朋友们、伙计们,我们又见面了,今天给大家带来的是LeetCode中234题:回文链表
数据结构 :数据结构专栏
作 者 :stackY、
LeetCode:LeetCode刷题训练营
LeetCode--234.回文链表:https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
牛客网 - OR36 - 链表的回文结构:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
目录
1.题目介绍
LeetCode:
给你一个单链表的头节点
head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。
牛客网:
对于一个链表,请设计一个时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,判断其是否为回文结构。给定一个链表的头指针A,请返回一个bool值,代表其是否为回文结构。保证链表长度小于等于900。
对于时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是有要求的,因此我们在LeetCode上面也进行要求。
2.实例演示
3.解题思路
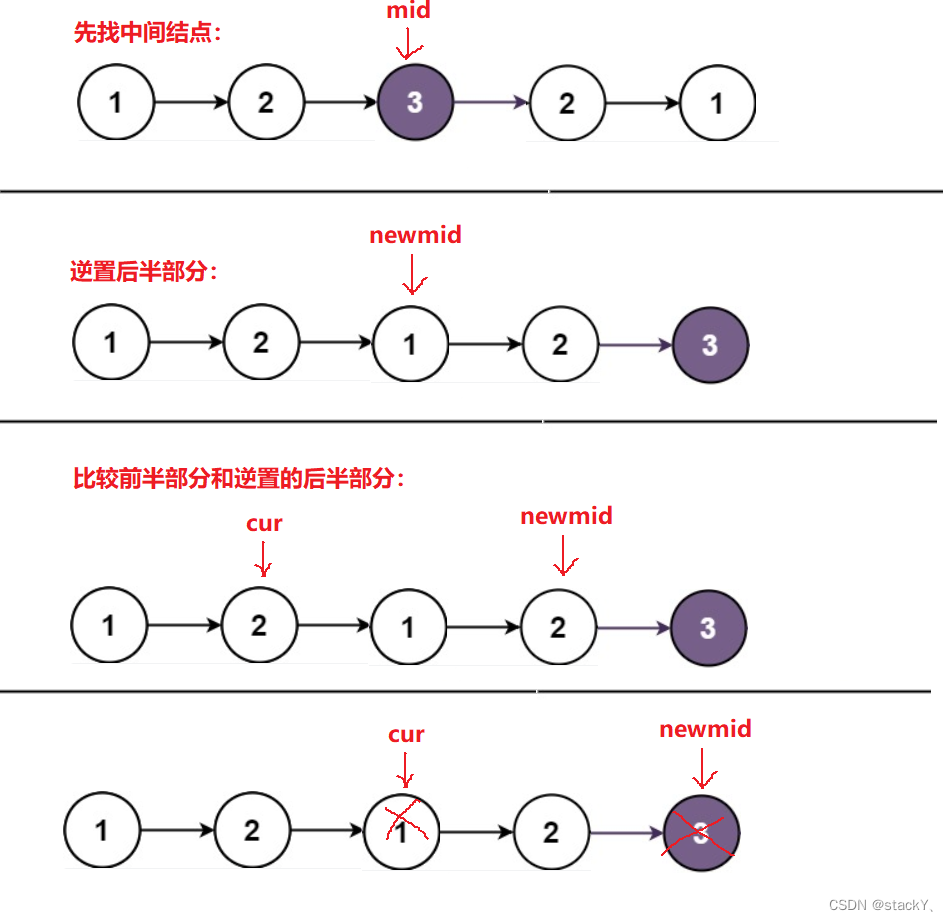
链表的回文可以转化为数组的回文,将链表拷贝至一个数组,然后转化成数组的回文然后使用快慢指针就可以解决,但是它的时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度就是O(N),就不符合题意,因此我们得换一种思路:先找链表的中间结点(可以参考LeetCode--876.链表的中间结点),然后将后半部分逆置(可以参考LeetCode--206.反转链表)然后再依次比较前半部分和逆置后的后半部分,如果不相等则返回false,若比较完两部分之后都相等则返回true,由于我们改变了原链表,因此在比较完之后需要恢复原链表,再将后半部分逆置就恢复到了原来的链表:
LeetCode - 代码演示(C语言实现):
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */ //找中间结点 struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) { //快慢指针 struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; //找中间结点 //如果只有一个结点也直接返回 while (fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; } //反转链表 struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* newhead = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { //保存头结点的下一个结点 struct ListNode* next = cur->next; //头插 cur->next = newhead; //更新新的头 newhead = cur; //迭代 cur = next; } return newhead; } bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head) { //找中间结点 struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(head); //反转 struct ListNode* newmid = reverseList(mid); struct ListNode* cur = head; //判断 while (newmid) { if (cur->val != newmid->val) { return false; } else { cur = cur->next; newmid = newmid->next; } } //恢复原链表 reverseList(newmid); return true; }牛客网 - 代码演示(C++实现):
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} };*/ class PalindromeList { public: //找中间结点 struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; while (fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; } // struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* newhead = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = newhead; newhead = cur; cur = next; } return newhead; } bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) { // write code here ListNode* mid = middleNode(A); ListNode* newmid = reverseList(mid); while (newmid) { if (A->val == newmid->val) { A = A->next; newmid = newmid->next; } else { return false; } } return true; } };
今天的博客就分享到这里,喜欢的老铁留下你的三连,感谢感谢!我们下期再见!!



























 235
235











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










