首先我们看一下@Aspect的简单实例代码
首先到Config类中添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解打开AOP功能
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.kennor.test")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class Config {
}
自定义注解StudyTrainAnnotation用于标识连接点Joinpoint
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface StudyTrainAnnotation {
}
自定义切面StudyTrainAspect类
在切面方法studyTrain中对目标方法进行增强,具体业务逻辑是增加分数。
@Component
@Aspect
public class StudyTrainAspect {
/**
* 设置切点Pointcut
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(StudyTrainAnnotation)")
public void studyTrainPointcut(){
}
/**
* 设置增强方法Advice
* @param joinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around("studyTrainPointcut()")
public Object studyTrain(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("进行考前强化训练,强化训练后初始分数增加30分");
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
args[0] = (Integer)args[0] + 30;
Integer score = (Integer) joinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("考后老师评分失误,多评10分");
score+=10;
return score;
}
}
增加Student接口
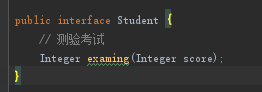
在StudentA和StudentB实现Student接口
在StudentA的examing方法中增加@StudyTrainAnnotation注解,标识StudentA的examing是需要增强的目标对象Target。


然后调用
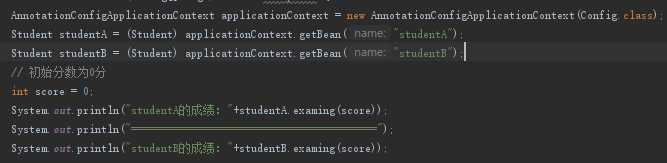
运行结果如下:

可以看到StudentA考试成绩增加到了90分,而StudentB没有使用AOP所以仍是50分。
为了做对比,看一下StudentB和StudentA的区别

通过Debug可以看到,StudentA的引用实际上是代理对象,然后代理对象的targetSource属性保存着StudentA。接下来我们将分析一下整个流程到底是怎么样的。
接下来我们就着这个实例,分析一下源码,看看Spring底层源码是如何实现的。
首先我们看到Config类上的@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解
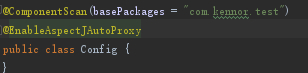
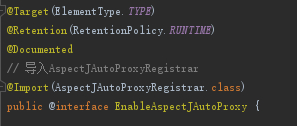
可以看到EnableAspectJAutoProxy使用了@Import标签导入了AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类
而关于@Import标签的处理在AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的构造方法中创建的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor中进行的,跟处理@ComponentScan注解一样,具体看下面方法注释的第4点,会将AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar注册到Spring中,这里不再赘述。
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass)
throws IOException {
// 1.处理类上的@Component注解
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
// 2.处理类上的@PropertySource注解
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
... ...
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
// 3.处理类上的@ComponentScan注解
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
... ...
}
// Process any @Import annotations
// 4.处理@Import注解
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
// 5.处理@ImportResource注解
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
... ...
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
// 6.处理@Bean注解
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
... ...
return null;
}
接着我们看一下AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar

可以看到AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,所以registerBeanDefinitions方法会在ApplicationContext的refresh方法中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors里被调用。

在AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar的registerBeanDefinitions方法中主要是往Spring注册了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
// AOP的处理入口
// 注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,主要用于处理@AspectJ注解
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
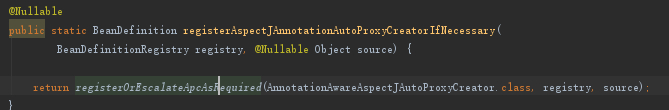

可以看到最终AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator被封装到BeanDefinition注册到Spring中。
而在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator所继承的父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口

其中实现了一个很重要的方法:postProcessAfterInitialization,这里会创建返回Bean对应的代理对象。

通过方法的名称我们也可以知道postProcessAfterInitialization会在Bean初始化完成后调用,这是我们回到Bean的创建方法doCreateBean中,我们在之前的文章有提过此方法中的第5点注释处的方法就是处理生成代理对象的。

接着我们继续看一下initializeBean的具体源码
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
... ...
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 1.调用BeanPostProcessor实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 2.调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
... ...
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 3.调用BeanPostProcessor实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
// 如果配置了代理,则AbstractAutoProxyCreator会在此处调用,生成代理对象
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
我们可以看到注释第3点处的applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法

最终调用到我们一开始所介绍的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中

可以看到核心流程在wrapIfNecessary里,具体源码如下:
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
// 判断当前bean的切面标识
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
// 1.根据当前beanMame对应的bean去扫描匹配bean类中的方法是否有符合Pointcut规则(@Pointcut)的切面方法(@Around、@Before、@After...)
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
// 将当前Bean标识为有切面方法
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 2.创建代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
// 将当前Bean标识为无切面方法
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
首先我们看wrapIfNecessary方法中注释第1点处的getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法的具体代码


继续看findEligibleAdvisors的具体是如何获取Advisor

这里我们继续看一下aspectJAdvisorsBuilder的buildAspectJAdvisors方法
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取容器中所有的beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
// 获取Class对象
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 1.判断类上是否有@Aspect注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
// 解析封装@Aspect注解信息
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 2.获取所有切面方法封装类Advisor集合
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
// 3.将Advisor添加到列表中
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
// 4.返回Advisor列表
return advisors;
}
}
}
... ...
return advisors;
}
此时我们示例代码中的StudyTrainAspect会通过buildAspectJAdvisors()注释1处的判断,走到注释2处的方法里面。
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. getAdvisorMethods返回没有@Pointcut注解的方法集合
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// 2. 创建Advisor
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
... ...
return advisors;
}
首先我们getAdvisors()注释1处getAdvisorMethods方法

getAdvisorMethods获取到没有@Pointcut的方法,所以method列表中会记录到示例代码StudyTrainAspect的studyTrain方法
接着我们返回getAdvisors()注释2处。

getPointcut方法会去解析studyTrain上的@Around注解的信息。



@Nullable
public static <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotation(Method method, @Nullable Class<A> annotationType) {
Assert.notNull(method, "Method must not be null");
if (annotationType == null) {
return null;
}
AnnotationCacheKey cacheKey = new AnnotationCacheKey(method, annotationType);
A result = (A) findAnnotationCache.get(cacheKey);
if (result == null) {
Method resolvedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
// 从当前方法上寻找annotationType类型的注解信息
result = findAnnotation((AnnotatedElement) resolvedMethod, annotationType);
if (result == null) {
// 从当前类实现的接口中寻找annotationType类型的注解
result = searchOnInterfaces(method, annotationType, method.getDeclaringClass().getInterfaces());
}
// 从父类中寻找annotationType类型的注解信息
Class<?> clazz = method.getDeclaringClass();
while (result == null) {
... ...
}
... ...
}
return result;
}
最后可以看到注释2处将信息封装到AspectJAnnotation中返回到getPointcut方法中,此时getPointcut注释1处获取到的aspectJAnnotation对象如下:

最后再到注释2处创建AspectJExpressionPointcut返回出去。

可以看到AspectJExpressionPointcut保存着示例代码StudyTrainAspect的studyTrain方法@Around注解的pointcut表达式:studyTrainPointcut()。
接着我们看回到getAdvisor方法的注释2处

通过入参我们可以发现这里的InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl装了示例代码pointcut表达式(studyTrainPointcut())和Advice增强方法(studyTrain())等信息。
接着我们看一下InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl类


可以看到这个类最终实现了Advisor接口,而且类中有几个重要的属性,我们看一下在构造方法中instantiatedAdvice属性是如何赋值的。

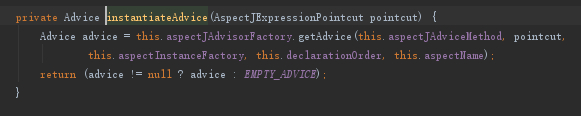
getAdvice具体代码如下
@Override
@Nullable
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
// 获取Method方法上的注解
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
... ...
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
// 忽略@Pointcut注解
return null;
case AtAround:
// 封装@Around注解
// AspectJAroundAdvice实现了MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
// 封装@Before注解
// AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice实现了MethodBeforeAdvice接口
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
// 封装@After注解
// AspectJAfterAdvice实现了MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
// 封装@afterReturning注解
// AspectJAfterReturningAdvice实现了AfterReturningAdvice接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
// 封装@afterThrowing注解
// AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice实现了MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
可以看到在getAdvice方法中根据注解封装成对应的Advice,其中封装Around注解和After注解的Advice实现了MethodInterceptor接口,而封装After注解的Before实现的是MethodBeforeAdvice接口。
所以在我们示例代码中StudyTrainAspect中的带有@Around注解的studyTrain方法会被封装成AspectJAroundAdvice对象

接着getAdvisor方法将Advisor返回到buildAspectJAdvisors中,buildAspectJAdvisors再将Advisor保存到列表里继续获取其他Advisor,最后将Advisor列表返回到findEligibleAdvisors。

接着我们继续看findEligibleAdvisors注释第2点处,看看Bean和Advisor是如何匹配,在我们示例代码就是StudentA的examing方法与StudyTrainAspect的studyTrain的匹配过程。

findEligibleAdvisors这块的匹配比较复杂,我们跟着断点大概看一下






上面这个方法中的FuzzyBoolean类会记录匹配结果

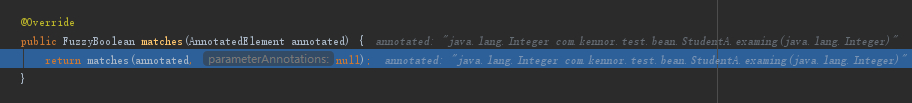

这里通过hasAnnotation判断examing方法是否包含StudyTraninAnnotation注解,由于examing是有添加@StudyTraninAnnotation注解的,所以会返回YES
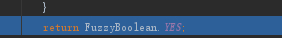


然后将match封装到ShadowMatchImpl中返回出去
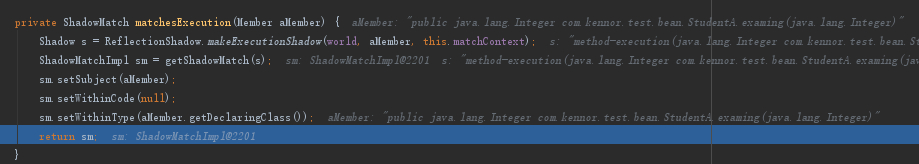
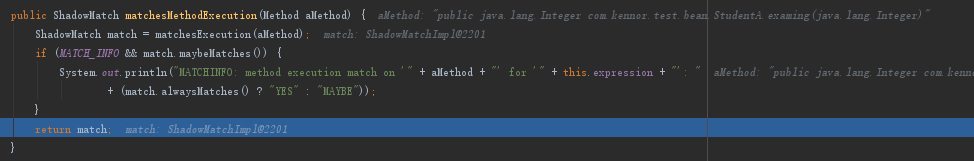


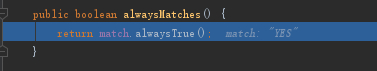



最后通过匹配,把Advisor添加到eligibleAdvisors中返回出去
接着回到findEligibleAdvisors方法中

此时就将StudentA匹配到的Advisor返回出去

接着就回到了一开始的wrapIfNecessary中

我们接下来将用注释1处获取到的Advisor用于注释2处创建StudentA的代理对象。

在createProxy方法中可以看到创建了代理工厂proxyFacotry,并且将Advisor添加到代理工厂中,然后通过proxyFacotry获取代理对象。
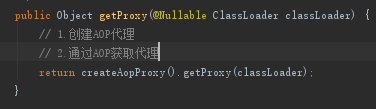
我们先看一下getProxy中的注释1处创建AOP代理
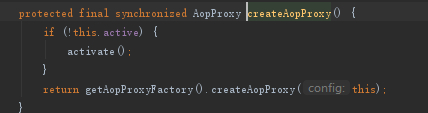

由于我们的StudentA实现了Student接口,所以采用JDK代理模式,因此会创建一个JDKDynamicAopProxy代理对象返回
而JDKDynamicAopProxy实现了动态代理的关键接口InvocationHandler,因此StudentA代理对象调用接口中的examing方法的时候会调用回此类的invoke方法中,这个我们在后面介绍。
接着我们先回到getProxy方法中的注释第2处,看看getProxy方法
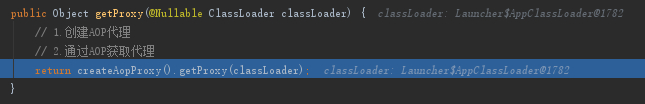
选择JDKDynamicAopProxy对象

 可以看到需要代理的接口中就包含了Student接口,接着继续往下走到Proxy.newProxyInstance方法中,接下来就是我们熟悉的动态代理相关的代码了
可以看到需要代理的接口中就包含了Student接口,接着继续往下走到Proxy.newProxyInstance方法中,接下来就是我们熟悉的动态代理相关的代码了


最后生成动态代理类返回到一开始提到的wrapIfNecessary方法中。




最后返回到doCreateBean方法中,此时exposedObject持有着StudentA的代理对象。

最后doCreateBean将exposedObject返回出去

接着进入到getSingleton中,最终studentA缓存的对象是StudentA的代理对象。
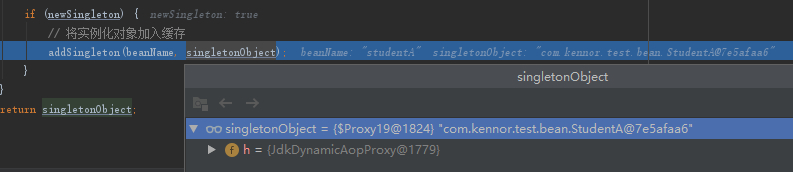
这也就是为什么在示例代码中我们获取到的StudentA是个代理对象的原因。
接着我们在前面分析的时候已经提到,StudentA代理对象调用接口中的examing方法的时候会调用代理对象的invoke方法,也就是JDKDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法。
接着我们看一下在JDKDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法中是如何调用到StudentA的examing方法和StudyTrainAspect的studyTrain方法
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
// 从advised中获取targetSource
// 代理实例就保存在targetSource的target属性中
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
... ...
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
// 获取代理示例
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// Get the interception chain for this method.
// 获取符合当前代理示例方法的切面执行链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 创建MethodInvocation
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
// 1.调用切面执行链方法
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
... ...
return retVal;
}
... ...
}
看到注释1处继续调用proceed方法

调用到我们的@Around注解的方法studyTrain的封装类AspectJAroundAdvice的invoke方法,继续进入到AspectJAroundAdvice的invoke方法中


这时就调用到StudyTrainAspect的studyTrain方法中了

然后我们修改参数后调用了joinPoint的proceed方法

再次来到proceed方法中
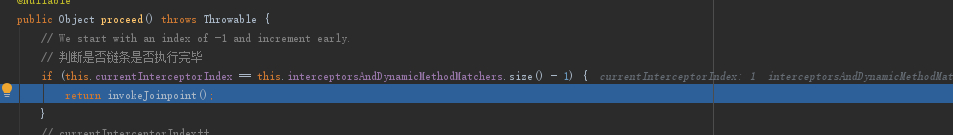
此时链条已经执行完毕,进入到invokeJoinponit方法中,最后会反射调用到StudentA的examing方法
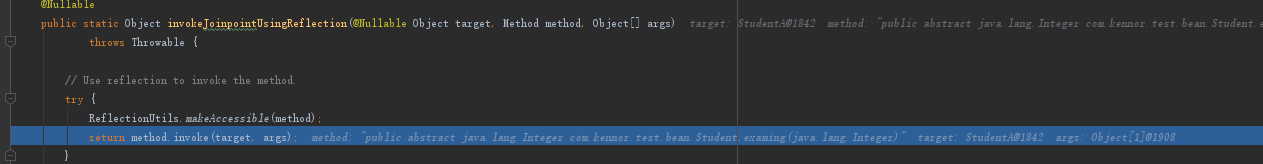
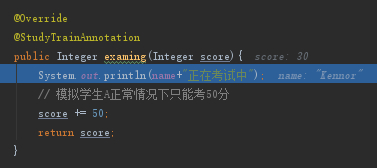
然后返回到proceed方法中

然后继续返回到StudyTrainAspect的studyTrain方法中的joinPoint.proceed处
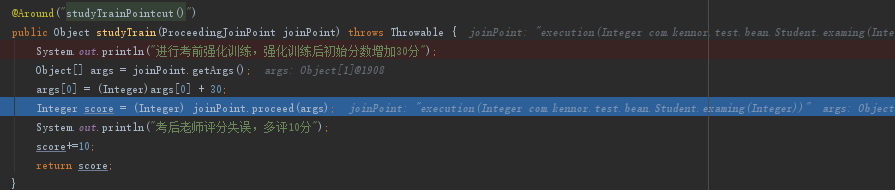
然后执行往studyTrain继续往上返回出去

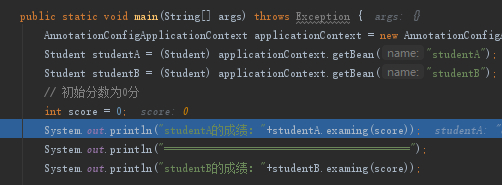
最后执行完毕。






















 710
710











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








