
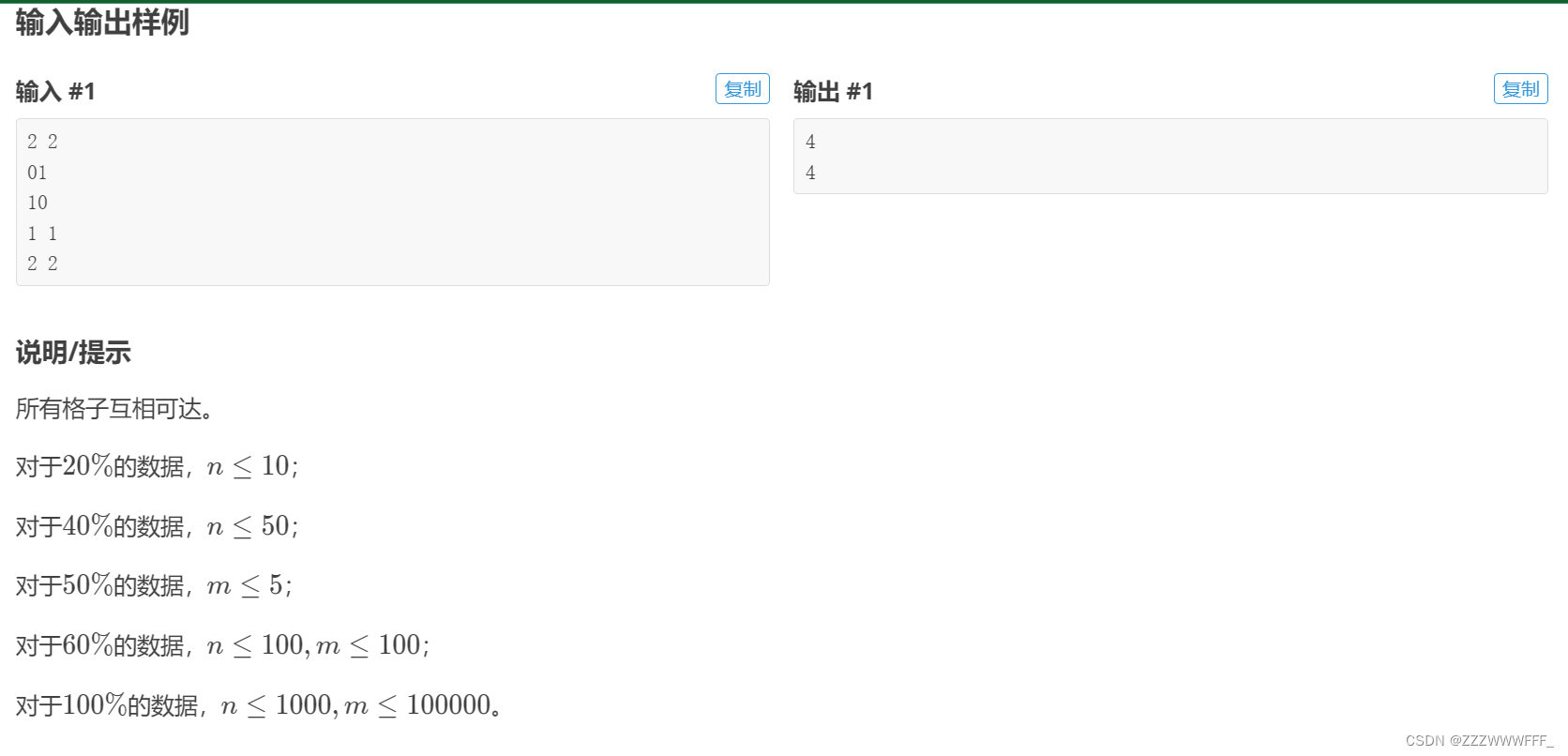
题目意思比较明确,我们需要认识到当什么时候时会出现不能输出n*n
考虑搜索(DFS/BFS)
第一思路:
对于输入的每一个起点,我们以该起点出发进行搜索,当(x,y)为0时,(tx,ty)的限制条件多一个map[tx][ty]==1即可,当(x,y)为1时同理
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#define MAX 1010
using namespace std;
int n, m, ans = 0;
char map[MAX][MAX];
bool visited[MAX][MAX];//记录走过的点
int nextt[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0} };
void dfs(int x, int y) {
if (map[x][y] == '0') {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tx = x + nextt[i][0];
int ty = y + nextt[i][1];
if (map[tx][ty]=='0' || visited[tx][ty] || tx<0 || ty<0 || tx == n || ty == n) {
continue;
}
ans++;
visited[tx][ty] = true;
dfs(tx, ty);
}
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tx = x + nextt[i][0];
int ty = y + nextt[i][1];
if (map[tx][ty] == '1' || visited[tx][ty] || tx < 0 || ty < 0 || tx == n || ty == n) {
continue;
}
ans++;
visited[tx][ty] = true;
dfs(tx, ty);
}
}
}
int main() {
int x, y;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
while (m--) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
memset(visited[i], false, sizeof(visited[i]));
}//初始化
ans = 1;
cin >> x >> y;
x--;
y--;
visited[x][y] = true;
dfs(x, y);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
但是该方法并不能通过所有样例,主要是数据量较大时被限制,于是我想是递归限制了时间,所以又按照BFS写了一遍,具体思路和上面一样
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#define MAX 1010
using namespace std;
int n, m, ans = 0;
char map[MAX][MAX];
bool visited[MAX][MAX];
int nextt[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0} };
void bfs(int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
q.push({ x,y });
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int>temp = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = temp.first;
int j = temp.second;
if (map[i][j] == '0') {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tx = i + nextt[k][0];
int ty = j + nextt[k][1];
if (map[tx][ty] == '0' || visited[tx][ty] || tx < 0 || ty < 0 || tx == n || ty == n) {
continue;
}
ans++;
visited[tx][ty] = true;
q.push({ tx,ty });
}
}
else {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tx = i + nextt[k][0];
int ty = j + nextt[k][1];
if (map[tx][ty] == '1' || visited[tx][ty] || tx < 0 || ty < 0 || tx == n || ty == n) {
continue;
}
ans++;
visited[tx][ty] = true;
q.push({ tx,ty });
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int x, y;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
while (m--) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
memset(visited[i], false, sizeof(visited[i]));
}
ans = 1;
cin >> x >> y;
x--;
y--;
bfs(x, y);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
然而还是不能通过大数据的样例,还是必须优化才行
我们可以多自己举几个样例进行测试
不难发现该问题可以抽象成一个连通块问题,并且如果以每一个连通块中的任意一点为起点得到的答案是一样的(都是对应的点所在的连通块大小)!!!
由此就可以写代码了
下面给出BFS和DFS的优化版本
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#define MAX 1010
using namespace std;
int num = 0;//第几个连通块
int n, m, ans = 0;
char map[MAX][MAX];
int visited[MAX][MAX];//记录某个点处于哪个连通块中+是否到过
int nextt[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0} };
int sizee[MAX * MAX];//记录每个连通块大小,当全为1或全为0时,有大约MAX*MAX个连通块
void bfs(int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
q.push({ x,y });
while (!q.empty()) {
int i = q.front().first;
int j = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tx = i + nextt[k][0];
int ty = j + nextt[k][1];
if ((tx >= 1 && tx <= n && ty >= 1 && ty <= n && !visited[tx][ty]) && ((map[i][j] == '0' && map[tx][ty] == '1') || (map[i][j] == '1' && map[tx][ty] == '0'))) {
//合法
visited[tx][ty] = num;//记录所处的连通块
sizee[num]++;//更新所在连通块大小
q.push({ tx,ty });
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int x, y;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));//初始化
memset(sizee, 0, sizeof(sizee));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {//遍历所有可能的连通块
if (visited[i][j] == 0) {//没到过
num++;
visited[i][j] = num;//记录所处的连通块
sizee[num]++;//更新所在连通块大小
bfs(i, j);
}
}
}
while (m--) {
cin >> x >> y;
ans = sizee[visited[x][y]];//得到(x,y)对应连通块大小
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#define MAX 1010
using namespace std;
int num = 0;//第几个连通块
int n, m, ans = 0;
char map[MAX][MAX];
int visited[MAX][MAX];//记录某个点处于哪个连通块中+是否到过
int nextt[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0} };
int sizee[MAX * MAX];//记录每个连通块大小,当全为1或全为0时,有大约MAX*MAX个连通块
void dfs(int x, int y) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tx = x + nextt[k][0];
int ty = y + nextt[k][1];
if ((tx >= 1 && tx <= n && ty >= 1 && ty <= n && visited[tx][ty]==0) && ((map[x][y] == '0' && map[tx][ty] == '1') || (map[x][y] == '1' && map[tx][ty] == '0'))) {
//合法
visited[tx][ty] = num;
sizee[num]++;
dfs(tx, ty);
}
}
}
int main() {
int x, y;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));//初始化
memset(sizee, 0, sizeof(sizee));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (visited[i][j] == 0) {//没到过
num++;
visited[i][j] = num;//记录所处的连通块
sizee[num]++;
dfs(i, j);
}
}
}
while (m--) {
cin >> x >> y;
ans = sizee[visited[x][y]];
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}























 98
98











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










