unordered系列关联式容器
在C++98中,STL提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容器,在查询时效率可达到O(log2N) ,即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的节点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11中,STL又提供了4个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同,本文中只对unordered_map和unordered_set进行介绍,unordered_multimap和unordered_multiset可查看文档介绍。
unordered_map
unordered_map的文档介绍
- unordered_map是存储<key, value>键值对的关联式容器,允许通过key快速的索引到与其对应的value。
- 在unordered_map中,键值通常用于唯一地标识元素,而映射值是一个对象,其内容与此键关联。键和映射值的类型可能不同。
- 在内部,unordered_map没有对<key, value>按照任何特定的顺序排序, 为了能在常数范围内找到key所对应的value,unordered_map将相同哈希值的键值对放在相同的桶中。
- unordered_map容器通过key访问单个元素要比map快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低。
- unordered_map实现了直接访问操作符(operator[]),它允许使用key作为参数直接访问value。
- 它的迭代器至少是前向迭代器。
unordered_map的接口说明
-
unordered_map的构造
函数声明 功能介绍 unordered_map 构造不同格式的unordered_map对象 -
unordered_map的容量
函数声明 功能介绍 bool empty() const 检测unordered_map是否为空 size_t size() const 获取unordered_map的有效元素个数 -
unordered_map的迭代器
不支持反向迭代
函数声明 功能介绍 begin 返回unordered_map第一个元素的迭代器 end 返回unordered_map最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 cbegin 返回unordered_map第一个元素的const迭代器 cend 返回unordered_map最后一个元素下一个位置的const迭代器 -
unordered_map的元素访问
函数声明 功能介绍 operator[] 返回与key对应的value,没有就返回一个value类型的默认值 注意:该函数中实际调用哈希桶的插入操作,用参数key与V()构造一个默认值往底层哈希桶中插入,如果key不在哈希桶中,插入成功,返回V(),插入失败,说明key已经在哈希桶中,将key对应的value返回。
-
unordered_map的查询
函数声明 功能介绍 iterator find(const K& key) 返回key在哈希桶中的位置 size_t count(const K& key) 返回哈希桶中关键码为key的键值对的个数 注意:unordered_map中key是不能重复的,因此count函数的返回值最大为1
-
unordered_map的修改操作
不支持修改key函数声明 功能介绍 insert 向容器中插入键值对 erase 删除容器中的键值对 void clear() 清空容器中有效元素个数 void swap(unordered_map&) 交换两个容器中的元素 -
unordered_map的桶操作
函数声明 功能介绍 size_t bucket_count()const 返回哈希桶中桶的总个数 size_t bucket_size(size_t n)const 返回n号桶中有效元素的总个数 size_t bucket(const K& key) 返回元素key所在的桶号
unordered_map使用
void test_unordered_map_set()
{
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
dict.insert(make_pair("money", "钱"));
dict["study"] = "学习";//此时dict中没有study,该语句就是插入
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_unordered_map_set();
return 0;
}
unordered_set
unordered_set 和set使用差不多
map/set和unordered_map/unordered_set比较
使用比较
map/set和unordered_map/unordered_set区别与联系
- 他们都可以实现key和key/value的搜索场景,并且功能和使用基本一样
- map/set的底层是使用红黑树实现的,遍历出来是有序的,增删查改的时间复杂度是O(log2N)
- unordered_map/unordered_set的底层是用哈希表实现的,遍历出来是无序的,增删查改的时间复杂度是O(1)
- map和set是双向迭代器,unordered_map/unordered_set是单向迭代器,不支持反向迭代器
性能比较
void testop()
{
unordered_map<int, int> um;
unordered_set<int> us;
map<int, int> m;
set<int> s;
vector<int> v;
const int num = 100000000;
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
v.push_back(rand());
}
//unordered_map的插入效率
//int begin1 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
um.insert(make_pair(e,e));
}
//int end1 = clock();
//map的插入效率
//int begin2 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
m.insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
//int end2 = clock();
//unordered_set的插入效率
//int begin3 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
us.insert(e);
}
//int end3 = clock();
//set的插入效率
//int begin4 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
s.insert(e);
}
//int end4 = clock();
/*cout << "unordered_map::insert:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;
cout << "map::insert:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;
cout << "unordered_set::insert:" << end3 - begin3 << endl;
cout << "set::insert:" << end4 - begin4 << endl;*/
//unordered_map的删除效率
int begin1 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
um.erase(e);
}
int end1 = clock();
//map的删除效率
int begin2 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
m.erase(e);
}
int end2 = clock();
//unordered_set的删除效率
int begin3 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
us.erase(e);
}
int end3 = clock();
//set的删除效率
int begin4 = clock();
for (auto& e : v)
{
s.erase(e);
}
int end4 = clock();
cout << "unordered_map::erase:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;
cout << "map::erase:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;
cout << "unordered_set::erase:" << end3 - begin3 << endl;
cout << "set::erase:" << end4 - begin4 << endl;
}
插入效率比较:release下多次测试,效率大概是十倍的差距
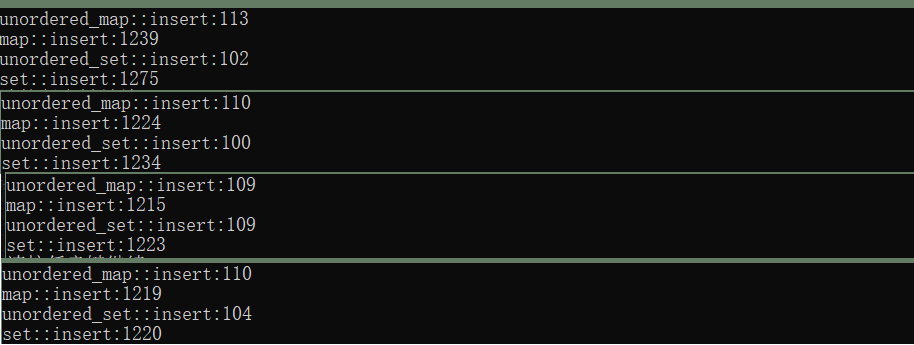
删除插入测试:release下多次测试,效率大概是两倍的差距

在线OJ
思路:用map/unordered_map统计数字出现次数,找出出现次数为n的数
class Solution {
public:
int repeatedNTimes(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : nums)
{
//统计出现次数
countMap[e]++;
}
int N = nums.size() / 2;
for (auto& e : countMap)
{
//找出出现次数为N的数字
if (e.second == N)
return e.first;
}
return -1;
}
};
思路:将nums1和nums2中的元素放入set中,进行去重,然后在两个set中查找相同元素
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
//将两个数组的内容放入set/unordered_set(map也可以)中,不能直接用数组判断
//因为数组中可能会存在重复的数,要用set/unordered_set去重
set<int> s1;
set<int> s2;
//用set去重
for (auto& e : nums1)
{
s1.insert(e);
}
for (auto& e : nums2)
{
s2.insert(e);
}
vector<int> ret;
for (auto& e : s1)
{
//在s2中查找s1中的元素,如果存在就放入ret中
if (s2.find(e) != s2.end())
{
ret.push_back(e);
}
}
return ret;
}
};
相比I,该题要把重复的数字也算进去,并且是重复的个数是出现次数较小的那个
比如:nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
nums2中虽然有重复的4和9,但nums1中4和9还是只出现了一次,所以4和9只能放入一次
思路:用两个哈希map统计分别统计两个数组中数字出现的次数,然后对比两个哈希map,重复放入都存在,且放入次数是两者的出现次数中较小的那个。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_map<int, int> countMap1;
unordered_map<int, int> countMap2;
//统计数字出现次数
for (auto& e : nums1)
{
countMap1[e]++;
}
for (auto& e : nums2)
{
countMap2[e]++;
}
vector<int> ret;
for (auto& e : countMap1)
{
//在countMap2中查找countMap1中的元素,如果存在就放入ret中
auto pos = countMap2.find(e.first);
if (pos != countMap2.end())
{
//重复元素也要考虑,所以取两个出现次数的较小的那个,放入较小次数的重复元素
int times = min(e.second, pos->second);
while (times--)
ret.push_back(e.first);
}
}
return ret;
}
};
统计出现次数
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.empty())
return false;
unordered_map<int, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : nums)
{
countMap[e]++;
if (countMap[e] > 1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
思路:先将句子中的单词依次取出,并放入哈希map中统计次数,再将两个map进行对照,找出不常见单词
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> uncommonFromSentences(string s1, string s2) {
unordered_map<string, int> countMap1;
unordered_map<string, int> countMap2;
vector<string> ret;
auto prev1 = s1.begin();
auto pos1 = s1.begin();
while (pos1 != s1.end())
{
//找到空格取出单词
pos1 = find(prev1, s1.end(), ' ');//到了最后一个单词,find找不到空格会返回end
//(prev1, pos1]刚好是左闭右开的区间
string tmp(prev1, pos1);
countMap1[tmp]++;
prev1 = pos1 + 1;
}
auto prev2 = s2.begin();
auto pos2 = s2.begin();
while (pos2 != s2.end())
{
pos2 = find(prev2, s2.end(), ' ');
string tmp(prev2, pos2);
countMap2[tmp]++;
prev2 = pos2 + 1;
}
//找出不常见单词,第一句在第二句中查找
for (auto& e : countMap1)
{
//该单词在第一句中只出现一次
if (e.second == 1)
{
//在第二句中寻找该单词
auto index = countMap2.find(e.first);
if (index == countMap2.end())
{
ret.push_back(e.first);
}
}
}
//找出不常见单词,第二句在第一句中查找
for (auto& e : countMap2)
{
//该单词在第一句中只出现一次
if (e.second == 1)
{
//在第二句中寻找该单词
auto index = countMap1.find(e.first);
if (index == countMap1.end())
{
ret.push_back(e.first);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};























 142
142











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










