一、操作对象流
ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream对以前使用ObjectOutputStream写入的基本数据和对象进行反序列化;
1. 构造函数:
ObjectInpuStream(InputStream in)
2. 常用方法:
××× read×××();×××基本数据类型或Object;
3. 注意:static修饰的成员变量不能被序列化;
4. transient关键字;对于非static修饰的成员如果不想被序列化可用该关键字修饰;
ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream对以前使用ObjectOutputStream写入的基本数据和对象进行反序列化;
1. 构造函数:
ObjectInpuStream(InputStream in)
2. 常用方法:
××× read×××();×××基本数据类型或Object;
3. 注意:static修饰的成员变量不能被序列化;
4. transient关键字;对于非static修饰的成员如果不想被序列化可用该关键字修饰;
示例:
import java.io.*;
class ObjectStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//writeObj();
readObj();
}
public static void readObj()throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.txt"));
Person p = (Person)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p);
ois.close();
}
public static void writeObj()throws IOException{
ObjectOutputStream oos =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("obj.txt"));
oos.writeObject(new Person("lisi0",399,"kr"));
oos.close();
}
}import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable{
public static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;//自定义序列号ID
private String name;
transient int age;//非静态成员如果不想被序列化,可以用关键字transient修饰;
static String country = "cn";//静态成员不能被序列化。
Person(String name,int age,String country){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.country = country;
}
public String toString(){
return name+":"+age+":"+country;
}
}二、 管道流
PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream:输入输出可以直接进行连接,通过结合线程使用。
示例:
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class PipedStream{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
PipedInputStream input = new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream output = new PipedOutputStream();
input.connect(output);
new Thread(new Input(input)).start();
new Thread(new Output(output)).start();
}
}
class Input implements Runnable{
private PipedInputStream in;
Input(PipedInputStream in){
this.in = in;
}
public void run(){
try{
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);
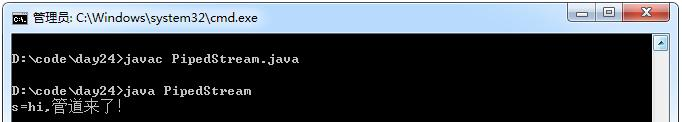
String s = new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println( "s=" + s);
in.close();
} catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable{
private PipedOutputStream out;
Output(PipedOutputStream out){
this.out = out;
}
public void run(){
try{
out.write( "hi,管道来了!" .getBytes());
out.close();
} catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
RandomAccessFile
随机访问文件,自身具备读写的方法;
通过skipBytes(int x);seek(int x);来达到随机访问;
此类的实例支持对随机访问文件的读取和写入;
特点:
1.该类不算是IO体系中的子类而是直接继承Object;但他是IO包中的成员,因为它具备读和写的功能,内部封装了一个数 组,而且通过指针对数组的元素进行操作,可以通过getFilePointer获取指针位置,同时可以通过seek改变指针的位置;
2.其实完成读写的原理就是内部封装了字节输入流和输出流,通过构造函数可以看出,该类只能操作文件,而且操作文件还 有模式:只读(r);读写(rw)等;
3.如果模式为只读r,不会创建文件,会去读取一个已存在文件,如果该文件不存在,则会出现异常;
4. 如果模式为只读rw,操作的文件不存在,会自动创建,如果存在则不会覆盖;
构造方法:
RandomAccessFile(File file,String mode);
RandomAccessFile(String name,String mode);
file-指定文件;
name-系统文件名;
mode-访问模式;
该类常用方法:
gerFilePointer();返回此文件的当前偏移量;
length();返回此文件的长度;
read();该功能与InputStream一样;
read×××;×××-基本数据类型;
readLine();读一行;
seek(long pos);设置指针偏移量;
setLength(long newLength);设置文件长度;
write(byte[] b)/(byte[] b,int off,int len)/(int b)该方法与OutputStream方法一样;
write×××(××× ~);×××基本数据类型;
skipBytes(int n);跳过指定的字节数;
注:该类的常用方式:通过seek()偏移指针,结合多线程实现分段数据同时读写,实际应用:迅雷下载;
示例:
class RandomAccessFileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//writeFile_2();
//readFile();
//System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(258));
}
public static void readFile()throws IOException{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","r");
//调整对象中指针。
//raf.seek(8*1);
//跳过指定的字节数
raf.skipBytes(8);
byte[] buf = new byte[4];
raf.read(buf);
String name = new String(buf);
int age = raf.readInt();
System.out.println("name="+name);
System.out.println("age="+age);
raf.close();
}
public static void writeFile_2()throws IOException{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","rw");
raf.seek(8*0);
raf.write("周期".getBytes());
raf.writeInt(103);
raf.close();
}
public static void writeFile()throws IOException{
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","rw");
raf.write("李四".getBytes());
raf.writeInt(97);
raf.write("王五".getBytes());
raf.writeInt(99);
raf.close();
}
}import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DataStreamDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
readData();
}
public static void readData() throws IOException {
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new
FileInputStream("data.txt" ));
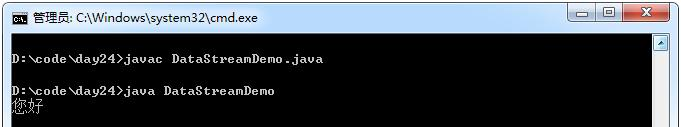
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(str);
dis.close();
}
}
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DataStreamDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
writeData();
}
public static void writeData() throws IOException {
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new
FileOutputStream("data.txt" ));
dos.writeUTF( "您好");
dos.close();
}
}
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteArrayStreamDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
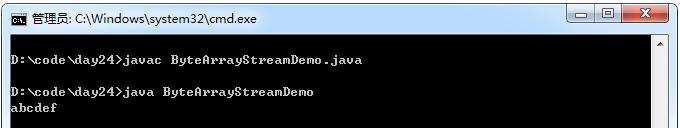
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("abcdef".getBytes());
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int ch = 0;
while((ch = bis.read()) != -1){
bos.write(ch);
}
System.out.println(bos.toString());
}
}
计算机只能识别二进制数据,早期由来是电信号。为了方便应用计算机,让它可以识别各个国家的文字。
就将各个国家的文字用数字来表示,并一一对应,形成一张表,这就是编码表。
ISO8859-1:拉丁码表。欧洲码表,用一个字节的8位表示。
GB2312:中国的中文编码表。
GBK:中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。
Unicode:国际标准码,融合了多种文字。
所有文字都用两个字节来表示,Java语言使用的就是unicode
UTF-8:最多用三个字节来表示一个字符。
3.编码
字符串变成字符数组
String——byte[]:str.getBytes(String charsetName);字符串String方法;charsetName-指定编码表的字符串名称;
4.解码
byte[]——String:new String(byte[],charsetName);
注:如果中文字符串用“GBK”编码,用“ISO8859-1”解码,会出现乱码(因为不识别),将解码后的乱码再 用“ISO8859-1”编码回去,则与“GBK”编码相同(因为不识别,编码未被改变,再用“GBK”解码,则结果为原中文 字符串,如果该字符用“UTF-8”去解码,再编码,则编码将发生变化与原“GBK”编码不同,用“GBK”去解码时,结 果不是原中文字符串,因为“UTF-8”页识别中文,用“UTF-8”解码再编码后,将按照“UTF-8”编码表中的字符对原解 出的乱码进行编码,则结果发生变化,所以只有不识别中文的编码表才能进行解码再编码后,结果不变);

import java.util.*;
class EncodeDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
String s = "哈哈";
byte[] b1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b1));
String s1 = new String(b1,"utf-8");
System.out.println("s1="+s1);
//对s1进行iso8859-1编码。
byte[] b2 = s1.getBytes("utf-8");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b2));
String s2 = new String(b2,"gbk");
System.out.println("s2="+s2);
}
}
import java.io.*;
class EncodeStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//writeText();
readText();
}
public static void readText()throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("utf.txt"),"gbk");
char[] buf = new char[10];
int len = isr.read(buf);
String str = new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
isr.close();
}
public static void writeText()throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("utf.txt"),"UTF-8");
osw.write("你好");
osw.close();
}
}练习:
但对应的字节数不同,一个汉字占两个字节。
定义一个方法,按照最大的字节数来取子串。
如:对于“ab你好”,如果取三个字节,那么子串就是ab与“你”字的半个。
那么半个就要舍弃。如果取四个字节就是“ab你”,取五个字节还是“ab你”。
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
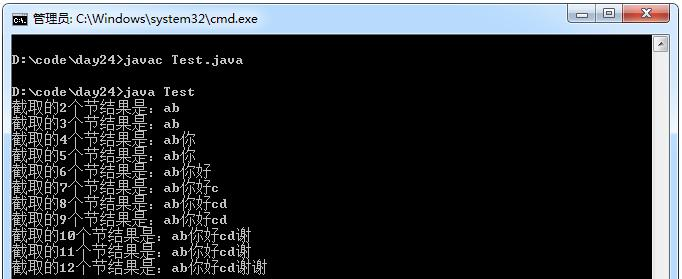
String str = "ab你好cd谢谢" ;
int len = str.getBytes("gbk" ).length;
for(int x = 1; x < len; x++){
System.out.println( "截取的" + (x + 1) + "个节结果是:" +cutStringByByte(str,x+1));
}
}
public static String cutStringByByte(String str,int len) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = str.getBytes("gbk" );
int count = 0;
for(int x = len - 1; x >= 0; x--){
//gbk编码的值两个字节值一般都为负,记录连续的负数个数,如果为奇数,则舍弃
if(buf[x] < 0)
count++;
else
break;
}
if(count % 2 == 0){
return new String(buf,0,len,"gbk");
}
else{
return new String(buf,0,len-1,"gbk");
}
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








