint8_t* Z = malloc(2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32), * ZA = malloc(32);
24.
25. Z[0] = ENTLAInBit >> 8;
26. Z[1] = ENTLAInBit & 0xff;
27. memcpy(Z + 2, IDA, ENTLAInBit / 8);
28. Uint256ToString(ZA, Ec->a);
29. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8, ZA, 32);
30. Uint256ToString(ZA, Ec->b);
31. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32, ZA, 32);
32. Uint256ToString(ZA, G->x);
33. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 2, ZA, 32);
34. Uint256ToString(ZA, G->y);
35. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 3, ZA, 32);
36. Uint256ToString(ZA, pubKey->x);
37. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 4, ZA, 32);
38. Uint256ToString(ZA, pubKey->y);
39. memcpy(Z + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 5, ZA, 32);
40. SM3(Z, 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32 + 32, ZA);//ZA = SM3(ENT LA ∥ IDA ∥ a ∥ b ∥ xG ∥ yG ∥ xA ∥ yA)。
41. free(Z);
42.
43. uint8_t* M_ = malloc(messageSizeInBit / 8 + 32), * e = malloc(32);
44. memcpy(M_, ZA, 32);
45. memcpy(M_ + 32, message, messageSizeInBit / 8);
46. SM3(M_, messageSizeInBit / 8 + 32, e); //e=H256(M_):
47. free(M_);
48.
49. uint256_t tmpR = { 0 }, tmpS = { 0 }, tmpT = { 0 };
50.
51. StringToUint256(tmpR, sign->r);
52. StringToUint256(tmpS, sign->s);
53. vli_modAdd(tmpT, tmpR, tmpS, tmpN); //t = (r' + s')modn
54.
55. EccPoint* point0 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)), * point00 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)),
56. * point1 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint));
57.
58. CurvePointMul(point0, G, tmpS); //point0 = s' * G
59. CurvePointMul(point00, pubKey, tmpT); //point00 = t * PA
60. CurvePointAdd(point1, point0, point00); //point1 = s'*G+t*PA
61. free(point0);
62. free(point00);
63.
64. uint8_t* r = malloc(32);
65. StringToUint256(tmpT, e); //只是把e存在tmpT里
66. vli_modAdd(tmpR, tmpT, point1->x, tmpN);
67. Uint256ToString(r, tmpR);
68. free(ZA);
69. free(e);
70. free(point1);
71.
72. for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
73. {
74. if (r[i] != sign->r[i])
75. {
76. free(r);
77. return FALSE;
78. }
79. }
80. free(r);
81. return TRUE;
82. }
3. 秘钥交换协议
密钥交换协议是两个用户A和B通过交互的信息传递,用各自的私钥和对方的公钥来商定一个只有他们知道的秘密密钥。这个共享的秘密密钥通常用在某个对称密码算法中。该密钥交换协议能够用于密钥管理和协商。



注:如果Z
A
_A
A、Z
B
_B
B不是用户A和B所对应的杂凑值,则自然不能达成一致的共享秘密值。
1. BOOL KeyExchangeCheck = TRUE;//可选项,是否要验证S2 == SA以及S1 == SB
2. BOOL SM2KeyExchange(char* IDA, uint32_t ENTLAInBit, char* IDB, uint32_t ENTLBInBit, EccPoint* G, int klenInBit)
3. {
4. EccPoint* RA = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)), * V = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)),
5. * U = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)),
6. * pubKeyA = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)), * pubKeyB = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)),
7. * RB = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint));
8. uint256_t tB = { 0 }, privKeyA = { 0 }, privKeyB = { 0 };
9. uint8_t* tmp = malloc(2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 6), * tmp1 = malloc(32);//用来算ZA ZB
10.
11. GenerateKeys(privKeyA, pubKeyA, G);
12. GenerateKeys(privKeyB, pubKeyB, G);
13. if (!(IsValidPoint(pubKeyA, Ec) && IsValidPoint(pubKeyB, Ec)))
14. {
15. return FALSE;
16. }
17.
18. #ifdef DEBUG_MODE
19. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //测试固定随机数
20. {
21. privKeyA[i] = exPrivateKey_A[3 - i];
22. privKeyB[i] = exPrivateKey_B[3 - i];
23. pubKeyA->x[i] = exPublicKey_Ax[3 - i];
24. pubKeyA->y[i] = exPublicKey_Ay[3 - i];
25. pubKeyB->x[i] = exPublicKey_Bx[3 - i];
26. pubKeyB->y[i] = exPublicKey_By[3 - i];
27. }
28. #endif
29. //双方的原始数据
30. KeyExchangeAOriginalInfoDef infoA =
31. { {0},{0},privKeyA[0],privKeyA[1],privKeyA[2],privKeyA[3],pubKeyA,pubKeyB,0,1,{0},G };
32. KeyExchangeBOriginalInfoDef infoB =
33. { {0},{0},privKeyB[0],privKeyB[1],privKeyB[2],privKeyB[3],pubKeyA,pubKeyB,0,1,{0},G };
34.
35. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
36. {
37. infoA.n[i] = ellipticCurve_n[3 - i];
38. infoB.n[i] = ellipticCurve_n[3 - i];
39. }
40. infoA.w = (int)(GetMSB(infoA.n) / 2 + 1) - 1; //w = [log2(n)/2] - 1 +1是向上取整,大质数取对数必带小数点
41. infoB.w = infoA.w;
42.
43. tmp[0] = ENTLAInBit >> 8;
44. tmp[1] = ENTLAInBit & 0xff;
45. memcpy(tmp + 2, IDA, ENTLAInBit / 8);
46. Uint256ToString(tmp1, Ec->a);
47. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8, tmp1, 32);
48. Uint256ToString(tmp1, Ec->b);
49. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32, tmp1, 32);
50. Uint256ToString(tmp1, G->x);
51. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 2, tmp1, 32);
52. Uint256ToString(tmp1, G->y);
53. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 3, tmp1, 32);
54. Uint256ToString(tmp1, pubKeyA->x);
55. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 4, tmp1, 32);
56. Uint256ToString(tmp1, pubKeyA->y);
57. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 5, tmp1, 32);
58. SM3(tmp, 2 + ENTLAInBit / 8 + 32 * 6, infoA.ZA);
59. memcpy(infoB.ZA, infoA.ZA, 32);
60.
61. tmp[0] = ENTLBInBit >> 8;
62. tmp[1] = ENTLBInBit & 0xff;
63. memcpy(tmp + 2, IDB, ENTLBInBit / 8);
64. Uint256ToString(tmp1, Ec->a);
65. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8, tmp1, 32);
66. Uint256ToString(tmp1, Ec->b);
67. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8 + 32, tmp1, 32);
68. Uint256ToString(tmp1, G->x);
69. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8 + 32 * 2, tmp1, 32);
70. Uint256ToString(tmp1, G->y);
71. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8 + 32 * 3, tmp1, 32);
72. Uint256ToString(tmp1, pubKeyB->x);
73. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8 + 32 * 4, tmp1, 32);
74. Uint256ToString(tmp1, pubKeyB->y);
75. memcpy(tmp + 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8 + 32 * 5, tmp1, 32);
76. SM3(tmp, 2 + ENTLBInBit / 8 + 32 * 6, infoB.ZB);
77. memcpy(infoA.ZB, infoB.ZB, 32);
78. free(tmp);
79. free(tmp1);
80.
81. uint256_t rA = { 0 };
82. SM2KeyExchange_AStep1To3(RA, rA, infoA); //A step1~3,generate RA
83.
84. SM2KeyExchange_BStep1To4(tB, RB, infoB); //B step1~4
85. if (!IsValidPoint(RA, Ec)) //B 判断RA是否满足曲线方程
86. {
87. return FALSE;
88. }
89. SM2KeyExchange_BStep5To6(V, tB, RA, infoB); //B step5~6
90. if (IsZeroPoint(V)) //B 判断V是否为(0,0)
91. {
92. return FALSE;
93. }
94.
95. uint8_t* SB = malloc(32), * KB = malloc(klenInBit / 8);
96. SM2KeyExchange_BStep7To9(KB, SB, *V, klenInBit, *RA, *RB, infoB); //B step7~9
97.
98. uint256_t tA = { 0 };
99. SM2KeyExchange_AStep4To5(tA, RA, rA, infoA); //A step4~5
100.
101. if (IsZeroPoint(RB)) //A 判断RB是否为(0,0)
102. {
103. return FALSE;
104. }
105.
106. SM2KeyExchange_AStep6To7(U, tA, RB, infoA); //A step6~7
107. if (IsZeroPoint(U)) //A 判断U是否为(0,0)
108. {
109. return FALSE;
110. }
111. uint8_t* S1 = malloc(32), * KA = malloc(klenInBit / 8);
112. SM2KeyExchange_AStep8To9(KA, S1, *U, klenInBit, *RA, *RB, infoA); //A step8~9
113.
114. if (KeyExchangeCheck)
115. {
116. for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)//A 判断S1是否==SB
117. {
118. if (S1[i] != SB[i])
119. {
120. return FALSE;
121. }
122. }
123. }
124.
125. uint8_t* SA = malloc(32);
126. SM2KeyExchange_AStep10(SA, *U, *RA, *RB, infoA); //A step10
127.
128. uint8_t* S2 = malloc(32);
129. SM2KeyExchange_BStep10(S2, *V, *RA, *RB, infoB); //B step10
130.
131. if (KeyExchangeCheck)
132. {
133. for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)//B 判断S2是否==SA
134. {
135. if (S2[i] != SA[i])
136. {
137. return FALSE;
138. }
139. }
140. }
141. free(RA);
142. free(V);
143. free(U);
144. free(pubKeyA);
145. free(pubKeyB);
146. free(RB);
147. free(SB);
148. free(KB);
149. free(S1);
150. free(KA);
151. free(SA);
152. free(S2);
153.
154. return TRUE;
155. }
4. 公钥加密算法
公钥加密算法规定发送者用接收者的公钥将消息加密成密文,接收者用自已的私钥对收到的密文进行解密还原成原始消息。
4.1 加密算法


1. uint8_t* SM2Encrypt(char* messagePlain, int messageSizeInBit, EccPoint* pubKey)
2. {
3. uint256_t randomK = { 0 };
4. EccPoint* pointC1 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)), * kPb = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint));
5. uint8_t* t = malloc(messageSizeInBit / 8), * x2 = malloc(64), * y2 = malloc(32),//t = KDF()
6. * C1 = malloc(65), * x1 = malloc(32), * y1 = malloc(32),
7. * C2 = malloc(messageSizeInBit / 8), * C3 = malloc(64 + messageSizeInBit / 8),
8. * C = malloc(65 + messageSizeInBit / 8 + 32);
9. GetRandomNumber(randomK, Ec->p);
10. #ifdef DEBUG_MODE
11. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //测试时随机数先固定
12. {
13. randomK[i] = exRandomK[3 - i];
14. }
15. #endif
16. CalculateC1(pointC1, randomK, G);
17. Uint256ToString(x1, pointC1->x);
18. Uint256ToString(y1, pointC1->y);
19. C1[0] = 0x04;
20. memcpy(C1 + 1, x1, 32);
21. memcpy(C1 + 33, y1, 32);//C1 = 04||x1||y1
22.
23. CalculateKPb(kPb, randomK, pubKey);
24. Uint256ToString(x2, kPb->x);
25. Uint256ToString(y2, kPb->y);
26.
27. memcpy(C3, x2, 32);
28. memcpy(C3 + 32, messagePlain, messageSizeInBit / 8);
29. memcpy(C3 + 32 + messageSizeInBit / 8, y2, 32);
30.
31. memcpy(x2 + 32, y2, 32);//x2 = x2 || y2
32. KDF(t, x2, 64 * 8, messageSizeInBit); //t = KDF()
33. CalculateC2(C2, messagePlain, t, messageSizeInBit / 8); //C2 = M^t
34. SM3((uint8_t*)C3, 64 + messageSizeInBit / 8, (uint8_t*)C3); //C3 = SM3(x2||M||y2)
35.
36. memcpy(C, C1, 65);
37. memcpy(C + 65, C2, messageSizeInBit / 8);
38. memcpy(C + 65 + messageSizeInBit / 8, C3, 32); //C = C1 || C2 || C3
39. free(pointC1);
40. free(kPb);
41. free(t);
42. free(x2);
43. free(y2);
44. free(C1);
45. free(x1);
46. free(y1);
47. free(C2);
48. free(C3);
49.
50. return C;
51. }
4.2 解密算法



1. uint8_t* SM2Decrypt(char* C, int lenInByte, uint64_t* privKey)
2. {
3. EccPoint* pointC1 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint)), * point2 = malloc(sizeof(EccPoint));
4. int lenOfMsg = lenInByte - 65 - 32;
5. uint8_t* C2 = malloc(lenOfMsg + 1), * msg = malloc(lenOfMsg + 1),
6. * x1 = malloc(32), * y1 = malloc(32),
7. * x2 = malloc(64), * y2 = malloc(32), * t = malloc(lenOfMsg);
8.
9. msg[lenInByte - 65 - 32] = '\0';
10. memcpy(C2, C + 65, lenInByte - 65 - 32);//密文msg
11. memcpy(x1, C + 1, 32);
12. memcpy(y1, C + 1 + 32, 32);
13. StringToUint256(pointC1->x, x1);
14. StringToUint256(pointC1->y, y1);
15. CurvePointMul(point2, pointC1, privKey);
16. Uint256ToString(x2, point2->x);
17. Uint256ToString(y2, point2->y);
18. memcpy(x2 + 32, y2, 32); //x2 = x2 || y2
19. KDF(t, x2, 64 * 8, (lenInByte - 65 - 32) * 8);//t = KDF(x2||y2,klenInBit)
20. CalculateMessage(msg, C2, t, lenOfMsg); //M' = C2 ^ t
21. free(pointC1);
22. free(point2);
23. free(C2);
24. free(x1);
25. free(y1);
26. free(x2);
27. free(y2);
28. free(t);
29.
30. return msg;
31. }






















 2793
2793

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










