目录
一、题目
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
插入一个字符
删除一个字符
替换一个字符
示例 1:
输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
输出:3
解释:
horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r')
rorse -> rose (删除 'r')
rose -> ros (删除 'e')
示例 2:
输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
输出:5
解释:
intention -> inention (删除 't')
inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e')
enention -> exention (将 'n' 替为 'x')
exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c')
exection -> execution (插入 'u')
提示:
0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
word1 和 word2 由小写英文字母组成换
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
二、自顶向下的解法(递归,采用备忘录)
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) // 自顶向下,使用备忘录
{
int i = word1.size(), j = word2.size();
vector<vector<int>> memo(i, vector<int>(j, -1)); // 设置备忘录初始值为-1
return DP(word1, word2, i - 1, j - 1, memo);
}
int DP(string& s1, string& s2, int i, int j, vector<vector<int>>& memo)
{
if (i == -1) // 此时s1缺少字符,向s1中加入j+1个字符需要执行j+1步
return j + 1;
if (j == -1) // 此时s1多出字符,向s1中删除i+1个字符需要执行i+1步
return i + 1;
if (memo[i][j] != -1) // 查询备忘录,避免重复计算
return memo[i][j];
if (s1[i] == s2[j]) // 当字符相等时,不需要执行操作
memo[i][j] = DP(s1, s2, i - 1, j - 1, memo);
else
{
memo[i][j] = min( // 判断哪个操作编辑距离最短
DP(s1, s2, i, j - 1, memo) + 1, // 在s1中插入一个字符
min(DP(s1, s2, i - 1, j, memo) + 1, // 在s1中删除一个字符
DP(s1, s2, i - 1, j - 1, memo) + 1) // 在s1中替换一个字符
);
}
return memo[i][j];
}
};三、自底向上的解法(采用DP table)
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int m = word1.size(), n = word2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
// base case
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i) // 删除word1中的i个字符,使word1 == word2(word2为空字符串)
dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j <= n; ++j) // 向word1中添加j个字符,使word1 == word2(word1为空字符串)
dp[0][j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
{
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) // 第i个字符在word1中的下标为i-1
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]; // 当字符相等时,不需要执行操作,执行跳过操作
else
{
dp[i][j] = min( // 判断替换、插入、删除哪个的编辑距离最短
dp[i - 1][j] + 1, // 在word1中删除一个字符
min(dp[i][j - 1] + 1, // 在word1中插入一个字符
dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1) // 在word1中替换一个字符
);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};注:dp(i, j)的返回值就是word1[0 .. i]和word[0 .. j]的最小编辑距离,无论是自顶向下还是自底向上,都是判断在对word1执行 跳过(word1[i] == word2[j]时不需要执行任何操作,直接跳过,此时最小编辑距离等于前i-1个字符的最小编辑距离,此时i和j都减一)、替换(将word1[i]替换为word2[j],此时i和j都减一)、删除(将word1[i]删除,此时i减一,j不动)、插入(在word1[i]后面插入word2[j],此时j减一,i不动)这四个操作哪个能够使编辑距离最小。
四、拓展——利用自定义结构打印每一步的具体操作
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class Node {
private:
int step; // 记录最短编辑距离(当前操作次数)
int choice; // 0代表跳过,1代表插入,2代表删除,3代表替换
public:
Node()
{
this->step = -1;
this->choice = -1;
}
Node(int step, int choice)
{
this->step = step;
this->choice = choice;
}
int getStep() const
{
return this->step;
}
int getChoice() const
{
return this->choice;
}
void setStep(const int step)
{
this->step = step;
}
void setChoice(const int choice)
{
this->choice = choice;
}
};
int minDistance(string word1, string word2);
Node min_dis(Node& n1, Node& n2, Node& n3);
void printResult(vector<vector<Node>>& dp, string& s1, string& s2);
int main()
{
string word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution";
std::cout << minDistance(word1, word2) << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int minDistance(string word1, string word2)
{
int m = word1.size(), n = word2.size();
Node node;
vector<vector<Node>> dp(m + 1, vector<Node>(n + 1, node));
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i)
dp[i][0] = Node(i, 2);
for (int j = 0; j <= n; ++j)
dp[0][j] = Node(j, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
{
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1])
dp[i][j] = Node(dp[i - 1][j - 1].getStep(), 0);
else
{
dp[i][j] = min_dis(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
}
}
printResult(dp, word1, word2);
return dp[m][n].getStep();
return 1;
}
Node min_dis(Node& n1, Node& n2, Node& n3)
{
int step, choice;
if (n1.getStep() < n2.getStep())
{
step = n1.getStep();
choice = 2;
}
else
{
step = n2.getStep();
choice = 1;
}
if (n3.getStep() < step)
{
step = n3.getStep();
choice = 3;
}
return Node(step + 1, choice);
}
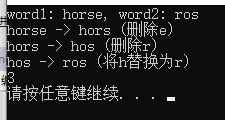
void printResult(vector<vector<Node>>& dp, string& s1, string& s2)
{
std::cout << "word1: " << s1 << ", word2: " << s2 << std::endl;
int i = s1.size();
int j = s2.size();
string word = s1;
string s = "";
while (i > 0 && j > 0) // 反向推导每一步的操作
{
int choice = dp[i][j].getChoice();
char c = s2[j - 1];
switch (choice)
{
case 0: i--; // 跳过
j--;
break;
case 1: s = word.substr(0, i) + c + word.substr(i, word.size() - i); // 插入
std::cout << word << " -> " << s << " (插入" << c << ")" << std::endl;
word = s;
j--;
break;
case 2: s = word.substr(0, i - 1) + word.substr(i, word.size() - i); // 删除
std::cout << word << " -> " << s << " (删除" << word[i-1] << ")" << std::endl;
word = s;
i--;
break;
case 3: s = word.substr(0, i - 1) + c + word.substr(i, word.size() - i); // 替换
std::cout << word << " -> " << s << " (将" << word[i-1] << "替换为" << c << ")" << std::endl;
word = s;
i--;
j--;
break;
default:break;
}
}
while (i > 0) // 删除多余字符
{
s = word.substr(0, i - 1) + word.substr(i, word.size() - i);
std::cout << word << " -> " << s << " (删除" << word[i - 1] << ")" << std::endl;
word = s;
i--;
}
while (j > 0) // 插入缺少的字符
{
char c = s2[j - 1];
s = c + word;
std::cout << word << " -> " << s << " (插入" << c << ")" << std::endl;
word = s;
j--;
}
}


参考资料:《labudadong的算法小抄》 作者:付东来























 2713
2713











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










