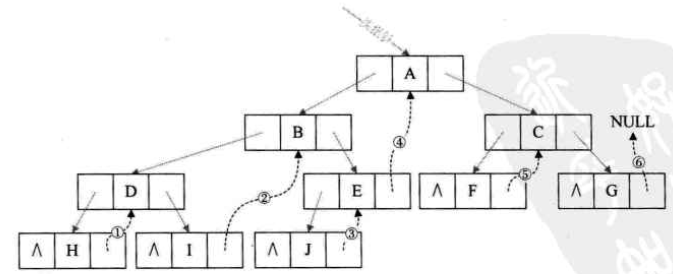
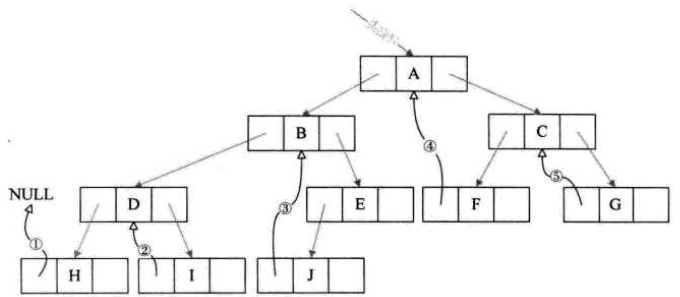
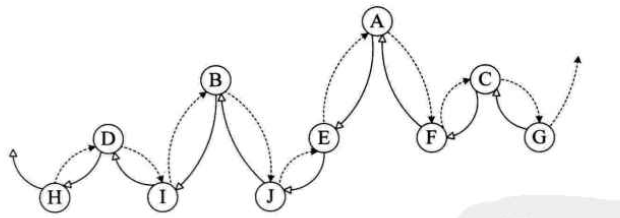
我们把二叉树进行中序遍历后,将所有的空指针域中的rchild,改为指向它的后继结点;将所有的空指针域中的lchild,改为指向当前结点的前驱。
如图:空心箭头实线为前驱,虚线黑箭头为后继
指向前驱和后继的指针称为线索,加上线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树就称为线索二叉树(Threaded Binary Tree)。
都二叉树以某种次序遍历使其变为线索二叉树的过程称做是线索化。
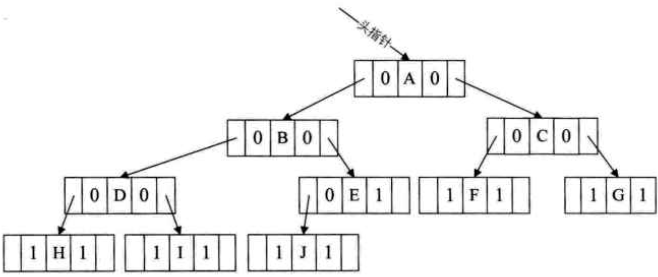
同时,为了知道lchild(rchild)是指向它的左孩子(右孩子)还是指向前驱(后继)。我们在每个结点再增设俩个标志域ltag和rtag,注意ltag和rtag只是存放0或1数字的布尔型变量,其占用的内存空间要小于像lchild和rchild的指针变量。
结点结构如图:
其中:ltag为0时指向该结点的左孩子,为1时指向该结点的前驱;
rtag为0时指向该结点的右孩子,为1时指向该结点的后继;
二叉链表如图:
如果所用的二叉树需经常遍历或查找结点时需要某种遍历序列中的前驱和后继,那么采用线索二叉链表的存储结构就是非常不错的选择。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "io.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 100 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef char TElemType;
typedef enum { Link, Thread } PointerTag; /* Link==0表示指向左右孩子指针, */
/* Thread==1表示指向前驱或后继的线索 */
typedef struct BiThrNode /* 二叉线索存储结点结构 */
{
TElemType data; /* 结点数据 */
struct BiThrNode *lchild, *rchild; /* 左右孩子指针 */
PointerTag LTag;
PointerTag RTag; /* 左右标志 */
} BiThrNode, *BiThrTree;
TElemType Nil = '#'; /* 字符型以空格符为空 */
Status visit(TElemType e)
{
printf("%c ", e);
return OK;
}
/* 按前序输入二叉线索树中结点的值,构造二叉线索树T */
/* 0(整型)/空格(字符型)表示空结点 */
Status CreateBiThrTree(BiThrTree *T)
{
TElemType h;
scanf_s("%c", &h);
if (h == Nil)
*T = NULL;
else
{
*T = (BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if (!*T)
exit(OVERFLOW);
(*T)->data = h; /* 生成根结点(前序) */
CreateBiThrTree(&(*T)->lchild); /* 递归构造左子树 */
if ((*T)->lchild) /* 有左孩子 */
(*T)->LTag = Link;
CreateBiThrTree(&(*T)->rchild); /* 递归构造右子树 */
if ((*T)->rchild) /* 有右孩子 */
(*T)->RTag = Link;
}
return OK;
}
BiThrTree pre; /* 全局变量,始终指向刚刚访问过的结点 */
/* 中序遍历进行中序线索化 */
void InThreading(BiThrTree p)
{
if (p)
{
InThreading(p->lchild); /* 递归左子树线索化 */
if (!p->lchild) /* 没有左孩子 */
{
p->LTag = Thread; /* 前驱线索 */
p->lchild = pre; /* 左孩子指针指向前驱 */
}
if (!pre->rchild) /* 前驱没有右孩子 */
{
pre->RTag = Thread; /* 后继线索 */
pre->rchild = p; /* 前驱右孩子指针指向后继(当前结点p) */
}
pre = p; /* 保持pre指向p的前驱 */
InThreading(p->rchild); /* 递归右子树线索化 */
}
}
/* 中序遍历二叉树T,并将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点 */
Status InOrderThreading(BiThrTree *Thrt, BiThrTree T)
{
*Thrt = (BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if (!*Thrt)
exit(OVERFLOW);
(*Thrt)->LTag = Link; /* 建头结点 */
(*Thrt)->RTag = Thread;
(*Thrt)->rchild = (*Thrt); /* 右指针回指 */
if (!T) /* 若二叉树空,则左指针回指 */
(*Thrt)->lchild = *Thrt;
else
{
(*Thrt)->lchild = T;
pre = (*Thrt);
InThreading(T); /* 中序遍历进行中序线索化 */
pre->rchild = *Thrt;
pre->RTag = Thread; /* 最后一个结点线索化 */
(*Thrt)->rchild = pre;
}
return OK;
}
/* 中序遍历二叉线索树T(头结点)的非递归算法 */
Status InOrderTraverse_Thr(BiThrTree T)
{
BiThrTree p;
p = T->lchild; /* p指向根结点 */
while (p != T)
{ /* 空树或遍历结束时,p==T */
while (p->LTag == Link)
p = p->lchild;
if (!visit(p->data)) /* 访问其左子树为空的结点 */
return ERROR;
while (p->RTag == Thread && p->rchild != T)
{
p = p->rchild;
visit(p->data); /* 访问后继结点 */
}
p = p->rchild;
}
return OK;
}
int main()
{
BiThrTree H, T;
printf("请按前序输入二叉树(如:'ABDH##I##EJ###CF##G##')\n");
CreateBiThrTree(&T); /* 按前序产生二叉树 */
InOrderThreading(&H, T); /* 中序遍历,并中序线索化二叉树 */
printf("中序遍历(输出)二叉线索树:\n");
InOrderTraverse_Thr(H); /* 中序遍历(输出)二叉线索树 */
printf("\n");
return 0;
}






















 6168
6168











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








