详情请参考博客: Top 50 matplotlib Visualizations
因编译更新问题,本文将稍作更改,以便能够顺利运行。
0 Introduction
新建项目文件夹为matplotlib_visualizations,以下所有的.py文件均默认在该位置。
0.2 Setup
Setup.py文件内容如下:
# !pip install brewer2mpl
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings; warnings.filterwarnings(action='once')
large = 22; med = 16; small = 12
params = {'axes.titlesize': large,
'legend.fontsize': med,
'figure.figsize': (16, 10),
'axes.labelsize': med,
'axes.titlesize': med,
'xtick.labelsize': med,
'ytick.labelsize': med,
'figure.titlesize': large}
plt.rcParams.update(params)
plt.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid')
sns.set_style("white")
# %matplotlib inline
# Version
print(mpl.__version__) #> 3.7.1
print(sns.__version__) #> 0.12.2
1 Correlation
常用于可视化2个及以上变量间的关系。也就是说,一个变量相对于另一个变量是如何变化的。
1.1 Scatter plot 散点图
散点图(Scatter plot)是用于研究两个变量之间关系的经典基本图。如果数据包含多个组,则可能需要以不同的颜色来可视化每个组。在matplotlib中,使用plt.scatterplot()来实现该功能。
新建文件Scatter plot.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import np
# Import dataset
midwest = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/midwest_filter.csv")
# Prepare Data
# Create as many colors as there are unique midwest['category']
categories = np.unique(midwest['category'])
colors = [plt.cm.tab10(i/float(len(categories)-1)) for i in range(len(categories))]
# Draw Plot for Each Category
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for i, category in enumerate(categories):
plt.scatter('area', 'poptotal',
data=midwest.loc[midwest.category==category, :],
s=20, c=colors[i], label=str(category))
# Decorations
plt.gca().set(xlim=(0.0, 0.1), ylim=(0, 90000),
xlabel='Area', ylabel='Population')
plt.xticks(fontsize=12); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Scatterplot of Midwest Area vs Population", fontsize=22)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
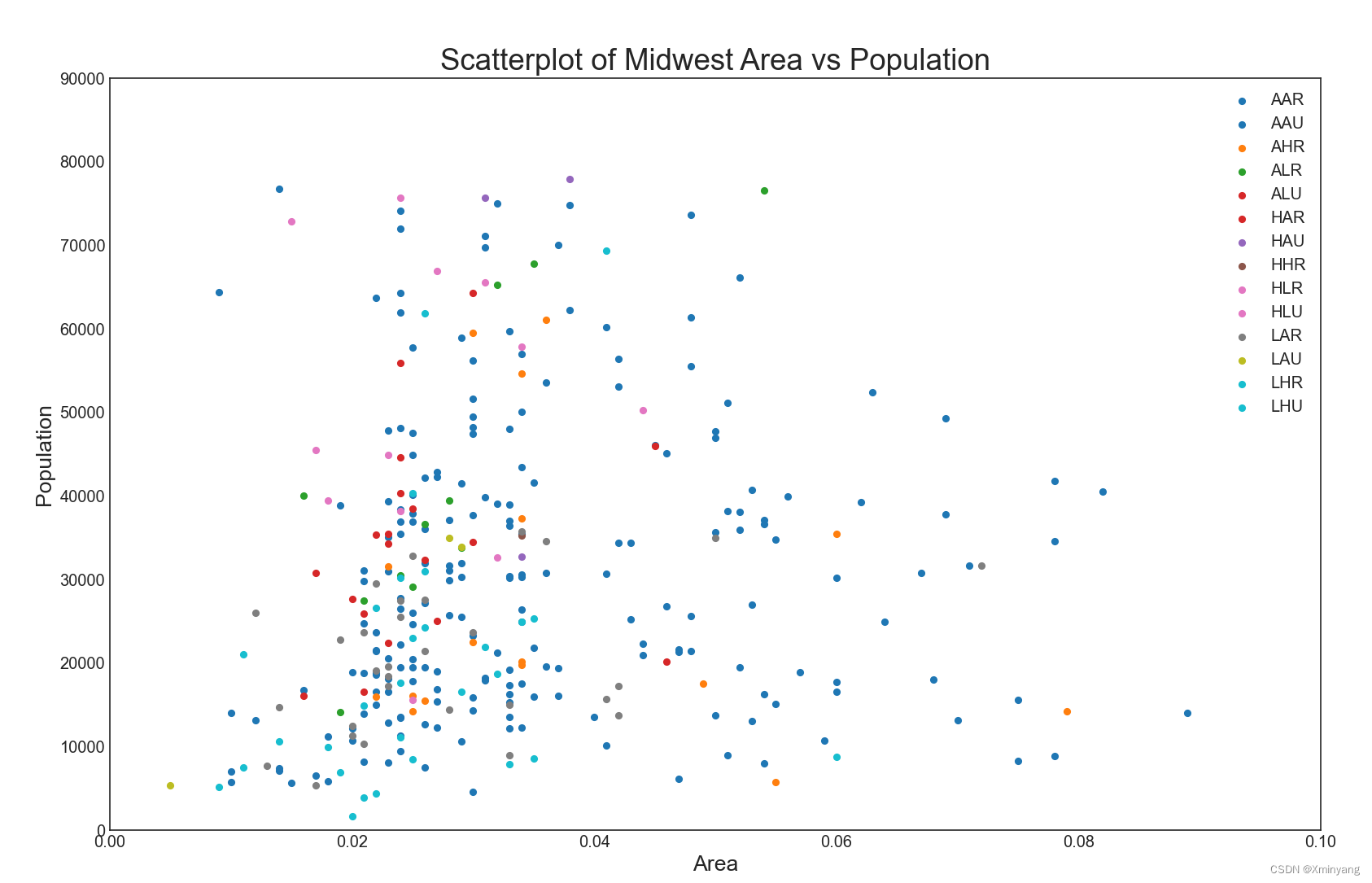
1.2 Bubble plot with Encircling 带边界的气泡图
有时候,会想展示一个边界内的一组点,以强调它们的重要性。在下面的示例中,将从数据帧中获取应该被圈出的记录,并将其传递给encircle()函数。
新建文件Bubble plot with Encircling.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import np
from Setup import sns
from matplotlib import patches
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
import warnings; warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
sns.set_style("white")
# Step 1: Prepare Data
midwest = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/midwest_filter.csv")
# As many colors as there are unique midwest['category']
categories = np.unique(midwest['category'])
colors = [plt.cm.tab10(i/float(len(categories)-1)) for i in range(len(categories))]
# Step 2: Draw Scatterplot with unique color for each category
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for i, category in enumerate(categories):
plt.scatter('area', 'poptotal', data=midwest.loc[midwest.category==category, :], s='dot_size', c=colors[i], label=str(category), edgecolors='black', linewidths=.5)
# Step 3: Encircling
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44575681/how-do-i-encircle-different-data-sets-in-scatter-plot
def encircle(x,y, ax=None, **kw):
if not ax: ax=plt.gca()
p = np.c_[x,y]
hull = ConvexHull(p)
poly = plt.Polygon(p[hull.vertices,:], **kw)
ax.add_patch(poly)
# Select data to be encircled
midwest_encircle_data = midwest.loc[midwest.state=='IN', :]
# Draw polygon surrounding vertices
encircle(midwest_encircle_data.area, midwest_encircle_data.poptotal, ec="k", fc="gold", alpha=0.1)
encircle(midwest_encircle_data.area, midwest_encircle_data.poptotal, ec="firebrick", fc="none", linewidth=1.5)
# Step 4: Decorations
plt.gca().set(xlim=(0.0, 0.1), ylim=(0, 90000),
xlabel='Area', ylabel='Population')
plt.xticks(fontsize=12); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Bubble Plot with Encircling", fontsize=22)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
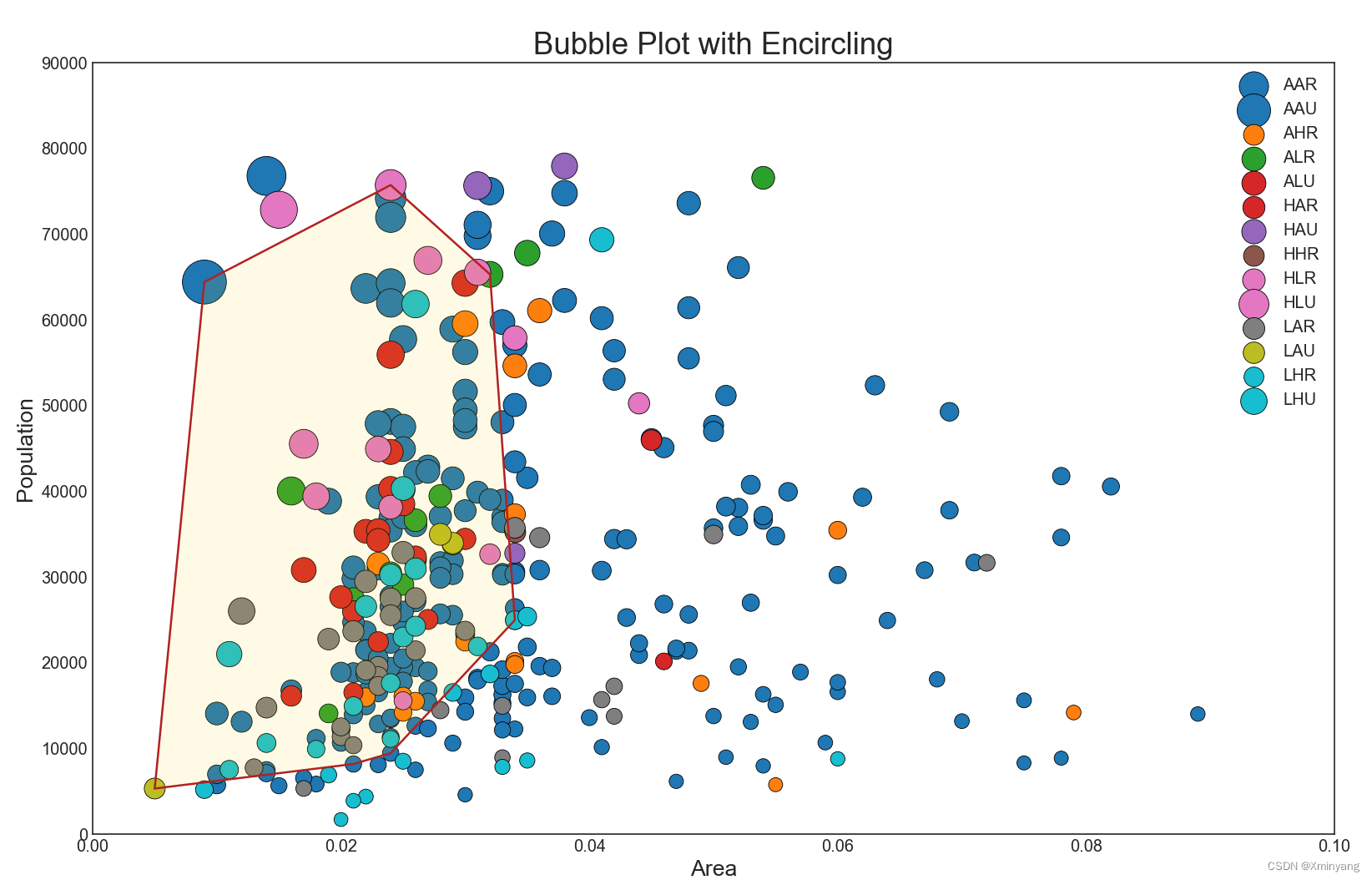
1.3 Scatter plot with linear regression line of best fit 具有最佳拟合的线性回归的散点图
通过最佳拟合线,你可以了解到两个变量是如何相互影响的。下图展示了数据中不同组之间最佳拟合线的差异。如果要禁用分组,并且仅为整个数据集绘制一个最近拟合线,可以在下面的sns.lmplot()调用中删除hue='cyl'参数。
1.3.1 groupings
新建文件Scatter plot with linear regression line of best fit.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_select = df.loc[df.cyl.isin([4,8]), :]
# Plot
sns.set_style("white")
gridobj = sns.lmplot(x="displ", y="hwy", hue="cyl", data=df_select,
height=7, aspect=1.6, robust=True, palette='tab10',
scatter_kws=dict(s=60, linewidths=.7, edgecolors='black'))
# Decorations
gridobj.set(xlim=(0.5, 7.5), ylim=(0, 50))
plt.title("Scatterplot with line of best fit grouped by number of cylinders", fontsize=20)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
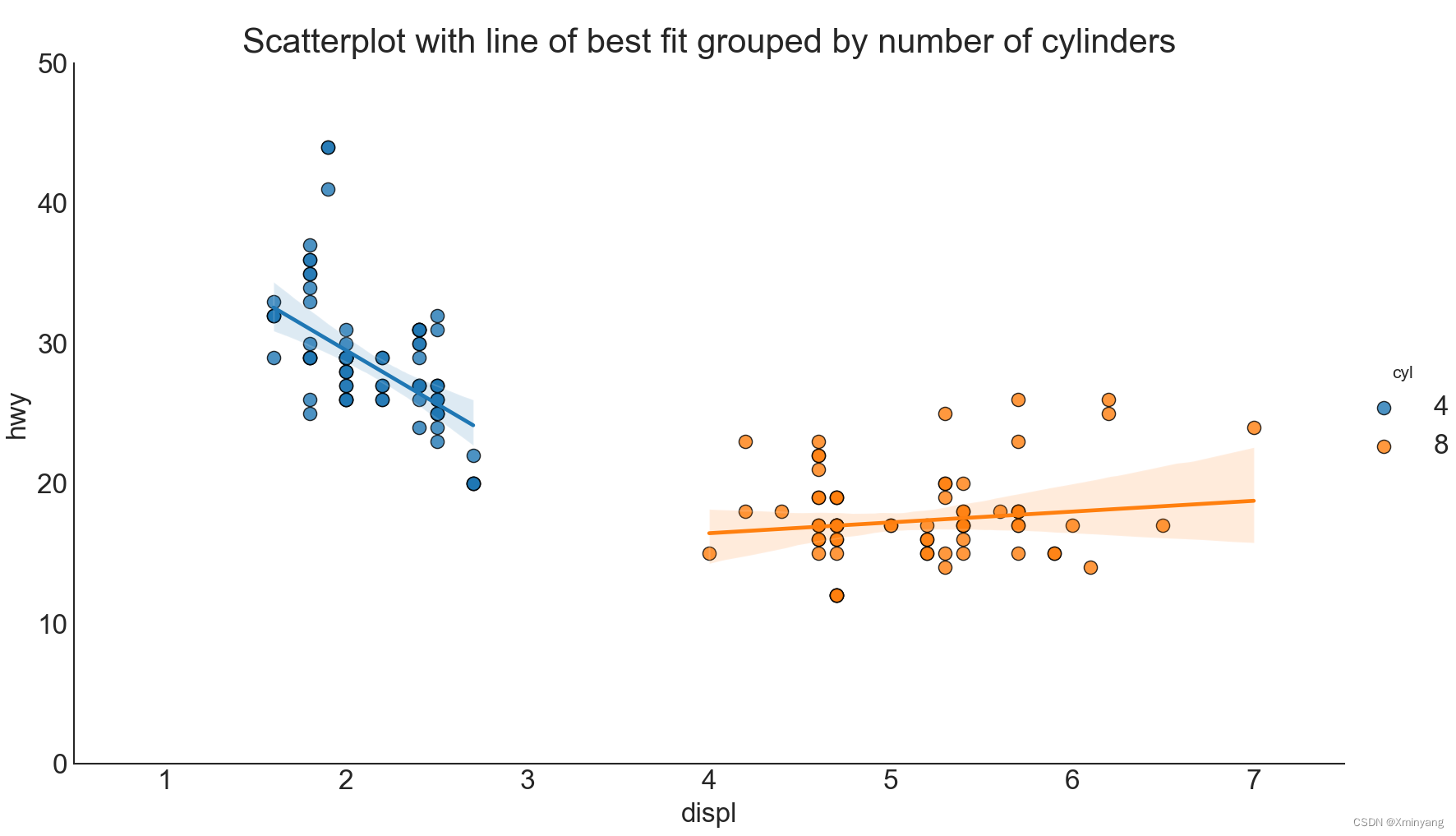
1.3.2 disable groupings
另一种方法是,在各自列中,展示每个组的最佳拟合线。可通过在sns.lmplot()中设置col=groupingcolumn参数来实现。
新建文件Scatter plot with linear regression line of best fit no groupings.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_select = df.loc[df.cyl.isin([4,8]), :]
# Plot
sns.set_style("white")
gridobj = sns.lmplot(x="displ", y="hwy", col="cyl", data=df_select,
height=7, robust=True, palette='Set1',
scatter_kws=dict(s=60, linewidths=.7, edgecolors='black'))
# Decorations
gridobj.set(xlim=(0.5, 7.5), ylim=(0, 50))
plt.show()
运行结果为:
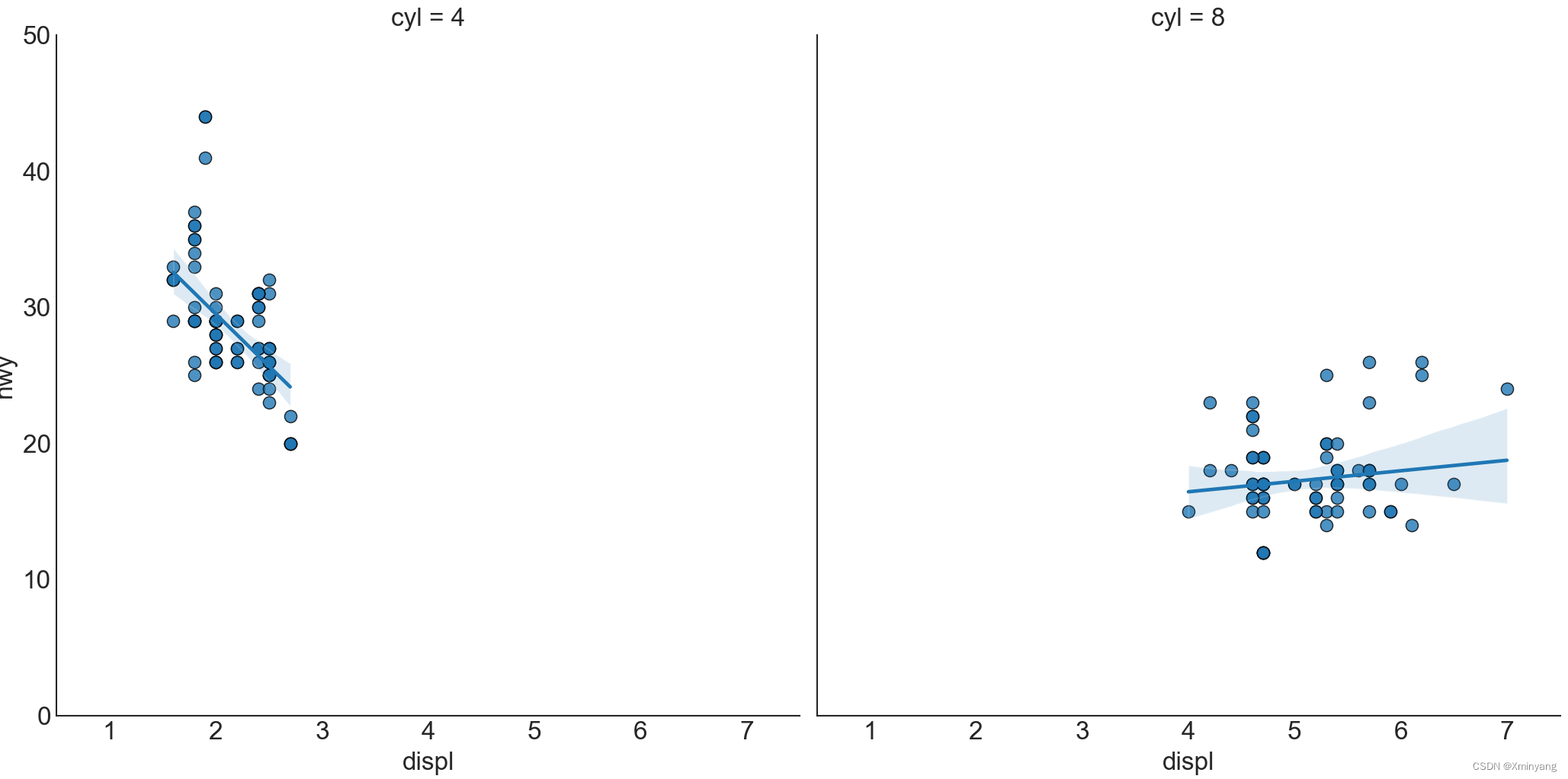
1.4 Jittering with stripplot 带状图
通常,因多个数据点具有完全相同的X和Y值,导致多个点相互绘制并隐藏掉。为了避免该情况,可将这些点进行抖动处理,以便能够更直观地观察。可以使用seaborn的stripplot()实现。
新建文件Jittering with stripplot.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Stripplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.stripplot(x=df.cty, y=df.hwy, jitter=0.25, size=8, ax=ax, linewidth=.5)
# Decorations
plt.title('Use jittered plots to avoid overlapping of points', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
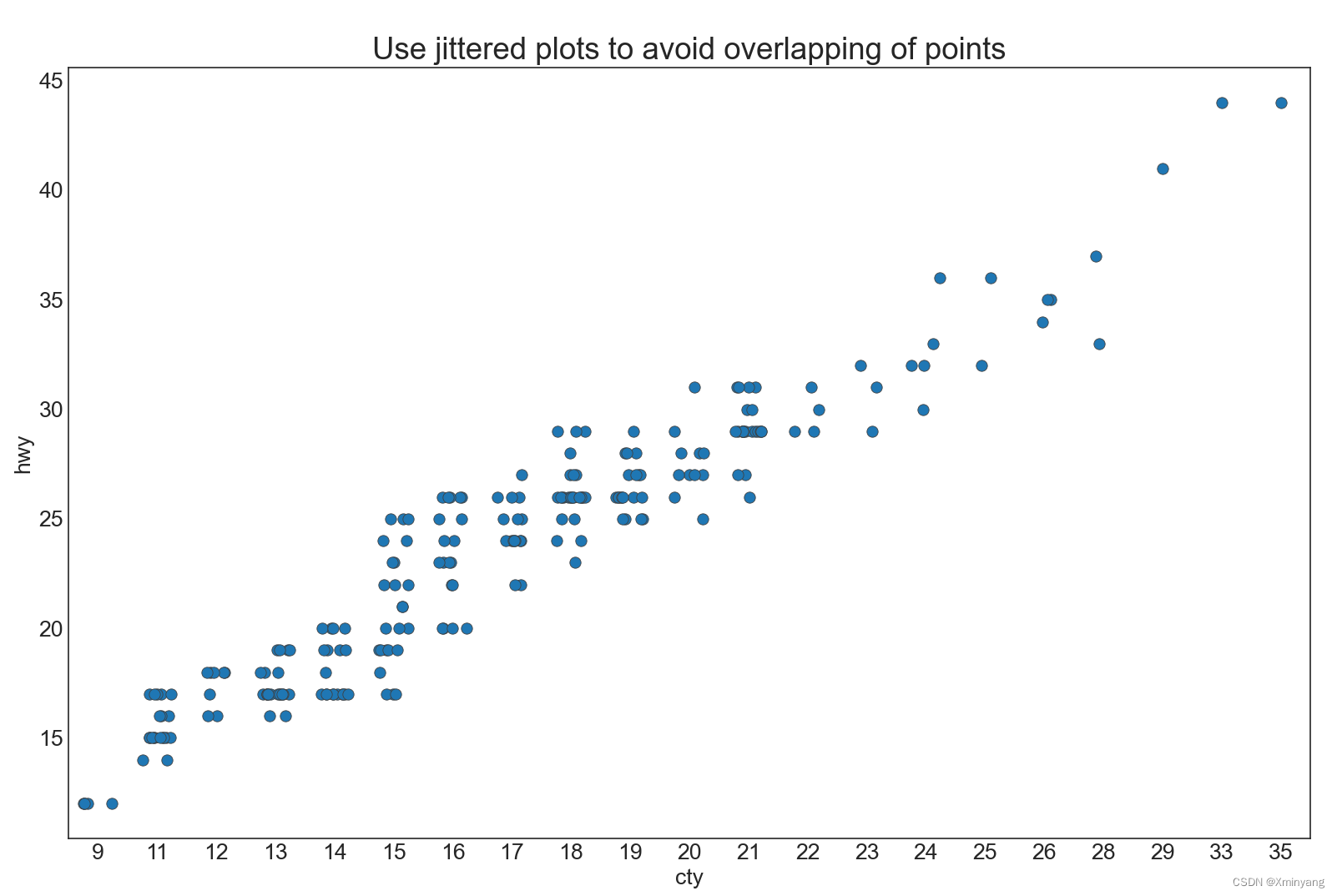
1.5 Counts Plot 计数图
避免点重叠问题的另一种方式是,根据该相同点的个数来调整点的大小。比如,点的大小越大,表明点周围的集中度就越大。
新建文件Counts Plot.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_counts = df.groupby(['hwy', 'cty']).size().reset_index(name='counts')
# Draw Stripplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
# sns.stripplot(df_counts.cty, df_counts.hwy, size=df_counts.counts*2, ax=ax)
sns.stripplot(df_counts,x=df_counts.cty, size=df_counts.counts*2, ax=ax)
# Decorations
plt.title('Counts Plot - Size of circle is bigger as more points overlap', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
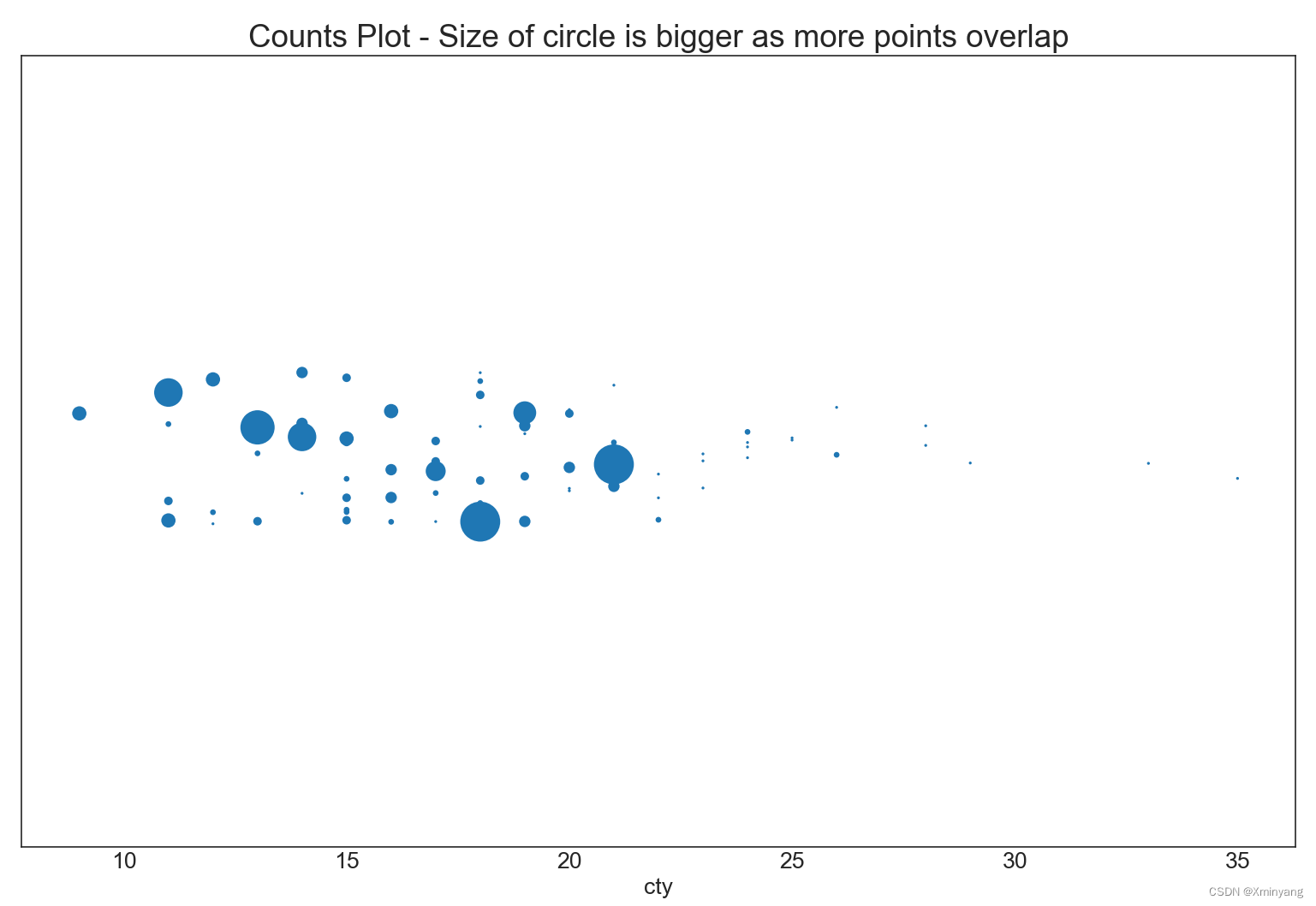
1.6 Marginal Histogram 边缘直方图
边缘直方图具有沿X轴和Y轴变量的直方图。这适用于可视化X和Y之间的关系,以及X和Y的单变量分布。
新建文件`Marginal Histogram.py`:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Create Fig and gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 4, hspace=0.5, wspace=0.2)
# Define the axes
ax_main = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, :-1])
ax_right = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, -1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
ax_bottom = fig.add_subplot(grid[-1, 0:-1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
# Scatterplot on main ax
ax_main.scatter('displ', 'hwy', s=df.cty*4, c=df.manufacturer.astype('category').cat.codes, alpha=.9, data=df, cmap="tab10", edgecolors='gray', linewidths=.5)
# histogram on the right
ax_bottom.hist(df.displ, 40, histtype='stepfilled', orientation='vertical', color='deeppink')
ax_bottom.invert_yaxis()
# histogram in the bottom
ax_right.hist(df.hwy, 40, histtype='stepfilled', orientation='horizontal', color='deeppink')
# Decorations
ax_main.set(title='Scatterplot with Histograms \n displ vs hwy', xlabel='displ', ylabel='hwy')
ax_main.title.set_fontsize(20)
for item in ([ax_main.xaxis.label, ax_main.yaxis.label] + ax_main.get_xticklabels() + ax_main.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(14)
xlabels = ax_main.get_xticks().tolist()
ax_main.set_xticklabels(xlabels)
plt.show()
运算结果为:
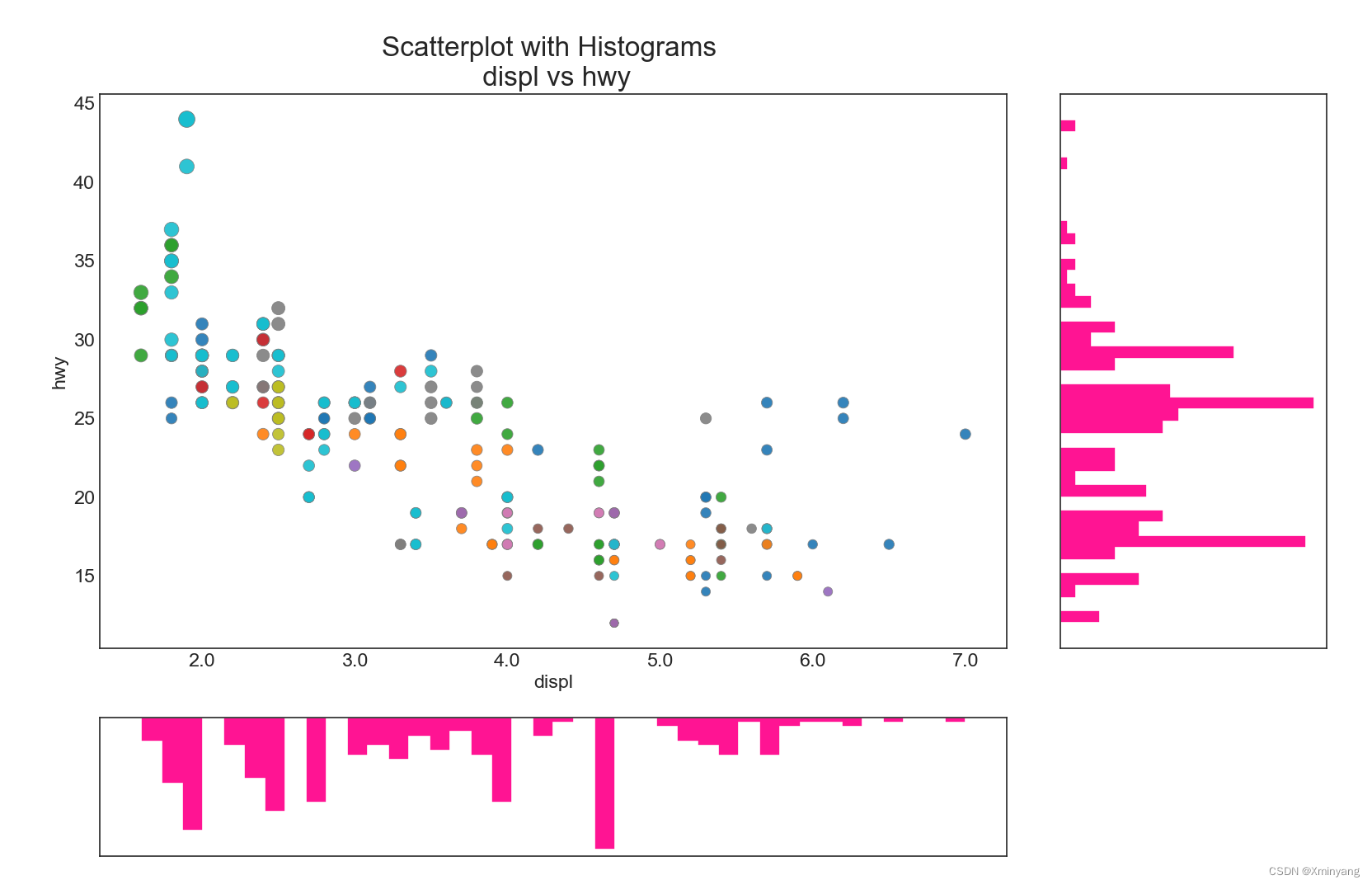
1.7 Marginal Boxplot 边缘箱线图
边缘箱线图与边缘直方图类似。但是,箱线图更有助于精确定位X和Y的中位数。
新建文件Marginal Boxplot.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Create Fig and gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 4, hspace=0.5, wspace=0.2)
# Define the axes
ax_main = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, :-1])
ax_right = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, -1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
ax_bottom = fig.add_subplot(grid[-1, 0:-1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
# Scatterplot on main ax
ax_main.scatter('displ', 'hwy', s=df.cty*5, c=df.manufacturer.astype('category').cat.codes, alpha=.9, data=df, cmap="Set1", edgecolors='black', linewidths=.5)
# Add a graph in each part
sns.boxplot(df.hwy, ax=ax_right, orient="v")
sns.boxplot(df.displ, ax=ax_bottom, orient="h")
# Decorations ------------------
# Remove x axis name for the boxplot
ax_bottom.set(xlabel='')
ax_right.set(ylabel='')
# Main Title, Xlabel and YLabel
ax_main.set(title='Scatterplot with Histograms \n displ vs hwy', xlabel='displ', ylabel='hwy')
# Set font size of different components
ax_main.title.set_fontsize(20)
for item in ([ax_main.xaxis.label, ax_main.yaxis.label] + ax_main.get_xticklabels() + ax_main.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(14)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
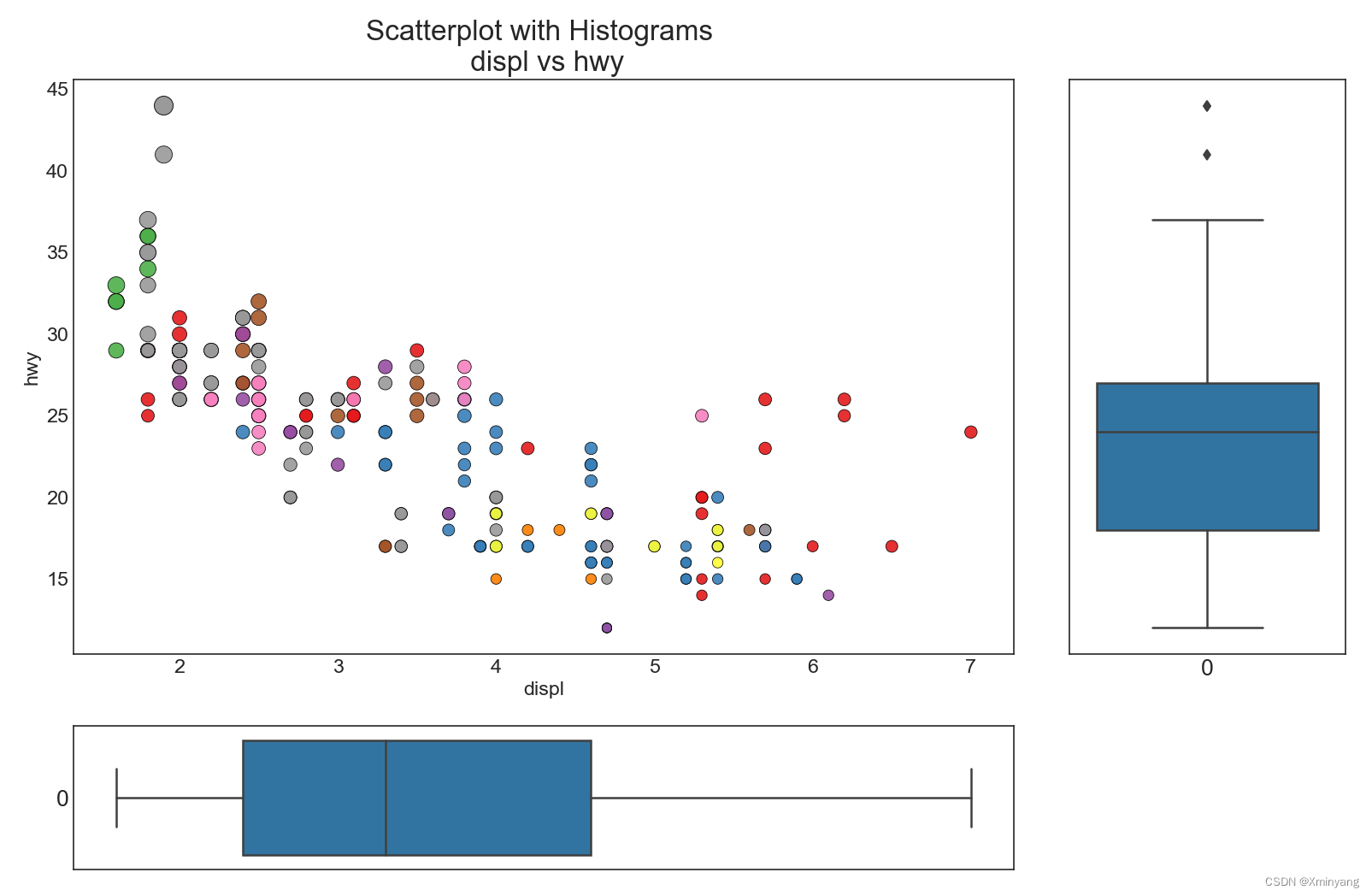
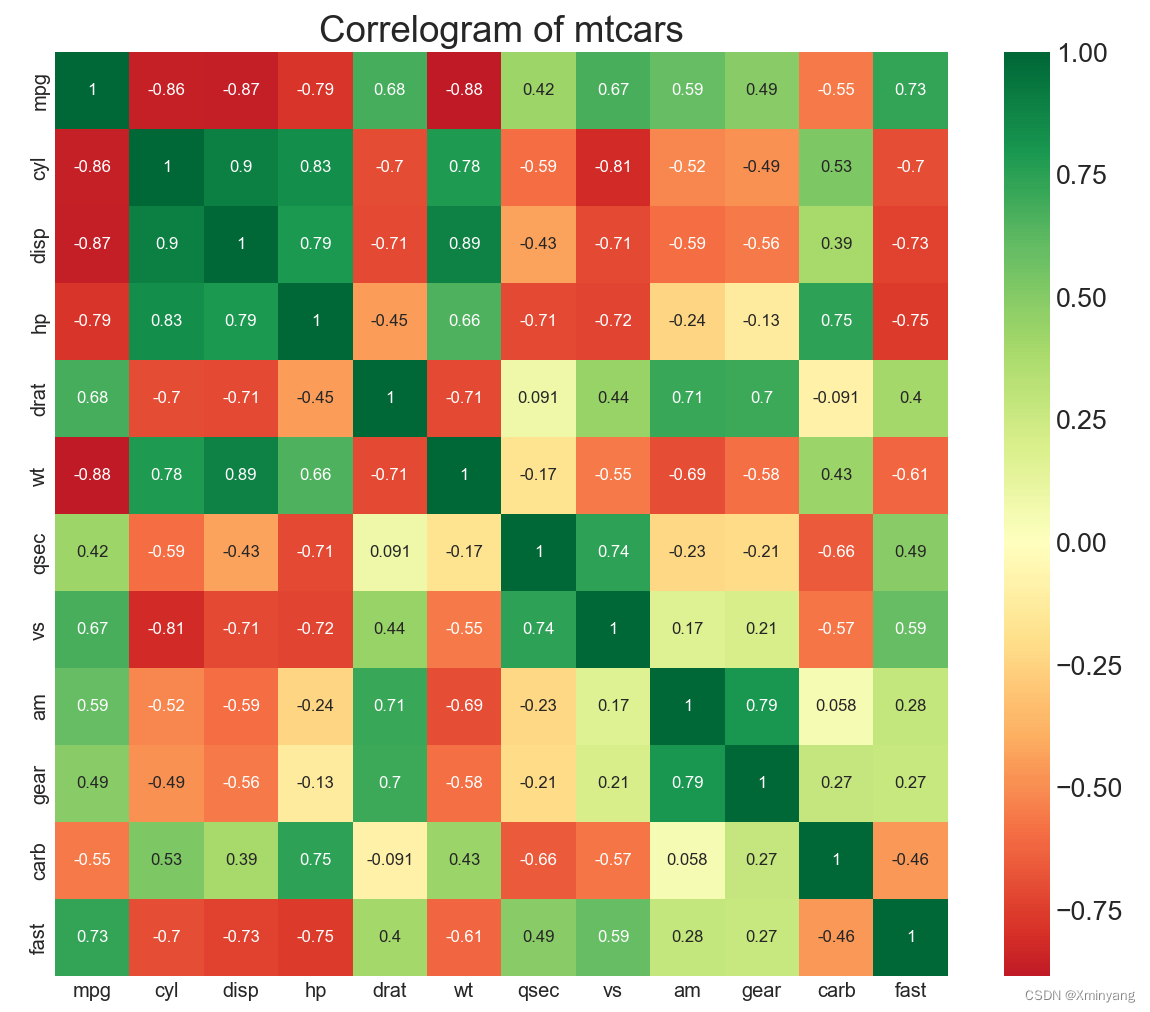
1.8 Correllogram 相关图
相关图用于查看给定数据帧(或2D数组)中,所有可能的数值变量对之间的相关指标。
新建文件Correlogram.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Import Dataset
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
# Drop the "cars" and "carname" columns
df = df.drop(["cars", "carname"], axis=1)
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10), dpi= 80)
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), xticklabels=df.corr().columns, yticklabels=df.corr().columns, cmap='RdYlGn', center=0, annot=True)
# Decorations
plt.title('Correlogram of mtcars', fontsize=22)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
运行结果为:
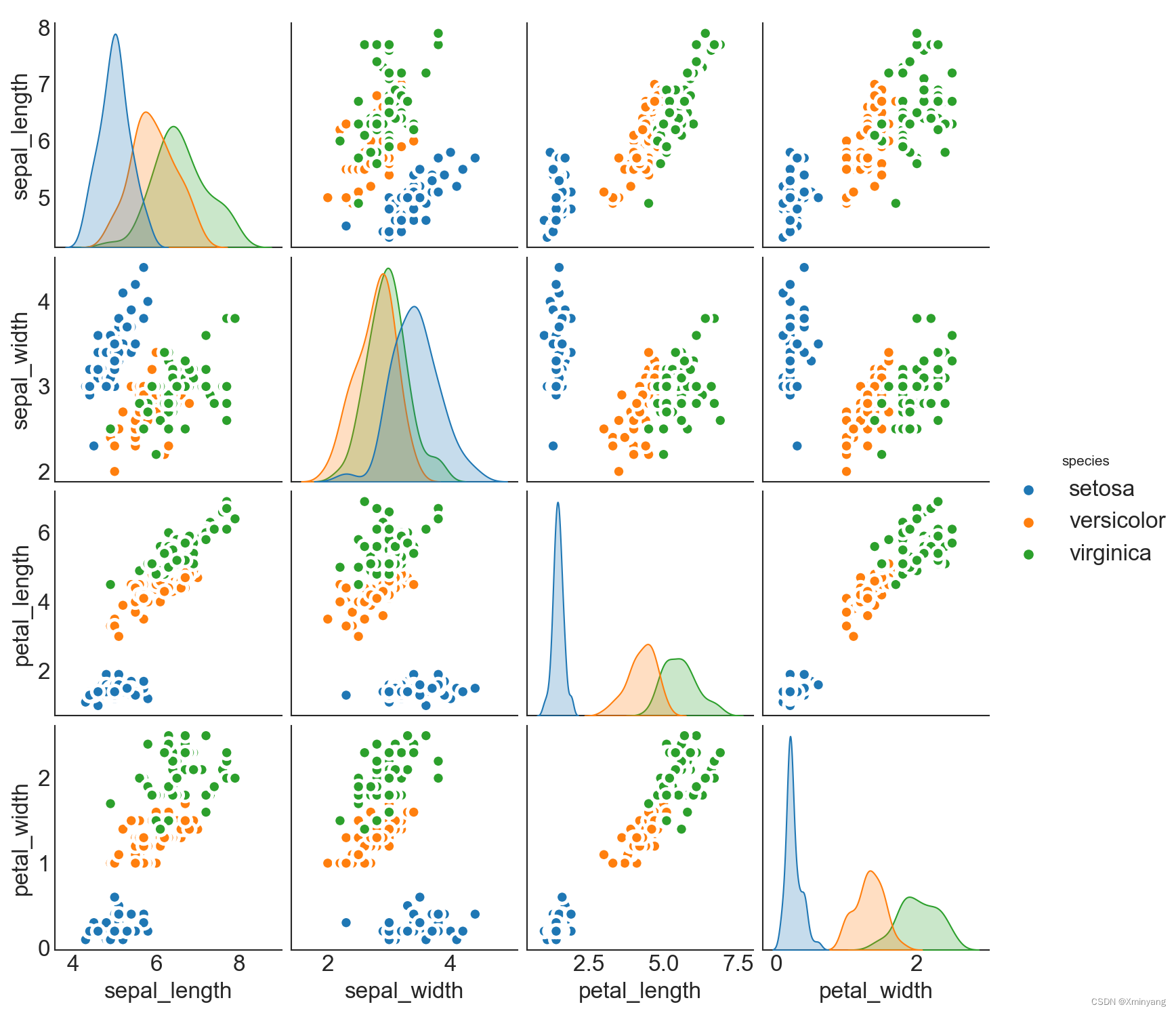
1.9 Pairwise Plot 矩阵图
矩阵图是探索性分析中最受欢迎的一种,用于理解所有可能的数值变量对之间的关系。它是双变量分析的必备工具。
新建文件Pairwise Plot.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Load Dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi= 80)
sns.pairplot(df, kind="scatter", hue="species", plot_kws=dict(s=80, edgecolor="white", linewidth=2.5))
plt.show()
运行结果为:
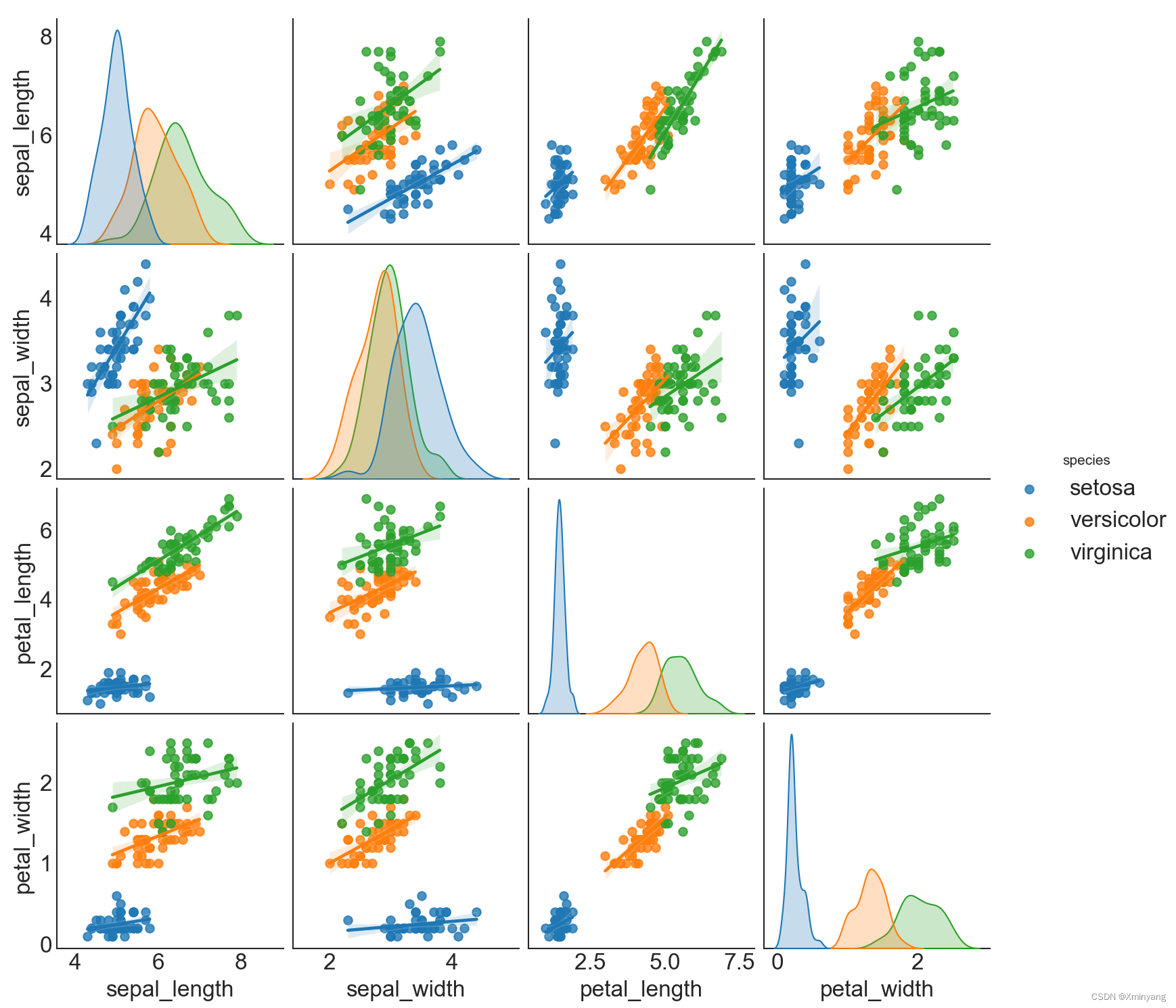
新建文件Pairwise Plot2.py:
# Import Setup
from Setup import pd
from Setup import plt
from Setup import sns
# Load Dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi= 80)
sns.pairplot(df, kind="reg", hue="species")
plt.show()
运行结果为:





















 1643
1643











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








