文章目录
1.二叉搜索树
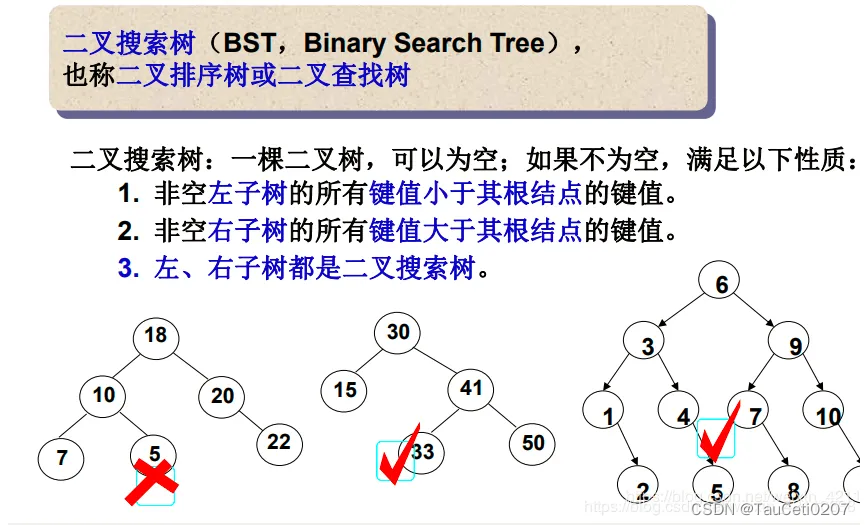
概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
二叉树节点
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
二叉树框架
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
private:
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
Node* _root = nullptr;
public:
~BSTree();
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t);
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t);
bool Insert(const K& key);
void InOrder();
bool Find(const K& key);
bool Erase(const K& key);
// 递归版本
bool FindR(const K& key);
bool InsertR(const K& key);
bool EraseR(const K& key);
};
查找
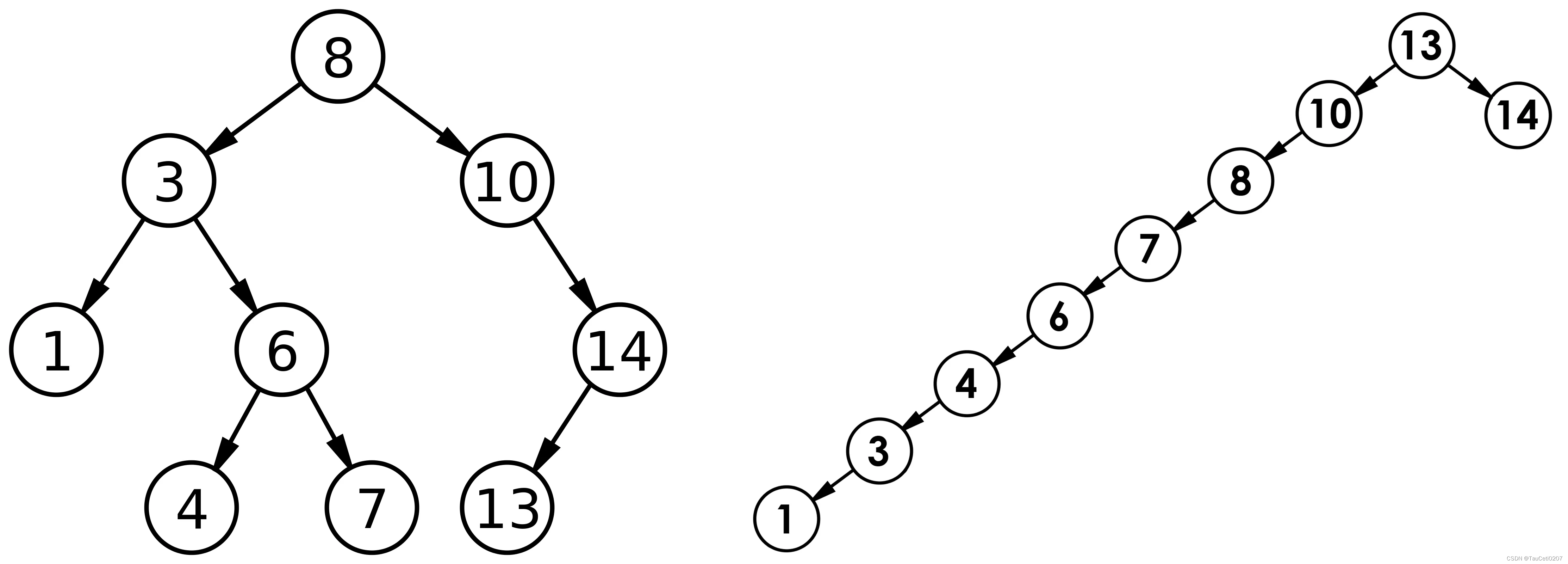
a、从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找。
b、最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,这个值不存在。
听到最多查找高度次,你是不是就以为查找效率特别高了?O(logN)?
不,最好情况(完全二叉树或接近完全二叉树)是这样,但要注意考虑极端场景。
最坏情况,二叉搜索树退化为单支树。
如果插入的数值有序或者相对有序,那就坏了,时间复杂度就变成 O(logN) 了。
非递归
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_left;
else
return true; // 找到了
}
return false; // 找不到
}
递归
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) // 找不到
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else
return true;
}
插入
a. 树为空,则直接新增节点,赋值给root指针
b. 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点
非递归

bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
// 不允许冗余
return false;
}
}
// 链接起来
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
void TestBSTree1()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
cout << endl;
t.Insert(16);
t.Insert(9);
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 13 14 16
cout << endl;
}
递归
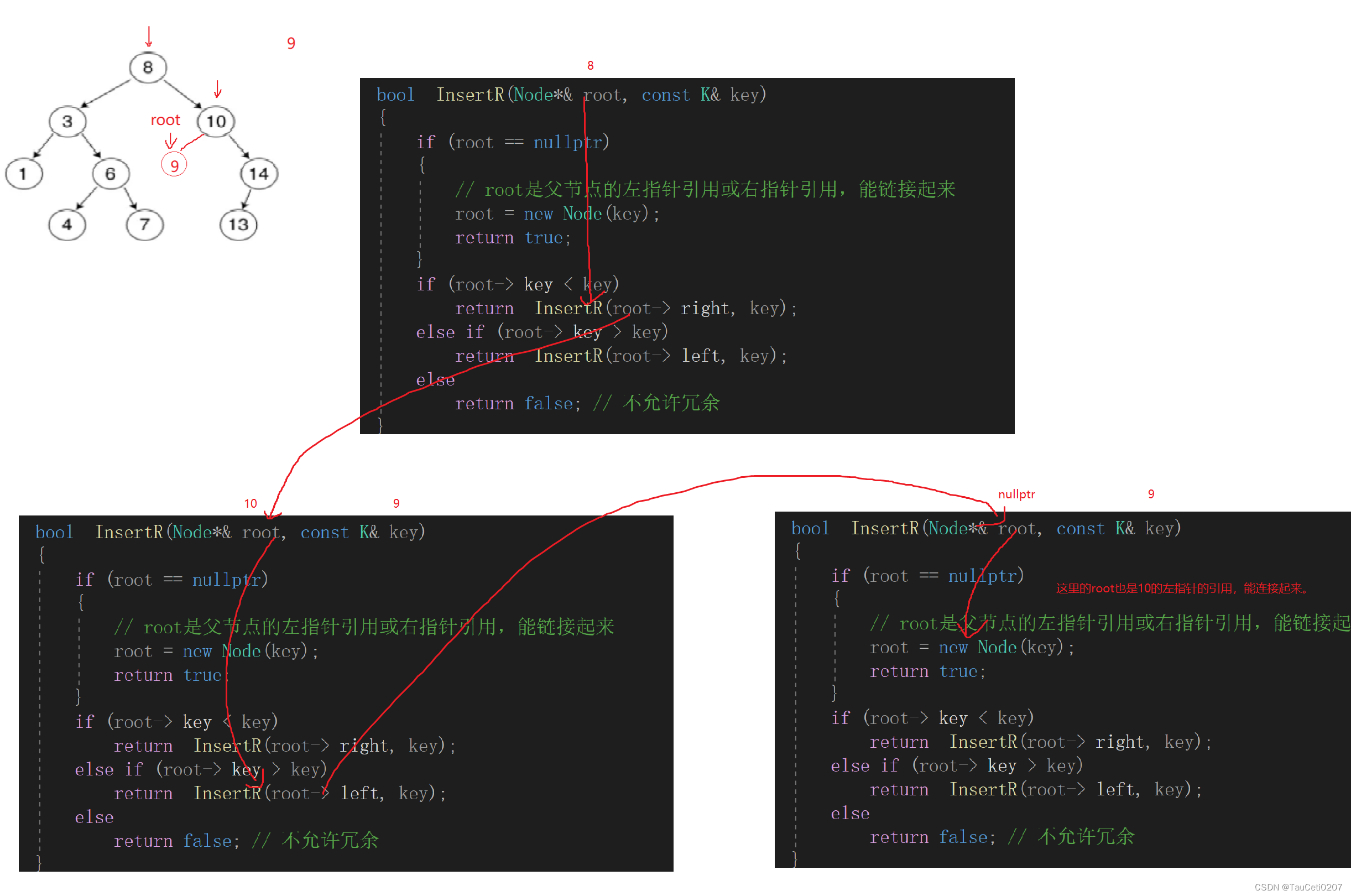
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
// root是父节点的左指针引用或右指针引用,能链接起来
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false; // 不允许冗余
}
中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root) // 左根右
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
注意,如果想在外界也能访问(因为外面无法传root过来),需要额外再套一层接口。
借助插入+中序遍历,能达到去重+排序的效果。
删除
非递归
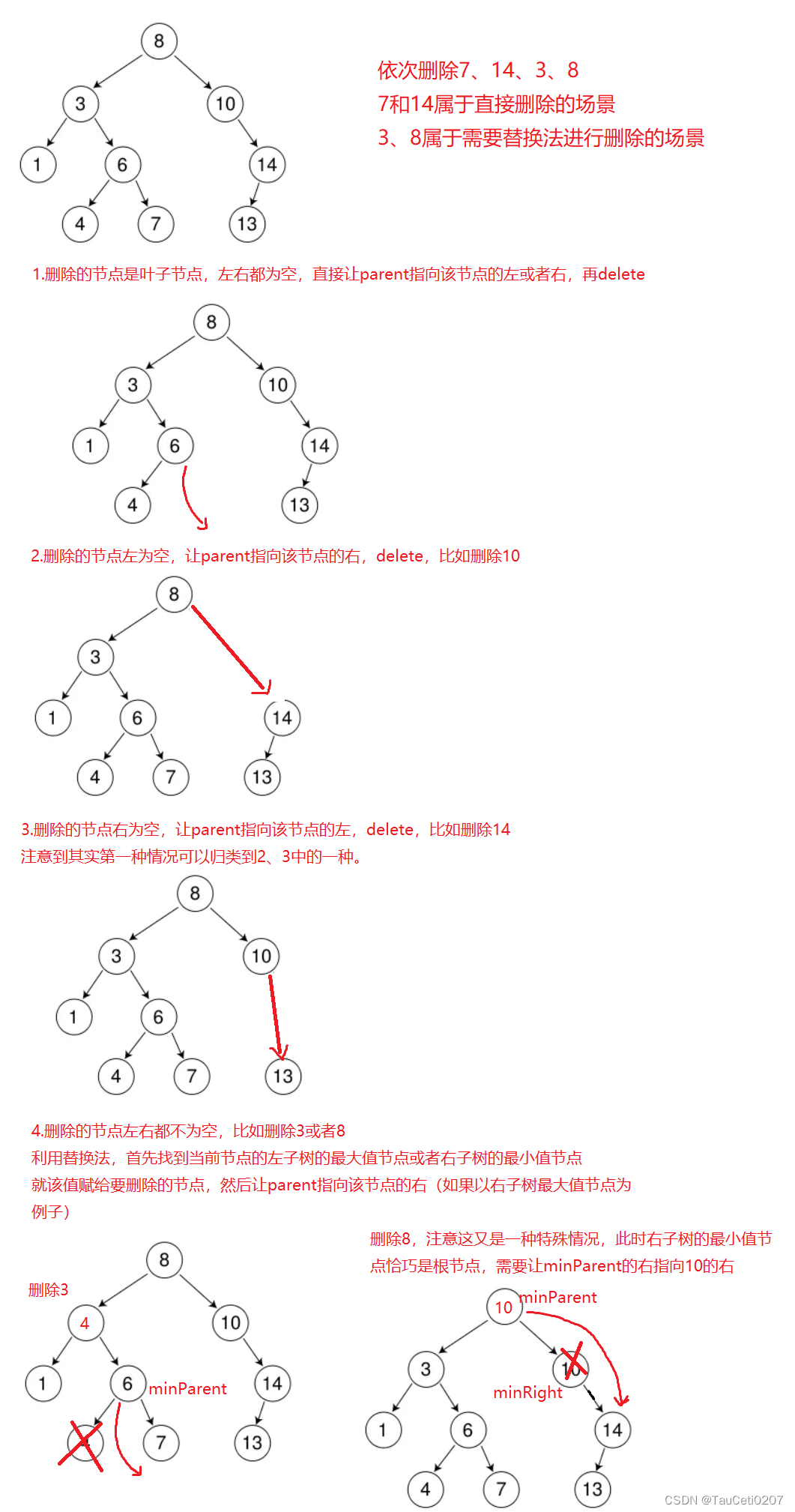
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
// 先看看有无要找的节点
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
// 找到了 key相等
// 3种情况
// 1.左为空 叶子节点也满足这种情况
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
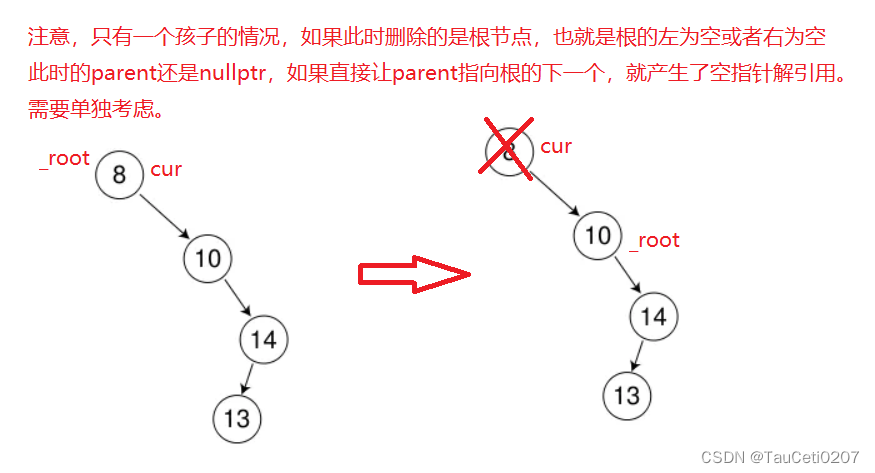
//单独考虑根节点也只有一个孩子的情况
if (cur == _root) // if(parent == nullptr)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
// 还需要考虑parent的是左指向还是右指向
// 也可以比大小来判断
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
// 删除cur节点
delete cur;
}
// 2.右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if(cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
// 2个孩子 替换法
else
{
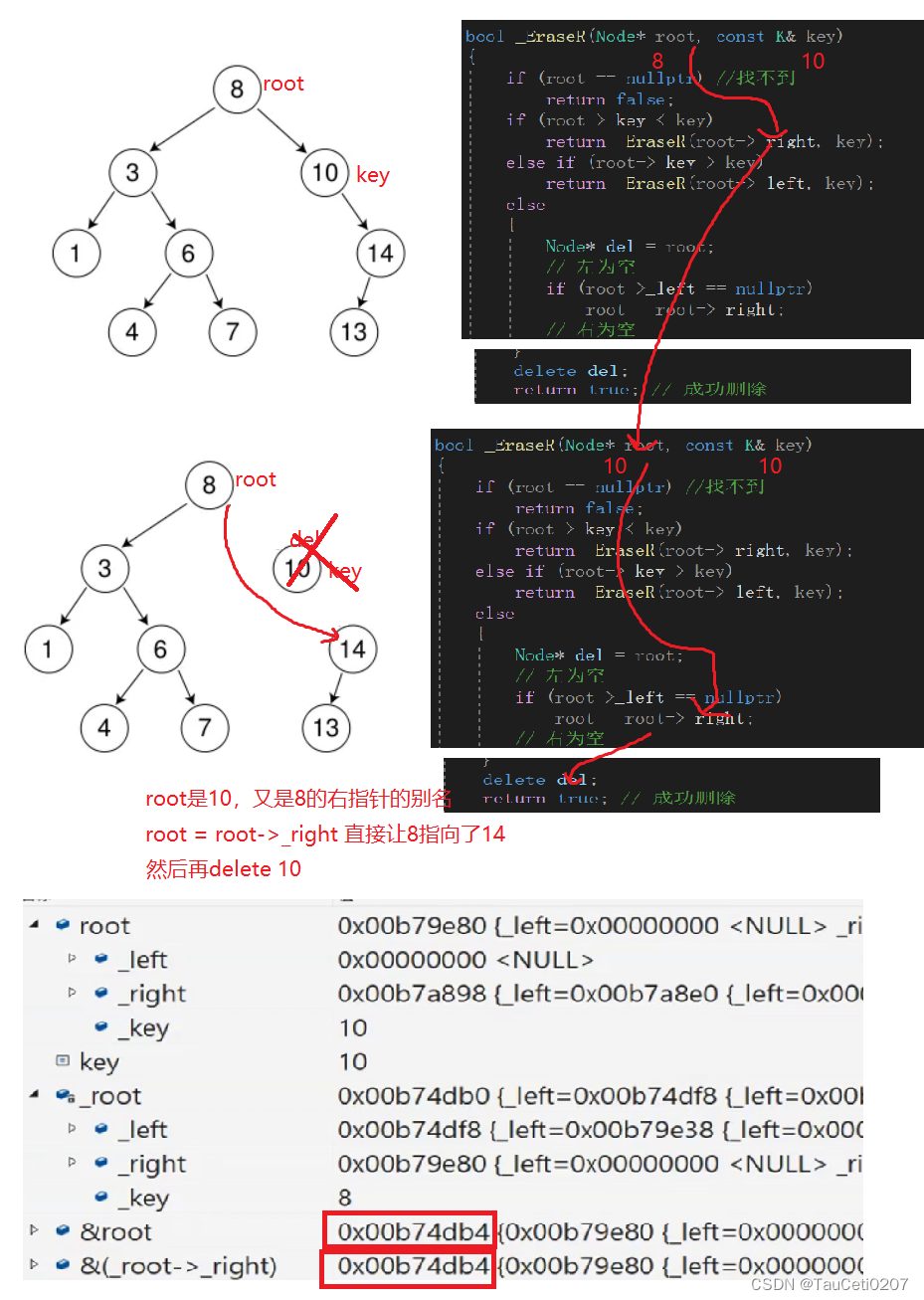
// 用右子树的最小值节点替代
// 如果右子树的第一个节点就是最小值节点,那么就是minRight的左为空 循环都不进去
// 后面就会产生空指针解引用的问题 因此minParent不能用nullptr初始化
//Node* minParent = nullptr; // 删除8的情况
Node* minParent = cur; // 找到minRight后,左一定为空,但可能还会有右孩子,因此不能直接delete minRight
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minParent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
// 找到右子树最小值
// 交换也可以
// swap(cur->_key, minRight->_key);
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
// 需要考虑minParent的左指向还是右指向
// 右子树的最小值节点是右子树根节点又是一个特殊情况 例如删除8
if (minParent->_left == minRight)
{
minParent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else if(minParent->_right == minRight)
{
minParent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
}
// 成功删除节点
return true;
}
}
// 出来时cur 为空,说明找不到
return false;
}
注意,有人在第三种情况时这么写
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while(minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(minRight->_key, cur->_key);
return Erase(key);
不能利用递归去删除,因为交换之后,比如要删除3,右节点的最小值4,交换之后,要去删掉key为3的节点,但3是比4小的,找的时候只会去4的左子树找,那么就永远找不到,实际上3是在右子树这边的。
测试:
void TestBSTree2()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
t.Erase(3);
t.Erase(8);
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 10 13 14
t.Erase(14);
t.Erase(7);
t.InOrder(); // 1 4 6 10 13
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Erase(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 空
}
递归
删除左为空的节点:
删除的节点有2个孩子

bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) //找不到
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
else
{
Node* del = root;
// 左为空
if (root->_left == nullptr)
root = root->_right; // 这恰巧也能解决 要删除的如果是根节点且根节点也只有一个孩子的问题
// 右为空
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
root = root->_left;
// 有2个孩子
else
{
// 替换法 右子树最小值节点
// 引用不能改变指向,因此不能给minRight 加引用解决问题
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
// 引用不起作用了,怎么删除呢 再加个parent? 太麻烦了
// 换下来的值肯定是右子树中最小的,因此直接去右子树中删就行了
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true; // 成功删除
}
}
深拷贝
拷贝构造:
Node* CopyTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key);
// 递归拷贝左右子树
copyNode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);
copyNode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);
return copyNode;
}
// 拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = CopyTree(t._root);
}
赋值重载:
// t1 = t2 现代写法
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
// t是t2的拷贝 t1赋值给*this
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
默认构造:
// 强制编译器自己生成默认构造 C++11才支持
// 因为我们自己写了拷贝构造,编译器就不会再生成默认构造,而我们写的又不是默认构造
// 因此必须有一个默认构造才能完成编译
BSTree() = default;
析构
void DestroyTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
DestroyTree(root->_left);
DestroyTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
~BSTree()
{
DestroyTree(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
源代码
#pragma once
#include <algorithm>
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
private:
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
Node* _root = nullptr;
void DestroyTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
DestroyTree(root->_left);
DestroyTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* CopyTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key);
// 递归拷贝左右子树
copyNode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);
copyNode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);
return copyNode;
}
public:
~BSTree()
{
DestroyTree(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
// 强制编译器自己生成默认构造 C++11才支持
// 因为我们自己写了拷贝构造,编译器就不会再生成默认构造,而我们写的又不是默认构造
// 因此必须有一个默认构造才能完成编译
BSTree() = default;
// 拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = CopyTree(t._root);
}
// t1 = t2 现代写法
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
// t是t2的拷贝 t1赋值给*this
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
// 不允许冗余
return false;
}
}
// 链接起来
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
// 封装一层,以便外面也能使用
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_left;
else
return true; // 找到了
}
return false; // 找不到
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
// 先看看有无要找的节点
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
// 找到了 key相等
// 3种情况
// 1.左为空 叶子节点也满足这种情况
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//单独考虑根节点也只有一个孩子的情况
if (cur == _root) // if(parent == nullptr)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
// 还需要考虑parent的是左指向还是右指向
// 也可以比大小来判断
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if(cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
// 删除cur节点
delete cur;
}
// 2.右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if(cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
// 2个孩子 替换法
else
{
// 用右子树的最小值节点替代
// 如果右子树的第一个节点就是最小值节点,那么就是minRight的左为空 循环都不进去
// 后面就会产生空指针解引用的问题 因此minParent不能用nullptr初始化
//Node* minParent = nullptr; // 删除8的情况
Node* minParent = cur; // 找到minRight后,左一定为空,但可能还会有右孩子,因此不能直接delete minRight
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minParent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
// 找到右子树最小值
// 交换也可以
// swap(cur->_key, minRight->_key);
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
// 需要考虑minParent的左指向还是右指向
// 右子树的最小值节点是右子树根节点又是一个特殊情况 例如删除8
if (minParent->_left == minRight)
{
minParent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else if(minParent->_right == minRight)
{
minParent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
}
// 成功删除节点
return true;
}
}
// 出来时cur 为空,说明找不到
return false;
}
// 递归版本
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) //找不到
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
else
{
Node* del = root;
// 左为空
if (root->_left == nullptr)
root = root->_right; // 这恰巧也能解决 要删除的如果是根节点且根节点也只有一个孩子的问题
// 右为空
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
root = root->_left;
// 有2个孩子
else
{
// 替换法 右子树最小值节点
// 引用不能改变指向,因此不能给minRight 加引用解决问题
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
// 引用不起作用了,怎么删除呢 再加个parent? 太麻烦了
// 换下来的值肯定是右子树中最小的,因此直接去右子树中删就行了
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true; // 成功删除
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
// root是父节点的左指针引用或右指针引用,能链接起来
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false; // 不允许冗余
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) // 找不到
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else
return true;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
};
void TestBSTree1()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
t.Insert(16);
t.Insert(9);
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 13 14 16
}
void TestBSTree2()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
t.Erase(3);
t.Erase(8);
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 10 13 14
t.Erase(14);
t.Erase(7);
t.InOrder(); // 1 4 6 10 13
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Erase(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 空
}
void TestBSTree3()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder();
BSTree<int> copy(t);
copy.InOrder();
BSTree<int> copy2 = copy;
copy2.InOrder();
}
void TestBSTree4()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);
}
t.InOrder();
BSTree<int> copy(t);
copy.InOrder();
BSTree<int> copy2 = copy;
copy2.InOrder();
}
void TestBSTree5()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
t.EraseR(3);
t.EraseR(8);
t.InOrder(); // 1 3 4 6 7 10 13 14
t.EraseR(14);
t.EraseR(7);
t.InOrder(); // 1 4 6 10 13
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Erase(e);
}
t.InOrder(); // 空
}
2.二叉搜索树应用
K模型
K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树,
在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
KV模型
每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。该种方式在现实生活中非常常见:
- 比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,
英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对; - 再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,
单词与其出现次数就是<word, count>就构成一种键值对。
源代码
namespace key_value
{
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
const K _key; // key 不能修改,value可以修改
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
: _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
private:
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
Node* _root = nullptr;
public:
// 封装一层,以便外面也能使用
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
// 只保留递归版本
// 只需通过查找key就能找到value,且要能修改
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) //找不到
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
else
{
Node* del = root;
// 左为空
if (root->_left == nullptr)
root = root->_right; // 这恰巧也能解决 要删除的如果是根节点且根节点也只有一个孩子的问题
// 右为空
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
root = root->_left;
// 有2个孩子
else
{
// 替换法 右子树最小值节点
// 引用不能改变指向,因此不能给minRight 加引用解决问题
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
// 引用不起作用了,怎么删除呢 再加个parent? 太麻烦了
// 换下来的值肯定是右子树中最小的,因此直接去右子树中删就行了
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true; // 成功删除
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
// root是父节点的左指针引用或右指针引用,能链接起来
root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);
else
return false; // 不允许冗余
}
// 找到之后要能修改value
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) // 找不到
return nullptr;
if (root->_key < key)
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else
return root;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ": " << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
};
}
字典
// 中英文字典
void TestBSTree1()
{
BSTree<string, string> EToCDict;
EToCDict.InsertR("root", "根");
EToCDict.InsertR("left", "左边");
EToCDict.InsertR("right", "右边");
EToCDict.InsertR("man", "男人");
EToCDict.InsertR("vector", "容器");
EToCDict.InsertR("string", "字符串");
EToCDict.InsertR("file", "文件");
EToCDict.InsertR("project", "项目");
EToCDict.InsertR("debug", "调试");
// 。。。
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = EToCDict.FindR(str);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
cout << "对应的中文: " << ret->_value << endl;
// 也可以修改value 但不能修改key
ret->_value = "****";
}
else
{
cout << "无此单词,请重新输入:" << endl;
}
}
}

统计水果
// 统计水果出现次数
void TestBSTree2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
BSTreeNode<string, int>* ret = countTree.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
countTree.InsertR(str, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
// 输出统计结果
countTree.InOrder();
}

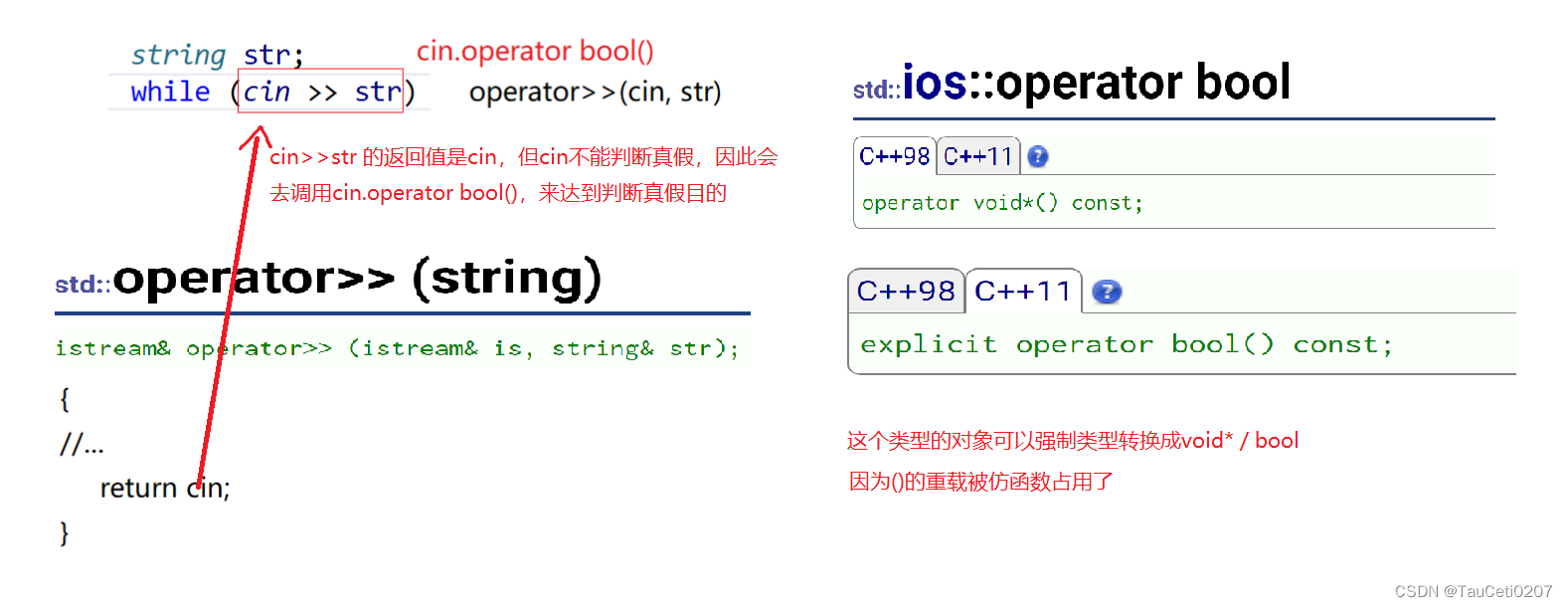
关于while(cin)
class A
{
public:
A(int a = 0)
:_a(a)
{}
//operator bool()
explicit operator bool()
{
if (_a < 10)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void Print()
{
cout << _a << endl;
}
void Set(int a)
{
_a = a;
}
private:
int _a;
};
void test()
{
A aa = 2; // 如果构造函数加了explicit 就不允许这样的隐式类型转换
A a;
//bool ret = a; // operator bool 加了 explicit 才避免的自定义类型往bool类型的转换
int x;
//while (a.operator bool()) 与这个等价
while (a)
{
a.Print();
cin >> x;
a.Set(x);
}
}
尾声
🌹🌹🌹
写文不易,如果有帮助烦请点个赞~ 👍👍👍
Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ🌹🌹🌹
😘😘😘
👀👀由于笔者水平有限,在今后的博文中难免会出现错误之处,本人非常希望您如果发现错误,恳请留言批评斧正,希望和大家一起学习,一起进步ヽ( ̄ω ̄( ̄ω ̄〃)ゝ,期待您的留言评论。
附GitHub仓库链接
























 2872
2872











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








