javax.wx.rs RESTful 接口详解
Restful介绍
java.ws.rs是jax-rs规范中定义的包名.jax-rs全称Java API for RESTful Services.jax-rs规范目前版本是2.0规范文档.
jax-rs中定义了
- 一组启动方式 (以jee作为http容器 还是配合servlet作为http容器)
- 一组注解@GET, @POST, @DELETE, @PUT, @Consumes … 通过 POJO Resource类 提供Rest服务
如JSR规范定义Servlet是以继承HttpServlet 并重写doGet doPost do…方法一样。遵循这套标准都可以称为Servlet 写的Servlet程序,可以不经过任何修改放到任何实现Servlet容器中运行,写的jax-rs程序可以不经任何修改和任何jax-rs框架配合使用。
而Spring MVC是以Servlet为http容器 并自己构建了一套Api没有遵循jax-rs规范。
目前实现jax-rs标准的框架有很多:
- Apache CXF开源的Web服务框架
- Jersey 由Sun提供的JAX-RS的参考实现
- RESTEasy JBoss的实现
- Restlet 由Jerome Louvel和Dave Pawson开发 是最早的REST框架 先于JAX-RS出现
- Apache Wink 一个Apache软件基金会孵化器中的项目 其服务模块实现JAX-RS规范
准备
创建这样一个微服务用于体验,测试这些注解

请求路径、请求方式
@Path,GET,POST,PUT,DELETE
- 标注class时 表明该类是个资源类 凡是资源类必须使用该注解
- 标注method时 表示具体的请求资源的路径
Path不能单独使用,至少需要和请求方式配合使用。
比如
@Path("path")
public class PathController {
@GET
public String defaultMethod() {
return "default method for path";
}
}
如果没有请求方式编译器会有检测:
Class doesn't contain any JAX-RS annotated methods

@Consumes
指定HTTP请求的MIME类型
默认是*/* 表示任意的MIME类型
该注解支持多个值设定
可以使用MediaType来指定MIME类型
MediaType的类型大致有
- application/xml
- application/atom+xml
- application/json
- application/svg+xml
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/octet-stream
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
- text/xml
- text/html
@Consumes
指定HTTP请求的MIME类型
默认是*/* 表示任意的MIME类型
该注解支持多个值设定
可以使用MediaType来指定MIME类型
MediaType的类型大致有
- application/xml
- application/atom+xml
- application/json
- application/svg+xml
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/octet-stream
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
- text/xml
- text/html
@Produces
指定HTTP响应的MIME类型
默认是*/*表示任意的MIME类型
MediaType的类型大致有
- application/xml
- application/atom+xml
- application/json
- application/svg+xml
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/octet-stream
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
- text/xml
- text/html
@PathParam
参数注解,从url中获取参数
@QueryParam
参数注解,从url中获取参数,用于GET请求。
GET请求会将参数拼接在url中。
http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=x
其中的wd就是GET请求的参数
@FormParam
用于获取POST请求且以form(MIME类型为application/x-www-form-urlencoded)方式提交的表单的参数
@BeanParam
如果传递的较多 使用@FormParam等参数注解一个一个的接收每个参数可能显得太臃肿
可以通过Bean方式接收自定义的Bean
在自定义的Bean中字段使用@FormParam等参数注解
只需定义一个参数接收即可
@DefaultValue
配合前面的参数注解等使用 用来设置默认值
如果请求指定的参数中没有值
通过该注解给定默认值
@FormDataParam
用于获取POST请求且以form(MIME类型为multipart/form-data)方式提交的表单的参数
通常是在上传文件的时候
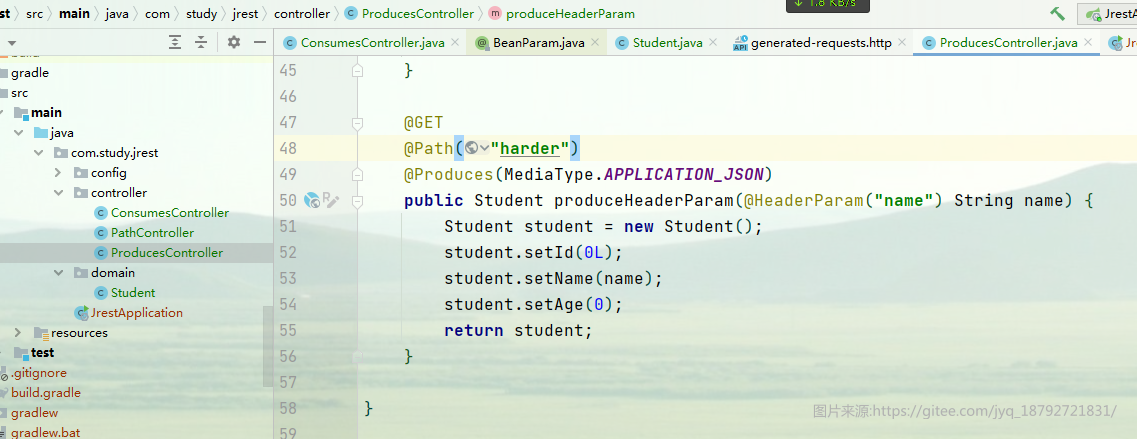
@HeaderParam
用于获取HTTP请求头中的参数值

@CookieParam
用于获取HTTP请求cookie中的参数值


@MatrixParam
可以用来绑定包含多个property (属性)=value(值) 方法参数表达式
用于获取请求URL参数中的键值对
必须使用’;'作为键值对分隔符
注意MatrixParam与QueryParam的区别
QueryParam请求url的格式为 url?key1=value1&key2=value2&…
MatrixParam请求url的格式为 url;key1=value1;key2=value2;…
@Context
用来用来解析上下文参数
和Spring中的AutoWired效果类似
通过该注解可以获取
ServletConfig
ServletContext
HttpServletRequest
HttpServletResponse
HttpHeaders
等信息
@Path("/user")
publicclass Resource {
@Context
HttpServletRequest req;
@Context
ServletConfig servletConfig;
@Context
ServletContext servletContext;
@GET
public String get(@Context HttpHeaders hh) {
MultivaluedMap<String, String> headerParams = hh.getRequestHeaders();
Map<String, Cookie> pathParams = hh.getCookies();
}
}
@Encoded
禁止解码
客户端发送的参数是什么样
服务器就原样接收
例子
我们写了8个方法:
@Path("path")
public class PathController {
@GET
public String defaultGetMethod() {
return "default method for get path";
}
@POST
public String defaultPostMethod() {
return "default method for post path";
}
@PUT
public String defaultPutMethod() {
return "default method for put path";
}
@DELETE
public String defaultDeleteMethod() {
return "default method for delete path";
}
@GET
@Path("hello")
public String getHello() {
return "hello method for get path";
}
@POST
@Path("hello")
public String postHello() {
return "hello method for post path";
}
@PUT
@Path("hello")
public String putHello() {
return "hello method for put path";
}
@DELETE
@Path("hello")
public String deleteHello() {
return "hello method for delete path";
}
}
请忽略我不正确的请求方式的使用。
使用postMan测试,或者使用idea的web Client的插件
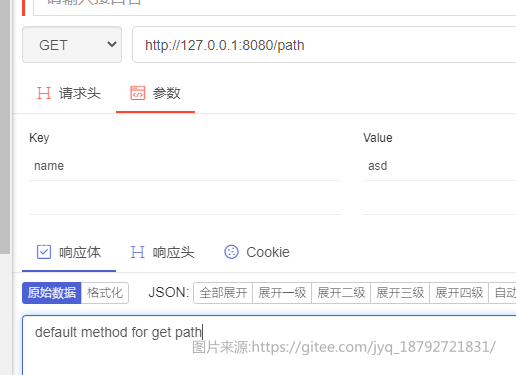
使用httpClient
GET http://localhost:8080/path
###
POST http://localhost:8080/path
###
PUT http://localhost:8080/path
###
DELETE http://localhost:8080/path
###
GET http://localhost:8080/path/hello
###
POST http://localhost:8080/path/hello
###
PUT http://localhost:8080/path/hello
###
DELETE http://localhost:8080/path/hello

这是consumes的例子
import com.study.jrest.domain.Student;
import javax.ws.rs.*;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
/**
* @author jiayq
* @Date 2021-04-03
*/
@Path("consumes")
public class ConsumesController {
@GET
@Consumes(MediaType.WILDCARD)
public String consumeGet(@QueryParam("name") String name) {
return "consume get , " + name;
}
@GET
@Path("{name}")
public String consumeGetPath(@PathParam("name") String name) {
return "consume get path , " + name;
}
@POST
public String consumePost(@MatrixParam("name") String name) {
return "consume post , " + name;
}
@POST
@Path("/post/{name}")
public String consumePostPath(@PathParam("name") String name) {
return "consume post path , " + name;
}
@Path("stu")
@POST
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public String consumeStu(Student student) {
return "consume student , " + student;
}
@Path("stu/bean")
@POST
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
public String consumeStuBean(@BeanParam Student student) {
return "consume student bean , " + student;
}
}
import lombok.Data;
import javax.ws.rs.FormParam;
/**
* @author jiayq
* @Date 2021-04-01
*/
@Data
public class Student {
@FormParam("id")
private Long id;
@FormParam("name")
private String name;
@FormParam("age")
private Integer age;
}
GET http://localhost:8080/consumes?name=xiaohua
###
GET http://localhost:8080/consumes/xiaomei
###
POST http://localhost:8080/consumes;name=xiaomei
###
POST http://localhost:8080/consumes/post/xiaomei
###
POST http://localhost:8080/consumes/stu
Content-Type: application/json
{"id":1,"name":"demoData","age":1}
###
POST http://localhost:8080/consumes/stu
id=1;name=demoData;age=1
###
POST http://localhost:8080/consumes/stu/bean
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
id=1&name=xiaomei&age=23
comsumes是请求的传参类型,也就是请求头中的Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded字段

这是Produces的例子
import com.study.jrest.domain.Student;
import javax.ws.rs.*;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author jiayq
* @Date 2021-04-03
*/
@Path("produces")
public class ProducesController {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
public String produceGet(@QueryParam("name") String name) {
return "produces get query param , " + name;
}
@POST
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_HTML)
public String producePost(@MatrixParam("name") String name) {
return "produces post query param , <b>" + name + "</b>";
}
@GET
@Path("get/{name}")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Map<String, String> produceGetPath(@PathParam("name") String name) {
return Map.of("result", "produces get path", "param",name);
}
@POST
@Path("post")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
public Student producesGetStudent(@FormParam("name") String name) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(0L);
student.setName(name);
student.setAge(0);
return student;
}
}
这是测试的报文
GET http://localhost:8080/produces?name=xiaomei
Accept: text/plain
###
POST http://localhost:8080/produces;name=xiaomei
Accept: text/html
###
GET http://localhost:8080/produces/get/xiaomei
Accept: application/json
###
POST http://localhost:8080/produces/post
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=xiaomei
Produces配置的是返回结果的类型,也就是请求头中的Accept字段

扩展–mvc实现的rest注解
| mvc注解 | ws.rs注解 | 等价的mvc注解 |
|---|---|---|
| RequestMapping | Path | |
| GetMapping | GET | RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) |
| PostMapping | POST | RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) |
| PutMapping | PUT | RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT) |
| DeleteMapping | DELETE | RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE) |
| PathVariable | PathParam | |
| MatrixVariable | MatrixParam | |
| RequestHeader | HeaderParam | |
| RequestBody | Encoded | |
| RequestParam | QueryParam | |
| RequestPart | FormDataParam | |
| CookieValue | CookieParam |
其实mcv和rs实现的功能都非常类似,甚至用法也类似,只是注解略有不同。











 本文详细介绍了Java API for RESTful Services (JAX-RS) 中的RESTful接口注解,包括@Path、GET/POST/PUT/DELETE、@Consumes/@Produces、@PathParam/@QueryParam/@FormParam等,以及它们在实际应用中的例子。
本文详细介绍了Java API for RESTful Services (JAX-RS) 中的RESTful接口注解,包括@Path、GET/POST/PUT/DELETE、@Consumes/@Produces、@PathParam/@QueryParam/@FormParam等,以及它们在实际应用中的例子。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










