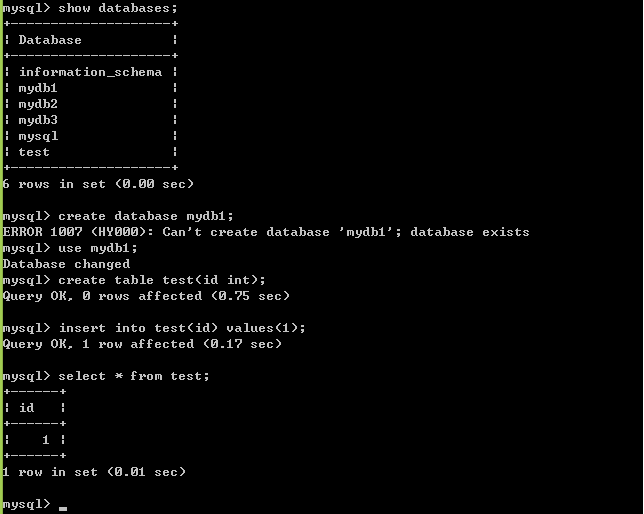
一、SQL语句:数据库、表
1、删除前面创建的数据库
- drop database mydb1;
2、修改库
- 是不能修改库名的,只能修改库的一些细节
- alter database mydb2 character set gb2312;
- show create database mydb2;
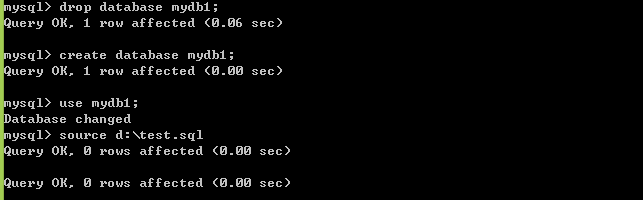
3、备份、恢复数据库
- 准备库的数据:
- 备份库:2.1:退出mysql客户端:quit;2.2:在windows命令行窗口下执行:mysqldump -uroot -p mydb1>d:test.sql,备份成功。(这是一个windows命令,所以要退到windows的cmd去执行,脚本文件)
- 删除库:drop database mydb1;
- show databases;
- 恢复库,法1(恢复库只能恢复数据库的数据,不能恢复这个数据库):5.1:创建库:create database mydb1; 5.2:source d:\test.sql(注意:source后面没有分号。这是通过执行脚本文件实现。以后会遇到很多.sql,用source命令执行)。如图:
- 恢复库,法2:mysql -uroot -p mydb1<d:\test.sql(windows命令)
4、创建表
- 注意:创建表前,要先使用use db语句使用库
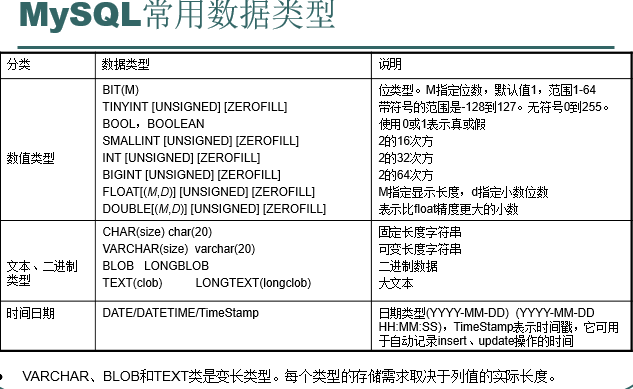
- MySql常用数据类型:
- 案例:创建一个员工表:
查看库中所以表:show tables;create table employee ( id int, name varchar(20), gender varchar(4), birthday date, entry_date date, job varchar(40), salary double, resume text ) character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; - 查看表的创建细节:show create table employee;
- 查看表的结构:desc employee;
5、修改表
- 在上面员工表的基础上增加一个image列:alter table employee add image blob;
- 修改job列,使其长度为60:alter table employee modify job varchar(60);
- 删除sex列:alter table employee drop gender;
- 表名改为user:rename table employee to user; show tables;
- 修改表的字符集为gb2312,再改为utf8:alter table user character set gb2312; show create table user; alter table user character set utf8;
- 列名name修改为username:alter table user change column name username varchar(20); desc user;
二、SQL语句:数据库CRUD语句(增删改查)
1、insert语句:
- 插入的数据应与字段的数据类型相同;
- 字符和日期型数据应包含在单引号中;
- 插入空值,不指定或insert into table value(null);
- 先把刚才那个user表的名字改为employee:rename table user to employee;
- 使用insert语句向表中插入一个员工的信息:
insert into employee(id, username, birthday, entry_date, job, salary, resume) values(1, 'aaa', '1992-02-04', '1993-03-05', 'bbb', 1000, 'bbbbbbbbb');
select * from employee; - 此时,如果插入的名字为中文,就不行。
插入失败后的解决方案:
show variables like 'chara%';(variables变量)
set character_set_client=gb2312;
insert into employee(id, username, birthday, entry_date, job, salary, resume) values(1, '小李子', '1992-02-04', '1993-03-05', 'bbb', 1000, 'bbbbbbbbb');
OK!
select * from employee;(此时,显示又出乱码了)
显示失败后的解决方案:
set character_set_results=gb2312;
select * from employee;
OK!
开了新的窗口,又要重新设置。改配置文件:D:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.0\my.ini(没事别去改)
2、update语句:
- where子句指定应更新哪些行。如没有where子句,则更新所有的行。
- 将所有员工薪水修改为5000元:
update employee set salary=5000;
select * from employee; - 将姓名为’aaa’的员工薪水修改为3000元:
update employee set salary=3000 where username='aaa';
select * from employee; - update employee where(最好一开始就把where写上)
- 将姓名为’aaa’的员工薪水修改为4000元,job改为ccc:
update employee set salary=4000,job='ccc' where username='aaa';
select * from employee; - 将aaa的薪水在原有基础上增加1000元:
update employee set salary=salary+1000 where username='aaa';
select * from employee;
3、delete语句:
- 如果不使用where子句,将删除表中所有数据
- delete语句不能删除某一列的值(可用update,把那一列置位空)
- delete语句仅删除记录,不删除表本身。如果要删除表,使用drop table 表名
- 同insert和update一样,从一个表中删除记录将引起其它表的参照完整性问题,在修改数据库数据时,头脑中应该始终不要忘记这个潜在的问题。
- 删除表中数据也可使用TRUNCATE TABLE 语句,它和delete有所不同,参看mysql文档。
- 练习:
- 删除表中名称为’小李子’的记录:
delete from employee where username='小李子'; - 删除表中所有记录:
delete from employee; - 使用truncate删除表中记录:
truncate table employee; - delete和truncate的区别:
delete是一行一行删的;
truncate是先把摧毁,再重建表的结构。
4、select语句:(是最难的,难在多表查询,后面再学)
- distinct过滤掉重复数据
- 练习:
- 脚本文件:student.sql
source d:\student.sql(通过脚本导入这张表)create table student( id int, name varchar(20), chinese float, english float, math float ); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(1,'张小明',89,78,90); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(2,'李进',67,98,56); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(3,'王五',87,78,77); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(4,'李一',88,98,90); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(5,'李来财',82,84,67); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(6,'张进宝',55,85,45); insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(7,'黄蓉',75,65,30);
select * from student; - 查询表中所有学生的信息:
select * from student;(千万不要这么写,因为在程序里面就没有可读性了)
select id, name, chinese, english, math from student;(这样写,就好了) - 查询表中所有学生的姓名和对应的英语成绩:
select name, english from student; - 过滤表中重复数据:
select distinct english from student;
select distinct name, english from student;(过滤名字和英语成绩都一样的) - 在所有学生的英语分数上加10分特长分:
select name, english + 10 from student;(没有改变数据库的值,只是查询出来加了10) - 统计每个学生的总分:
select name, (english + chinese + math) from student; - 使用别名表示学生分数:
select name as 姓名, (english + chinese + math) as 总分 from student;
select name 姓名, (english + chinese + math) 总分 from student;(as可以省掉,一样的) - 查询姓名为王五的学生成绩:
select * from student where name='王五'; - 查询英语成绩大于90分的同学:
select * from student where english > 90; - 查询总分大于200分的所有同学:
select * from student where (english + chinese + math) > 200; - <>不等于
- 查询英语分数在80-90之间的同学:
select * from student where english > 80 and english < 90;
select * from student where english between 80 and 90; - 查询数学分数为89,90,91的同学:
select * from student where math = 80 or math = 90 or math = 91;
select * from student where math in(80, 90, 91); - 查询所有姓李的学生成绩:(模糊查询)
select * from student where name like '李%';(%代表多个任意字符)
select * from student where name like '李_';(_ 代表一个字符) - order by:
对数学成绩排序后输出:
select name, math from student order by math;(默认升序asc)
对总分排序后输出,然后再按从高到低的顺序输出:(desc)
select name from student order by (math + chinese + english) desc;
对姓李的学生成绩排序输出:
select name 姓名, (math + chinese + english) 总分 from student where name like '李%' order by (math + chinese + english) desc; - 合计函数-count:
统计一个班级共有多少学生:
select count(*) from student;(一般用这个)
select count(name) from student;(一样的)(注意了,如果有个name为空,就少比*少记了一个数了)
统计数学成绩大于90的学生有多少个:
select count(*) from student where math <> 90;(不等于)
统计总分大于250的人数有多少:
select count(*) from student where (math + chinese + english) > 250; - 合计函数-sun:
统计一个班级数学总成绩:
select sum(math) from student;(把math这一列的值加起来)
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学各科的总成绩:
select sum(math), sum(chinese), sum(english) from student;
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学的成绩总和:
select sum(math + chinese + english) from student;
统计一个班级语文成绩平均分:
select sum(chinese) / count(chinese) from student;
注意:sum只对数值有效。 - 合计函数-avg:
求一个班级数学平均分:
select avg(math) from student;
求一个班级总分平均分:
select avg(math + chinese + english) from student; - 合计函数-max/min:
求班级最高分和最低分(数值范围在统计中特别有用):
select max(math + chinese + english), min(math + chinese + english) from student; - group by:
脚本文件orders.sql:(order是个关键字,所以不能用order作为表名哦)
对订单表中商品归类后,显示每一类商品的总价:create table orders( id int, product varchar(20), price float ); insert into orders(id,product,price) values(1,'电视',900); insert into orders(id,product,price) values(2,'洗衣机',100); insert into orders(id,product,price) values(3,'洗衣粉',90); insert into orders(id,product,price) values(4,'桔子',9); insert into orders(id,product,price) values(5,'洗衣粉',90);
select product from orders group by product;(归类)
select product, sum(price) from orders group by product;(归类显示总价)
having和where的区别:
Having和where均可实现过滤,但having可以使用合计函数,having通常跟在group by后,它作用于组。where子句后面不能跟合计函数。
查询购买了几类商品,并且每类总价大于100的商品:
select product, sum(price) from orders group by product having sum(price) > 100; - 单表查询,学这么多就够了,后面再讲多表查询
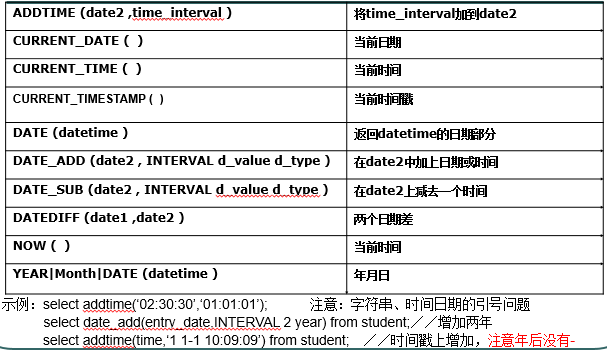
- 时间日期相关函数:(一般用select返回值)
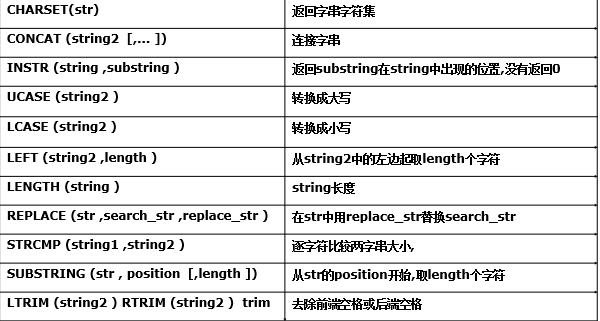
注意:字符串、时间日期的引号问题select date('1992-11-07');;时间戳上增加,年后没有- - 字符串相关函数:
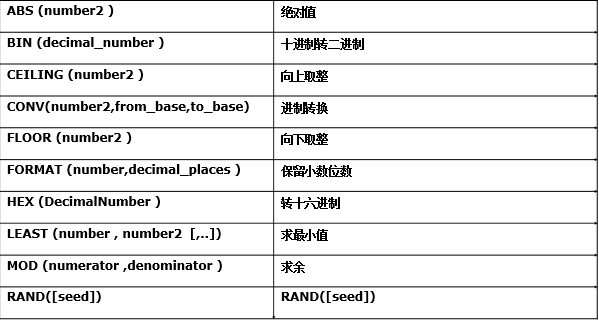
- 数学相关函数:
三、定义表的约束
1、定义表的约束
- 定义主键约束:
primary key:不允许为空,不允许重复
删除主键:alter table tablename drop primary key ;
create table test1
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20),
password varchar(20)
);
desc test1;
insert into test1(id, name) values(1, 'aaa');
此时再插入id为1的记录就插不进去了,因为加了约束。(设计表的时候,把约束设置得约言越好) - 定义主键自动增长:(做开发的时候,这个技术最好不要用)
auto_increment。
定义一个主键 自动增长的表:
create table test2
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
password varchar(20)
);
insert into test2(name) values('aaa'); - 定义唯一约束:
unique。
create table test3
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique
);
insert into test3(name) values('aaa');
此时再插入name为aaa就不行了 - 定义非空约束:
not null。
create table test4
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique not null
);
insert into test4(name) values(null);(name为空就不能插入了) - 定义外键约束:
constraint ordersid_FK foreign key(ordersid) references orders(id),
show tables;create table husband ( id int primary key, name varchar(20) ); create table wife ( id int primary key, name varchar(20), husband_id int, constraint husband_id_FK foreign key(husband_id) references husband(id) );
insert into husband(id,name) values(1, '张三');
insert into wife(id, name, husband_id) values(1, '阿三', 1);
2、设计表
- 一对多:多的那方加个外键(部门和员工)
- 一个实体一张表
- 多对多:(老师和学生)
加一张中间表(teacher_id和studetn_id)
o/r mapping工具,插入数据create table teacher ( id int primary key, name varchar(20), salary double ); create table student ( id int primary key, name varchar(20) ); create table teacher_student ( teacher_id int, student_id int, primary key(teacher_id, student_id), constraint teacher_id_FK foreign key(teacher_id) references teacher(id), constraint student_id_FK foreign key(student_id) references student(id) ); - 在数据库里面描述关系,都是使用外键
- 一对一:
create table person ( id int primary key, name varchar(20) ); create table idcard ( id int primary key, address varchar(4), constraint id_FK foreign key(id) references person(id) );
四、HTTP响应头
1、响应头
- Location: 服务器通过这个头,来告诉浏览器跳到哪里
浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/fanglixun_day04/ServletDemo1访问就跳到http://localhost:8080/fanglixun_day04/1.html了(请求重定向)protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setStatus(302); response.setHeader("location", "/fanglixun_day04/1.html"); } - Server:服务器通过这个头,告诉浏览器服务器的型号
- Content-Encoding:服务器通过这个头,告诉浏览器,数据的压缩格式(代码不怎么懂了)
@WebServlet("/ServletDemo1") public class ServletDemo1 extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { test2(request, response); } public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { String data = "abcd"; System.out.println("原始数据的大小为:" + data.getBytes().length); ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); GZIPOutputStream gout = new GZIPOutputStream(bout); //buffer gout.write(data.getBytes()); gout.close(); //得到压缩后的数据 byte g[] = bout.toByteArray(); response.setHeader("Content-Encoding", "gzip"); response.setHeader("Content-Length", g.length + ""); response.getOutputStream().write(g); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { } }

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








