目录标题
一、IO多路复用的三种机制Select,Poll,Epoll
I/O多路复用(multiplexing)的本质是通过一种机制(系统内核缓冲I/O数据),让单个进程可以监视多个文件描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读就绪或写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作。
推荐看一下原文: IO多路复用的三种机制Select,Poll,Epoll
二、ByteBuffer
(一)ByteBuffer 结构(重要需要理解)
ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性
- capacity(缓冲区容量)
- position(读写指针)
- limit(读写限制-ps:能读的最大值、能写的最大值)
- 一开始
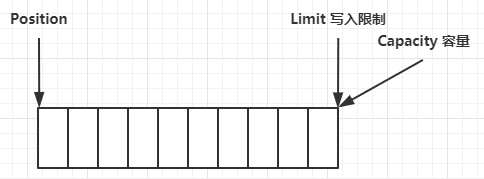
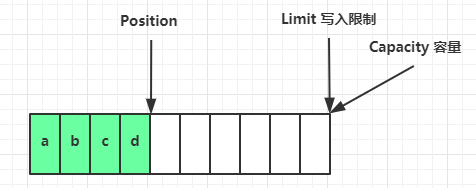
- 写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态
- flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制
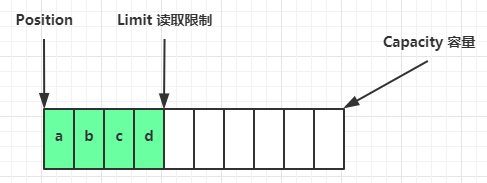
- 读取 4 个字节后,状态
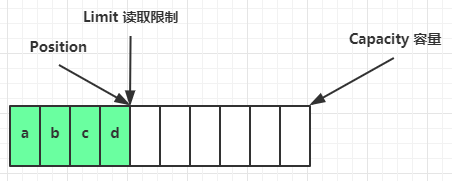
-
clear 动作发生后,状态
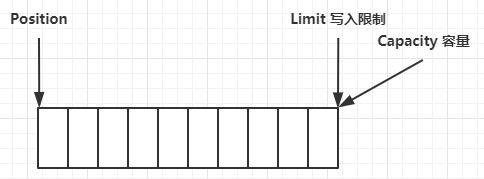
-
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式

(二) ByteBuffer 正确使用姿势
- 向 buffer 写入数据,例如调用 channel.read(buffer)
- 调用 flip() 切换至读模式
- 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用 buffer.get()
- 调用 clear() 或 compact() 切换至写模式
- 重复 1~4 步骤
(三)ByteBuffer 常见方法
1、分配空间——allocate(16);
可以使用 allocate 方法为 ByteBuffer 分配空间,其它 buffer 类也有该方法
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
2、向 buffer 写入数据channel.read(buffer)
有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 read 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
和
buf.put((byte)127);
注意:写入buffer时一般会搭配clear()方法使用。将重置position 、limit、mark 的值。
clear()方法源码:
public final Buffer clear() {
//0表示缓冲区的开头
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
3、从 buffer 读取数据
同样有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 write 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
和
byte b = buf.get();
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
- 可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
- 或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
注意:读取buffer存放的内容时需要搭配flip();方法使用。重置position 、limit、mark 的值。
flip()方法源码:
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
4、mark 和 reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
注意
rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
5、并发使用多个buffer进行读写
- 使用如下方式读取,可以将数据填充至多个 buffer
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/3parts.txt", "rw")) {
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer a = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer c = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{a, b, c});
a.flip();
b.flip();
c.flip();
debug(a);
debug(b);
debug(c);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
- 使用如下方式写入,可以将多个 buffer 的数据填充至 channel
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/3parts.txt", "rw")) {
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer d = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
ByteBuffer e = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
channel.position(11);
d.put(new byte[]{'f', 'o', 'u', 'r'});
e.put(new byte[]{'f', 'i', 'v', 'e'});
d.flip();
e.flip();
debug(d);
debug(e);
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{d, e});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
三、FileChannel
(一)获取FileChannel
不能直接打开 FileChannel,必须通过 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 来获取 FileChannel,它们都有 getChannel 方法
- 通过 FileInputStream 获取的 channel 只能读
- 通过 FileOutputStream 获取的 channel 只能写
- 通过 RandomAccessFile 是否能读写根据构造 RandomAccessFile 时的读写模式决定
(二)通过FileChannel读取文件
会从 channel 读取数据填充 ByteBuffer,返回值表示读到了多少字节,-1 表示到达了文件的末尾。
int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);
(三)关闭通道
channel 必须关闭,不过调用了 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 的 close 方法会间接地调用 channel 的 close 方法。
(四)位置
获取当前位置
long pos = channel.position();
设置当前位置
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos);
设置当前位置时,如果设置为文件的末尾
- 这时读取会返回 -1
- 这时写入,会追加内容,但要注意如果 position 超过了文件末尾,再写入时在新内容和原末尾之间会有空洞(00)
注意:position 这个方法FileChannel和ByteBuffer都有。
大小
使用 size 方法获取文件的大小
强制写入
操作系统出于性能的考虑,会将数据缓存,不是立刻写入磁盘。可以调用 force(true) 方法将文件内容和元数据(文件的权限等信息)立刻写入磁盘






















 2532
2532











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








